nervous system
... sheath which provides the electrical insulation for certain neurons in the CNS ...
... sheath which provides the electrical insulation for certain neurons in the CNS ...
Nervous System Notes File
... ii. Sensory receptors are found in places like the skin that sense pressure, temperature or pain The Central Nervous System a. Brain – integrates and controls the activities of the nervous system i. Helps you receive and process messages, think, remember, reason, and coordinate muscle movements ii. ...
... ii. Sensory receptors are found in places like the skin that sense pressure, temperature or pain The Central Nervous System a. Brain – integrates and controls the activities of the nervous system i. Helps you receive and process messages, think, remember, reason, and coordinate muscle movements ii. ...
1. Learning Depends on Integration of Brain Structures
... movement of their eyes to follow the the words on a page while listening to stories and attempt to write their names, the earlier they while learn to read. ...
... movement of their eyes to follow the the words on a page while listening to stories and attempt to write their names, the earlier they while learn to read. ...
Addiction as a Disease PowerPoint Slides
... • Three mechanisms at the synaptic junction of brain nerve cells • Neural – acute exposure • Cellular (regulation of ion channels and electrical properties) – long term exposure • Molecular mechanisms – long term exposure ...
... • Three mechanisms at the synaptic junction of brain nerve cells • Neural – acute exposure • Cellular (regulation of ion channels and electrical properties) – long term exposure • Molecular mechanisms – long term exposure ...
Opioids
... o MOA: opiate antagonist that does NOT cross BBB (therefore, will not affect analgesia) o Administration: injectable o Use: approved recently for opioid-induced constipation in terminal patients under palliative care ...
... o MOA: opiate antagonist that does NOT cross BBB (therefore, will not affect analgesia) o Administration: injectable o Use: approved recently for opioid-induced constipation in terminal patients under palliative care ...
The Nervous System
... • All of the nerves that are not a part of the central nervous system. • Somatic nervous System - regulates activities that are under conscious control (muscles) and pain reflexes. • Autonomic Nervous System – regulates activities that are automatic or involuntary. • Ex: heart rate, blood flow, musc ...
... • All of the nerves that are not a part of the central nervous system. • Somatic nervous System - regulates activities that are under conscious control (muscles) and pain reflexes. • Autonomic Nervous System – regulates activities that are automatic or involuntary. • Ex: heart rate, blood flow, musc ...
The Role of Neuroimaging in Clinical Trials and Drug Discovery In
... Or do TCAs behave completely different from SSRIs, due to their broad pharmacological actions at many different molecular targets? ...
... Or do TCAs behave completely different from SSRIs, due to their broad pharmacological actions at many different molecular targets? ...
our fact sheet.
... • In healthy elderly human subjects, supplementation with 500 mg/day citicoline for 6 weeks was shown by magnetic resonance spectroscopy to stimulate phosphatidylcholine synthesis.6 2. Enhances cell signaling by increasing the synthesis of neurotransmitters • Citicoline administration in laboratory ...
... • In healthy elderly human subjects, supplementation with 500 mg/day citicoline for 6 weeks was shown by magnetic resonance spectroscopy to stimulate phosphatidylcholine synthesis.6 2. Enhances cell signaling by increasing the synthesis of neurotransmitters • Citicoline administration in laboratory ...
HOMEWORK 1 SOME BASIC TERMS CNS / PNS
... Part of above system, receives smell info from olfactory receptors Forebrain structure including Caudate Nucleus, Putamen & Globus Pallidus, involved in organization of movement sequences Forebrain structure including Nucleus Accumbens, involved in arousal of cortex, attention & reinforcement Forebr ...
... Part of above system, receives smell info from olfactory receptors Forebrain structure including Caudate Nucleus, Putamen & Globus Pallidus, involved in organization of movement sequences Forebrain structure including Nucleus Accumbens, involved in arousal of cortex, attention & reinforcement Forebr ...
Outline for cognitive neuroscience Chapter 1 Introduction to Method
... Principle: active neurons also produce small magnetic fields that propagates to the scale without distortion. Record the time course and distribution of magnetic fields time-locked to specific event-> event-related field. Advantage of ERF: similar temporal resolution with ERP but higher spatial re ...
... Principle: active neurons also produce small magnetic fields that propagates to the scale without distortion. Record the time course and distribution of magnetic fields time-locked to specific event-> event-related field. Advantage of ERF: similar temporal resolution with ERP but higher spatial re ...
Antipsychotics - TOP Recommended Websites
... Etiology is unknown..... but... combination of genetic and environmental factors associated with neurodevelopmental disorder affects several brain areas ...
... Etiology is unknown..... but... combination of genetic and environmental factors associated with neurodevelopmental disorder affects several brain areas ...
June 14_Neuroanatomy & Audition
... This is known as the threshold potential. If the potential does not reach the threshold, no action potential will occur…thus it is an “All or None” phenomenon. ...
... This is known as the threshold potential. If the potential does not reach the threshold, no action potential will occur…thus it is an “All or None” phenomenon. ...
05First2yearsBiosocial
... • If starving, the body stops growing, but not the brain • The brain is the last part of the body to be damaged by malnutrition Intrauterine Growth Restriction ...
... • If starving, the body stops growing, but not the brain • The brain is the last part of the body to be damaged by malnutrition Intrauterine Growth Restriction ...
Study Guide – Unit 3 Psych 2022, Fall 2003 Psychological Disorders
... 31. Review the components of dopaminergic synaptic transmission (e.g. transport of precursor, neurotransmitter synthesis, transport into vesicles, influx of calcium, exocytosis, re-uptake, and degradation). 32. What is the direct synaptic mechanism of action of the drugs chlorpromazine and haloperid ...
... 31. Review the components of dopaminergic synaptic transmission (e.g. transport of precursor, neurotransmitter synthesis, transport into vesicles, influx of calcium, exocytosis, re-uptake, and degradation). 32. What is the direct synaptic mechanism of action of the drugs chlorpromazine and haloperid ...
Neural Conduction
... • Alcohol is a depressant - it reduces neural firing by reducing the flow of Ca++ ions into neurons by acting on ion channels, and thus not releasing as many vessicles with neurotransmitter (many kinds) into the synapse (antagonistic) • Also is agonistic, increasing the binding of GABA to its recept ...
... • Alcohol is a depressant - it reduces neural firing by reducing the flow of Ca++ ions into neurons by acting on ion channels, and thus not releasing as many vessicles with neurotransmitter (many kinds) into the synapse (antagonistic) • Also is agonistic, increasing the binding of GABA to its recept ...
Module 1:Human Nervous System Lecture 5:Spinal cord The
... In the previous section we saw that the neurons of the brain and spinal cord are centrally located in the body. Contrary to this, the neurons of peripheral nervous system are spread in the other zones of the body. This system comprises of the autonomic nervous system and the somatic nervous system. ...
... In the previous section we saw that the neurons of the brain and spinal cord are centrally located in the body. Contrary to this, the neurons of peripheral nervous system are spread in the other zones of the body. This system comprises of the autonomic nervous system and the somatic nervous system. ...
Cognitive Neuroscience
... and single-cell recordings) + magnetophysiological methods (MEG) record the electrical/magnetic properties of neurons • Functional imaging methods (PET and fMRI) record physiological changes associated with blood supply to the brain which evolve more slowly over time = Haemodynamic methods ...
... and single-cell recordings) + magnetophysiological methods (MEG) record the electrical/magnetic properties of neurons • Functional imaging methods (PET and fMRI) record physiological changes associated with blood supply to the brain which evolve more slowly over time = Haemodynamic methods ...
Heart
... lipid double-layer … gives basic physical features to plasmalema … on / in: floating or anchored proteins (ion channels) proteins … anchored in lipid double-layer in different ways … give biological activity and specificity to plasmalema glykokalyx … protective cover of some cells formed of oligosac ...
... lipid double-layer … gives basic physical features to plasmalema … on / in: floating or anchored proteins (ion channels) proteins … anchored in lipid double-layer in different ways … give biological activity and specificity to plasmalema glykokalyx … protective cover of some cells formed of oligosac ...
Title: Mapping social brain circuit in the mouse brain by serial two
... brain regions activated by specific external stimuli. However, conventional detection methods such as in situ hybridization or immunohistochemistry are labor intensive and semi-quantiative, thus hard to implement to examine neuronal activation throughout the entire brain. In this talk, I will presen ...
... brain regions activated by specific external stimuli. However, conventional detection methods such as in situ hybridization or immunohistochemistry are labor intensive and semi-quantiative, thus hard to implement to examine neuronal activation throughout the entire brain. In this talk, I will presen ...
questions - Hatboro
... 10. What is the space between neurons called? 11. The sending cell converts the electrical signal to a chemical signal at the axon terminal. These chemical signals are called __________________________________ and are contained in bags called _____________________________. 12. What’s the neurotransm ...
... 10. What is the space between neurons called? 11. The sending cell converts the electrical signal to a chemical signal at the axon terminal. These chemical signals are called __________________________________ and are contained in bags called _____________________________. 12. What’s the neurotransm ...
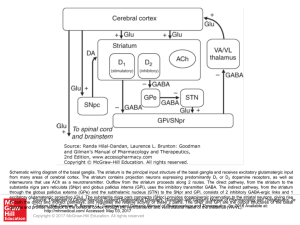
Slide ()
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
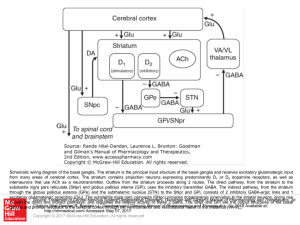
Slide ()
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...