brain - The Institute of Mathematical Sciences
... cells in the hippocampus — that region involved in storing memories — fired when mice slept, the scientists found. The photo shows the hippocampus region of the brain of a mouse that was genetically modified with a gene that creates a green fluorescent protein. So the neurons glow green when they fi ...
... cells in the hippocampus — that region involved in storing memories — fired when mice slept, the scientists found. The photo shows the hippocampus region of the brain of a mouse that was genetically modified with a gene that creates a green fluorescent protein. So the neurons glow green when they fi ...
psychology_midterm_review
... Temporal Lobe: The temporal lobe controls visual and auditory memories. It includes areas that help manage some speech and hearing capabilities, behavioral elements, and language. It is located in the cerebral hemisphere. ...
... Temporal Lobe: The temporal lobe controls visual and auditory memories. It includes areas that help manage some speech and hearing capabilities, behavioral elements, and language. It is located in the cerebral hemisphere. ...
Introduction to the Pharmacology of CNS Drugs: Introduction Drugs
... be discovered by primitive humans and are still the most widely used group of pharmacologic agents. In addition to their use in therapy, many drugs acting on the CNS are used without prescription to increase one's sense of well-being. The mechanisms by which various drugs act in the CNS have not alw ...
... be discovered by primitive humans and are still the most widely used group of pharmacologic agents. In addition to their use in therapy, many drugs acting on the CNS are used without prescription to increase one's sense of well-being. The mechanisms by which various drugs act in the CNS have not alw ...
Slide ()
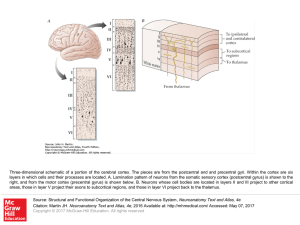
... Three-dimensional schematic of a portion of the cerebral cortex. The pieces are from the postcentral and and precentral gyri. Within the cortex are six layers in which cells and their processes are located. A. Lamination pattern of neurons from the somatic sensory cortex (postcentral gyrus) is shown ...
... Three-dimensional schematic of a portion of the cerebral cortex. The pieces are from the postcentral and and precentral gyri. Within the cortex are six layers in which cells and their processes are located. A. Lamination pattern of neurons from the somatic sensory cortex (postcentral gyrus) is shown ...
Chp 7 (part 1)
... membrane than outside 1. Mainly K+ inside and Na+ ions outside 2. As long as it stays more negative inside the neuron will remain inactive c. Many stimuli such as light, pressure, sound, or temp can stimulate a neuron 1. However, most neurons in the body are excited by neurotransmitters released by ...
... membrane than outside 1. Mainly K+ inside and Na+ ions outside 2. As long as it stays more negative inside the neuron will remain inactive c. Many stimuli such as light, pressure, sound, or temp can stimulate a neuron 1. However, most neurons in the body are excited by neurotransmitters released by ...
Optogenetics
... Epilepsy. Quenching or blocking epileptogenic activity is an exciting prospect. Many epilepsy patients have a stereotyped pattern of activity spread resulting from an epileptogenic focus. Brief activation of NpHR could be used to suppress the abnormal activity before it spreads, or to truncate the a ...
... Epilepsy. Quenching or blocking epileptogenic activity is an exciting prospect. Many epilepsy patients have a stereotyped pattern of activity spread resulting from an epileptogenic focus. Brief activation of NpHR could be used to suppress the abnormal activity before it spreads, or to truncate the a ...
PAC Newsletter - March 2015
... The Early Life of the Brain — continued from Page 1 The “wiring” of the brain has been compared to the wiring of a telephone .Billions and billions of neurons are reaching out to billions and billions of other neurons to make connections. These synaptic connections are enhanced by repeated use throu ...
... The Early Life of the Brain — continued from Page 1 The “wiring” of the brain has been compared to the wiring of a telephone .Billions and billions of neurons are reaching out to billions and billions of other neurons to make connections. These synaptic connections are enhanced by repeated use throu ...
Falling Over Sideways - Texas Library Association
... Traumatic Encephalopathy, also known as traumatic brain injury. If you have more students that need topics, assign epilepsy, meningitis, and cerebral palsy, depending on how many students are in your class. If more topics are needed, refer to this list from the National Institutes of Health: https:/ ...
... Traumatic Encephalopathy, also known as traumatic brain injury. If you have more students that need topics, assign epilepsy, meningitis, and cerebral palsy, depending on how many students are in your class. If more topics are needed, refer to this list from the National Institutes of Health: https:/ ...
Dear Editor, I am writing with regard to the increasingly acute
... not be able to be erased. Without doubt, the anti-drug message in schools must be clear and strong enough to prevent students from experimenting with drugs. Family members, especially parents, have to show care and concern for their children and be aware of any signs of them using drugs. While it is ...
... not be able to be erased. Without doubt, the anti-drug message in schools must be clear and strong enough to prevent students from experimenting with drugs. Family members, especially parents, have to show care and concern for their children and be aware of any signs of them using drugs. While it is ...
Psychology study guide chapter 2 Phrenology Developed by Franz
... Study of bumps on the skull and the relationship to mental abilities and character traits Yielded one big idea: different areas of the brain so different things Location and function Structure of neuron ...
... Study of bumps on the skull and the relationship to mental abilities and character traits Yielded one big idea: different areas of the brain so different things Location and function Structure of neuron ...
doc Behavioural_Neuroscience_Jan_11
... Myelin Sheath: insulates the axon and prevents messages spreading between adjacent axons Terminal buttons: button-like endings of the axon branch o They release neurotransmitters after receiving an action potential. o They connect with another neuron via a synapse. ...
... Myelin Sheath: insulates the axon and prevents messages spreading between adjacent axons Terminal buttons: button-like endings of the axon branch o They release neurotransmitters after receiving an action potential. o They connect with another neuron via a synapse. ...
Introduction to Psychology
... cell body of the receiving neuron. This tiny gap is called the synaptic gap or cleft. ...
... cell body of the receiving neuron. This tiny gap is called the synaptic gap or cleft. ...
Nerve Impulse Transmission
... 5. Once the neurotransmitters have passed along the impulse, the “extra” neurotransmitters still remaining in the synapse are either: a) broken down by enzymes or b) transported back into vesicles in the synaptic knob by endocytosis. ...
... 5. Once the neurotransmitters have passed along the impulse, the “extra” neurotransmitters still remaining in the synapse are either: a) broken down by enzymes or b) transported back into vesicles in the synaptic knob by endocytosis. ...
13.1- neurons
... The areas between the sections of myelin sheath are known as the nodes of Ranvier. All nerve fibres found within the peripheral nervous system have a thin outer membrane called the neurilemma, which surrounds the ...
... The areas between the sections of myelin sheath are known as the nodes of Ranvier. All nerve fibres found within the peripheral nervous system have a thin outer membrane called the neurilemma, which surrounds the ...
ben_slides2
... emergence of novel perceptual qualities that were not present in each individual odorant ...
... emergence of novel perceptual qualities that were not present in each individual odorant ...
In your journal, take notes by writing the name of
... peripheral nervous system (PNS). • The CNS includes the brain and spinal cord. The brain is protected by the skull, and the spinal cord by the skeletal vertebrae. • The PNS includes all other nervous system structures that sit outside the CNS but that help connect the CNS to areas of the body. ...
... peripheral nervous system (PNS). • The CNS includes the brain and spinal cord. The brain is protected by the skull, and the spinal cord by the skeletal vertebrae. • The PNS includes all other nervous system structures that sit outside the CNS but that help connect the CNS to areas of the body. ...
Another fragment in the death puzzle
... The activation of apoptotic cascades triggers a series of events, one of which is the condensation and fragmentation of chromosomal DNA. In mammals, at least three proteins have been implicated in this process — DFF40/CAD, the apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) and a mitochondrial endonuclease termed e ...
... The activation of apoptotic cascades triggers a series of events, one of which is the condensation and fragmentation of chromosomal DNA. In mammals, at least three proteins have been implicated in this process — DFF40/CAD, the apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) and a mitochondrial endonuclease termed e ...
Slide 1
... Electrical properties of neuron Neurons carry a negative electrical charge relative to the extra cellular fluid bathing them The plasma membrane is a semi permeable because certain ions can cross at certain times but there is not a free exchange The opening and closing of specific ion channels can ...
... Electrical properties of neuron Neurons carry a negative electrical charge relative to the extra cellular fluid bathing them The plasma membrane is a semi permeable because certain ions can cross at certain times but there is not a free exchange The opening and closing of specific ion channels can ...
Mirror Neurons & You
... Ontogeny(how an organism develops)- Many animals are programmed to imitate actions during development-part of the natural growth process. ...
... Ontogeny(how an organism develops)- Many animals are programmed to imitate actions during development-part of the natural growth process. ...
CLASS #1: 9 Jan 2001
... by post-synaptic neuron; ● glial uptake; ● enzyme deactivation. D. Actions at post-synaptic membrane: If receptors in post-synaptic membrane recognize the transmitter (=ligand-gated channels), the membrane’s conformation changes, causing a change in ion movement across the post-synaptic membrane and ...
... by post-synaptic neuron; ● glial uptake; ● enzyme deactivation. D. Actions at post-synaptic membrane: If receptors in post-synaptic membrane recognize the transmitter (=ligand-gated channels), the membrane’s conformation changes, causing a change in ion movement across the post-synaptic membrane and ...
Unit N Notes #1 – The Central Nervous System - Mr. Lesiuk
... Bones including the skull and vertebrae primarily protect the CNS from trauma. The brain and spine are also wrapped in three layers of protective membranes, which form the Meninges, in between these layers cerebro-spinal fluid is present to further cushion the CNS. A) Spinal Cord: i) Function1. To r ...
... Bones including the skull and vertebrae primarily protect the CNS from trauma. The brain and spine are also wrapped in three layers of protective membranes, which form the Meninges, in between these layers cerebro-spinal fluid is present to further cushion the CNS. A) Spinal Cord: i) Function1. To r ...
Nervous System
... different from the human brain in several ways. First, the human brain has many folds called gyri; the rat’s brain is smooth in appearance. Second, the olfactory bulbs (for smelling) of the rat brain are proportionately much larger than in the human brain. Third, the cerebral cortex (where higher le ...
... different from the human brain in several ways. First, the human brain has many folds called gyri; the rat’s brain is smooth in appearance. Second, the olfactory bulbs (for smelling) of the rat brain are proportionately much larger than in the human brain. Third, the cerebral cortex (where higher le ...
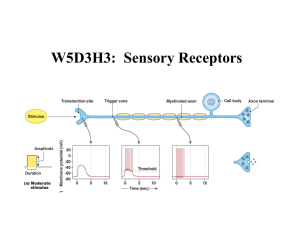
W5D3H3: Sensory Receptors
... • Understanding how external signals are detected and encoded by the nervous system is essential to a bigpicture understanding of how stimuli are detected and interpreted by the nervous system. Because defects in this process constrain the well-being and quality of life for many people and because c ...
... • Understanding how external signals are detected and encoded by the nervous system is essential to a bigpicture understanding of how stimuli are detected and interpreted by the nervous system. Because defects in this process constrain the well-being and quality of life for many people and because c ...