Biological Psychology
... Describe the different disciplines that contribute to the field of neuroscience Key Terms: o Neurons o Neuroanatomy o Neuropathology o Neuropharmacology o Neuropsychology o Cognitive Neuroscience Chapter 3: ...
... Describe the different disciplines that contribute to the field of neuroscience Key Terms: o Neurons o Neuroanatomy o Neuropathology o Neuropharmacology o Neuropsychology o Cognitive Neuroscience Chapter 3: ...
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM
... and then on to association areas ·where it is associated with other sensory information in order to form a complete representation of an object (looks like ice cream, smells like ice cream, tastes and feels like ice cream- and then it is identified, it must be ice cream) . Of course, as with other s ...
... and then on to association areas ·where it is associated with other sensory information in order to form a complete representation of an object (looks like ice cream, smells like ice cream, tastes and feels like ice cream- and then it is identified, it must be ice cream) . Of course, as with other s ...
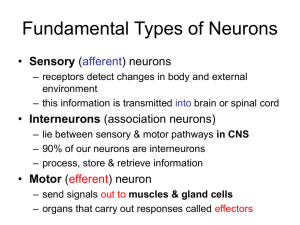
Fundamental Types of Neurons
... • Neuronal communication is based on mechanisms for producing electrical potentials & currents – electrical potential - difference in concentration of charged particles between different parts of the cell – electrical current - flow of charged particles from one point to another within the cell • Li ...
... • Neuronal communication is based on mechanisms for producing electrical potentials & currents – electrical potential - difference in concentration of charged particles between different parts of the cell – electrical current - flow of charged particles from one point to another within the cell • Li ...
nervous system jeopardy
... How does a nerve impulse move from the axon tips of one neuron to the dendrites of the next neuron? ...
... How does a nerve impulse move from the axon tips of one neuron to the dendrites of the next neuron? ...
Nervous System ppt
... Some involved with reflexes and can act without conscious control (see next slide) ...
... Some involved with reflexes and can act without conscious control (see next slide) ...
Mind, Brain & Behavior
... Different areas of the brain with different functions have different kinds of neurons. Brodmann mapped the areas based on the kinds of cells found: ...
... Different areas of the brain with different functions have different kinds of neurons. Brodmann mapped the areas based on the kinds of cells found: ...
STUDY GUIDE DRUGS
... E. Cocaine Schedule II drug 1. isolated from the coca plant, cocaine is a natural alkaloid with an extensive history in South America 2. crack = cocaine + baking soda 3. effects similar to meth F. MDMA also known as ecstasy 1. hallucinogenic stimulant causes euphoria 2. data shows beneficial use to ...
... E. Cocaine Schedule II drug 1. isolated from the coca plant, cocaine is a natural alkaloid with an extensive history in South America 2. crack = cocaine + baking soda 3. effects similar to meth F. MDMA also known as ecstasy 1. hallucinogenic stimulant causes euphoria 2. data shows beneficial use to ...
Neuroscience and Behavior - Bremerton School District
... synapses, often by either amplifying or blocking a neurotransmitter’s activity. ...
... synapses, often by either amplifying or blocking a neurotransmitter’s activity. ...
nerve net
... – Causes the release of NEUROTRANSMITTERS from terminal branches – **Neuron-Nerve-Ganglia-Brain ...
... – Causes the release of NEUROTRANSMITTERS from terminal branches – **Neuron-Nerve-Ganglia-Brain ...
Bradley`s.
... pass in and out of the cell When a cell is resting (not transmitting information) the ion channels are closed creating a slight negative charge. Outside the cell, the charge is positive making the resting neuron become what is known as polarized. The resting potential (the stable, negative charge of ...
... pass in and out of the cell When a cell is resting (not transmitting information) the ion channels are closed creating a slight negative charge. Outside the cell, the charge is positive making the resting neuron become what is known as polarized. The resting potential (the stable, negative charge of ...
The biological Approach
... • This is the way that genes are expressed through physical, behavioural and psychological characteristics. • The expression of a genotype is inevitably influenced by environmental factors. • For example, the maximum height of an individual is dictated by the genotype but environmental factors such ...
... • This is the way that genes are expressed through physical, behavioural and psychological characteristics. • The expression of a genotype is inevitably influenced by environmental factors. • For example, the maximum height of an individual is dictated by the genotype but environmental factors such ...
presentation source
... • The Hodgkin Cycle is triggered at one Node after another. This amplifies the signal. • The signal travels passively as an electrical current between Nodes. • The thick myelin insulation of the Internode allows the local circuit current to spread much further and faster than in un-myelinated fibres ...
... • The Hodgkin Cycle is triggered at one Node after another. This amplifies the signal. • The signal travels passively as an electrical current between Nodes. • The thick myelin insulation of the Internode allows the local circuit current to spread much further and faster than in un-myelinated fibres ...
P.1.a.016 Emotionally painful stress causes changes in L1 insertion
... involvement of KIF13A protein in some higher brain functions including anxiety. Variations in the KIF13A protein or expression may affect the transport or the abundance of specific synaptic vesicles. For some brain regions, including the hippocampus, many studies have found molecular evidence in supp ...
... involvement of KIF13A protein in some higher brain functions including anxiety. Variations in the KIF13A protein or expression may affect the transport or the abundance of specific synaptic vesicles. For some brain regions, including the hippocampus, many studies have found molecular evidence in supp ...
Drosophila melanogaster
... decisions in female. To investigate molecular and neural mechanisms underlying the post-mating food preference switch, we manipulated activities of neurons producing hugin peptides or its two receptors, CG8784 and CG8795. Virgin females carrying hugin cell-knockout (hugin-KO) showed the strong prefe ...
... decisions in female. To investigate molecular and neural mechanisms underlying the post-mating food preference switch, we manipulated activities of neurons producing hugin peptides or its two receptors, CG8784 and CG8795. Virgin females carrying hugin cell-knockout (hugin-KO) showed the strong prefe ...
Nervous System I - Laurel County Schools
... The neurotransmitter is released when a nerve impulse reaches the end of an axon, this opens two channels Na+ and Ca2+ This surge of Ca2+ acts as a messenger, directing synaptic vesicles to empty contents. Then the neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft A neurotransmitter reaching the d ...
... The neurotransmitter is released when a nerve impulse reaches the end of an axon, this opens two channels Na+ and Ca2+ This surge of Ca2+ acts as a messenger, directing synaptic vesicles to empty contents. Then the neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft A neurotransmitter reaching the d ...
Nervous System I - Laurel County Schools
... The neurotransmitter is released when a nerve impulse reaches the end of an axon, this opens two channels Na+ and Ca2+ This surge of Ca2+ acts as a messenger, directing synaptic vesicles to empty contents. Then the neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft A neurotransmitter reaching the d ...
... The neurotransmitter is released when a nerve impulse reaches the end of an axon, this opens two channels Na+ and Ca2+ This surge of Ca2+ acts as a messenger, directing synaptic vesicles to empty contents. Then the neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft A neurotransmitter reaching the d ...
Stereological estimates of neuronal loss in the primary motor cortex
... Stereological estimates of neuronal loss in the primary motor cortex of multiple sclerosis patients M.M. Papachatzaki, D. Carassiti, A. McDowell, K. Schmierer QMUL (London, GB) Introduction Whilst inflammatory demyelination (ID) is an important feature in the clinical and pathological diagnosis of M ...
... Stereological estimates of neuronal loss in the primary motor cortex of multiple sclerosis patients M.M. Papachatzaki, D. Carassiti, A. McDowell, K. Schmierer QMUL (London, GB) Introduction Whilst inflammatory demyelination (ID) is an important feature in the clinical and pathological diagnosis of M ...
Local Copy - Synthetic Neurobiology Group
... meant to celebrate the power or lament the futility of simply paying attention. Were he scientifically inclined, he might have added that mere observation is unsatisfying because many things can be learned only through experimentation—perturbing things, then seeing what happens next. So it is with c ...
... meant to celebrate the power or lament the futility of simply paying attention. Were he scientifically inclined, he might have added that mere observation is unsatisfying because many things can be learned only through experimentation—perturbing things, then seeing what happens next. So it is with c ...
Neurons are the cells that carry messages between parts of the body
... The cell remains at resting potential until a stimulus reaches the cell, either from another neuron or the environment. Channels in the membrane open to allow Na+ ions to enter the cell. The inside of the cell temporarily becomes more positive. This is called the action potential. Refer to fig. 35-7 ...
... The cell remains at resting potential until a stimulus reaches the cell, either from another neuron or the environment. Channels in the membrane open to allow Na+ ions to enter the cell. The inside of the cell temporarily becomes more positive. This is called the action potential. Refer to fig. 35-7 ...
ANATOMICAL ORGANIZATION of the NERVOUS SYSTEM
... Branches off the cell body that carry information to the cell body. Usually several to many. Relatively short. Often branched. Have receptors for neurotransmitters. Conduct local potentials. ...
... Branches off the cell body that carry information to the cell body. Usually several to many. Relatively short. Often branched. Have receptors for neurotransmitters. Conduct local potentials. ...
Pharmacokinetics & Pharmacodynamics
... Not all addictive drugs produce physical dependence. Some nonaddictive therapeutic drugs (e.g. SSRIs) can produce physical dependence. ...
... Not all addictive drugs produce physical dependence. Some nonaddictive therapeutic drugs (e.g. SSRIs) can produce physical dependence. ...
anti-depressants
... Therapeutic uses: Used to treat psychiatric disorders, posttraumatic stress disorder, panic disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder, and bulimia nervosa. Serotonin-Nor-epinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors: These agents, termed selective serotoninnor-epinephrine reuptake inhibitors ...
... Therapeutic uses: Used to treat psychiatric disorders, posttraumatic stress disorder, panic disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder, and bulimia nervosa. Serotonin-Nor-epinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors: These agents, termed selective serotoninnor-epinephrine reuptake inhibitors ...
Nervous system
... Medulla Oblongata lies within the midbrain between the pons and spinal cord,it forms the brainstem. The medulla controls heart rate, breathing swallowing, coughing and vomiting. The midbrain and the pons relay messages between the medulla oblongata and the cerebrum. ...
... Medulla Oblongata lies within the midbrain between the pons and spinal cord,it forms the brainstem. The medulla controls heart rate, breathing swallowing, coughing and vomiting. The midbrain and the pons relay messages between the medulla oblongata and the cerebrum. ...