Neural Basis of Motor Control
... reversing the depolarization. Also at about this time, sodium channels start to close. This causes the action potential to go back toward -70 mV (a repolarization). Gradually, the ion concentrations go back to resting levels and the cell returns to -70 mV. ...
... reversing the depolarization. Also at about this time, sodium channels start to close. This causes the action potential to go back toward -70 mV (a repolarization). Gradually, the ion concentrations go back to resting levels and the cell returns to -70 mV. ...
Worms
... for humans eating sheep meat • Say the dose rate of A in sheep is 0.2 mg/kg. • Let’s say the human ‘no observable effect level’ (NOEL) based on animal studies for A has been determined as 1.25 mg/kg body weight. • The safety factor applied is generally 200. • So, a the adult daily intake (ADI) is 6 ...
... for humans eating sheep meat • Say the dose rate of A in sheep is 0.2 mg/kg. • Let’s say the human ‘no observable effect level’ (NOEL) based on animal studies for A has been determined as 1.25 mg/kg body weight. • The safety factor applied is generally 200. • So, a the adult daily intake (ADI) is 6 ...
Sedative-Hypnotics
... from BZDs, but act as agonists on a specific subset of BZD receptors The non-BZD produce only hypnotic-amnesic action (not antianxiety, muscle relaxant and anticonvulsant effects). They have lower abuse potential than BZDs. They are being preferred over BZDs for the treatment of insomnia. ...
... from BZDs, but act as agonists on a specific subset of BZD receptors The non-BZD produce only hypnotic-amnesic action (not antianxiety, muscle relaxant and anticonvulsant effects). They have lower abuse potential than BZDs. They are being preferred over BZDs for the treatment of insomnia. ...
Sensation
... We look with our eyes, but we see with the brain. Visual images are imported through the optic nerve to ...
... We look with our eyes, but we see with the brain. Visual images are imported through the optic nerve to ...
Principles of Computational Modeling in NeuroscienceDavid Sterratt
... in a network of excitatory and inhibitory integrateand-fire neurons, and next presents more complex network models of conductance-based neurons where associative memory can be embedded. After that, it explores two different models of thalamocortical interactions: one with multi-compartmental neurons ...
... in a network of excitatory and inhibitory integrateand-fire neurons, and next presents more complex network models of conductance-based neurons where associative memory can be embedded. After that, it explores two different models of thalamocortical interactions: one with multi-compartmental neurons ...
LTP
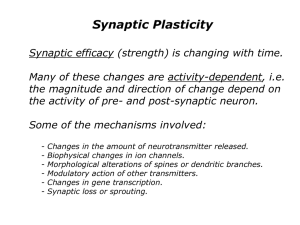
... Synaptic Plasticity Synaptic efficacy (strength) is changing with time. Many of these changes are activity-dependent, i.e. the magnitude and direction of change depend on the activity of pre- and post-synaptic neuron. Some of the mechanisms involved: ...
... Synaptic Plasticity Synaptic efficacy (strength) is changing with time. Many of these changes are activity-dependent, i.e. the magnitude and direction of change depend on the activity of pre- and post-synaptic neuron. Some of the mechanisms involved: ...
Cell Assemblies - CAAM @ Rice
... on to explain that these cell assemblies form via synaptic plasticity. He claims that if neuron A repeatedly fires neuron B, some metabolic activity occurs increasing the efficiency in which neuron A fires neuron B making it easier for neuron A to fire neuron B. This phenomenon is more commonly known as ...
... on to explain that these cell assemblies form via synaptic plasticity. He claims that if neuron A repeatedly fires neuron B, some metabolic activity occurs increasing the efficiency in which neuron A fires neuron B making it easier for neuron A to fire neuron B. This phenomenon is more commonly known as ...
Chapter Two
... Could mean a paradigm, school, or conceptual approach Could mean an emphasis on a specific cause of abnormal behavior Most paradigms are complex in considering causation Problems occur when information from other areas is ignored Multidimensional Models Interdisciplinary, eclectic, and i ...
... Could mean a paradigm, school, or conceptual approach Could mean an emphasis on a specific cause of abnormal behavior Most paradigms are complex in considering causation Problems occur when information from other areas is ignored Multidimensional Models Interdisciplinary, eclectic, and i ...
Effect of acute and chronic tianeptine on the action of classical
... co-existing with epilepsy. It soon became clear that the proper treatment of depression co-existing with epilepsy may improve the outcome of both disorders [43]. Therefore, the choice of appropriate drugs seems to be crucial for effectiveness of such a complex therapy. Nowadays, two classes of antid ...
... co-existing with epilepsy. It soon became clear that the proper treatment of depression co-existing with epilepsy may improve the outcome of both disorders [43]. Therefore, the choice of appropriate drugs seems to be crucial for effectiveness of such a complex therapy. Nowadays, two classes of antid ...
CB064-4.13 - Workforce Solutions
... and Training Administration. The solution was created by the grantee and does not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Labor. The Department of Labor makes no guarantees, warranties, or assurances of any kind, express or implied, with respect to such information, inclu ...
... and Training Administration. The solution was created by the grantee and does not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Labor. The Department of Labor makes no guarantees, warranties, or assurances of any kind, express or implied, with respect to such information, inclu ...
Memories of punishment and relief in a mini-brain - Schram
... Upon encountering this odour again, this memory trace is “read out” by output neurons that are post-synaptic to the MB, leading to learned avoidance. Recently, individual dopaminergic neuron-, MB neuron- and output neuron-types have been identified for carrying the punishment signal as well as for h ...
... Upon encountering this odour again, this memory trace is “read out” by output neurons that are post-synaptic to the MB, leading to learned avoidance. Recently, individual dopaminergic neuron-, MB neuron- and output neuron-types have been identified for carrying the punishment signal as well as for h ...
Toward STDP-based population action in large networks of spiking
... After a short relaxation (200 ms), the STDP plasticity is activated for 5 s on the excitatory synapses of excitatory neurons only. We represent in figure 1 the population response in both cases (aperiodic and periodic input signals). The two simulations are done on the same network. Only the input s ...
... After a short relaxation (200 ms), the STDP plasticity is activated for 5 s on the excitatory synapses of excitatory neurons only. We represent in figure 1 the population response in both cases (aperiodic and periodic input signals). The two simulations are done on the same network. Only the input s ...
Chapter 10: Nervous System I
... A. The nervous system is composed predominately of nervous tissue but also includes some blood vessels and connective tissue. B. Two cell types of nervous tissue are neurons and neuroglial cells. C. Neurons are specialized to react to physical and chemical changes in their surroundings. D. Dendrites ...
... A. The nervous system is composed predominately of nervous tissue but also includes some blood vessels and connective tissue. B. Two cell types of nervous tissue are neurons and neuroglial cells. C. Neurons are specialized to react to physical and chemical changes in their surroundings. D. Dendrites ...
FIGURE LEGNEDS FIGURE 24.1 A dorsal root ganglion cell is a
... FIGURE 24.11 The medial path taken by spinothalamic neurons in lamina I (driven by C fibers) differs from the lateral path taken by neurons in laminae IV and V (driven by C and Aδ nociceptors and Aβ mechanoreceptors). Anterior spinothalamic tract axons are given off by the deeper neurons and termina ...
... FIGURE 24.11 The medial path taken by spinothalamic neurons in lamina I (driven by C fibers) differs from the lateral path taken by neurons in laminae IV and V (driven by C and Aδ nociceptors and Aβ mechanoreceptors). Anterior spinothalamic tract axons are given off by the deeper neurons and termina ...
Simulation with NEST, an example of a full
... brain experimental data from animal experiments are widely available. Because of related structures these data is used to improve and validate models of the brain. In combination with neuronal simulations these data allows a first look into the functionality of nervous systems. The paper The cell-ty ...
... brain experimental data from animal experiments are widely available. Because of related structures these data is used to improve and validate models of the brain. In combination with neuronal simulations these data allows a first look into the functionality of nervous systems. The paper The cell-ty ...
Functional and structural adaptation in the central nervous system
... Sensory stimuli are converted into electrical signals Action potentials are electrical signals carried along neurons Synapses are chemical or electrical junctions that allow electrical signals to pass from neurons to other cells Changes in the amount of activity at a synapse can enhance or reduce it ...
... Sensory stimuli are converted into electrical signals Action potentials are electrical signals carried along neurons Synapses are chemical or electrical junctions that allow electrical signals to pass from neurons to other cells Changes in the amount of activity at a synapse can enhance or reduce it ...
Antineoplastic Agents
... receptors (e.g. receptors tyrosine kinase) • Restore function of tumor suppressor : gene ...
... receptors (e.g. receptors tyrosine kinase) • Restore function of tumor suppressor : gene ...
Jeopardy
... This is our body’s ultimate control and information processing center. It is an intricate covering of interconnected neural cells. ...
... This is our body’s ultimate control and information processing center. It is an intricate covering of interconnected neural cells. ...
the cerebral cortex
... body), area 18, 19, parietal cortex, temporal cortex. Dorsal stream – parietal cortex (where : rods, periphery of retina, area 7) Ventral stream – temporal cortex (whatcolors, form : cones, central area of retina, area 37, inferior. temporal cortex ...
... body), area 18, 19, parietal cortex, temporal cortex. Dorsal stream – parietal cortex (where : rods, periphery of retina, area 7) Ventral stream – temporal cortex (whatcolors, form : cones, central area of retina, area 37, inferior. temporal cortex ...
AP Biology - Pleasantville High School
... membrane in a lock and key manner. (Inhibitor substances stop the impulse because they can fit into the receptor sites and block the normal neurotransmitter.) -this generates an action potential in the postsynaptic membrane and the nerve impulse continues on -after their release the neurotransmitter ...
... membrane in a lock and key manner. (Inhibitor substances stop the impulse because they can fit into the receptor sites and block the normal neurotransmitter.) -this generates an action potential in the postsynaptic membrane and the nerve impulse continues on -after their release the neurotransmitter ...
Therapies, Careers in Psychology, and Ethics
... Instructor’s Resources for your text or earlier versions of your text. Other resources used include Ahmad (2010) and Huffman’s (2010) Psychology in Action. Many slides & activities are adapted from the instructor’s manual. Images are from Google Images or the Instructor’s Manual. ...
... Instructor’s Resources for your text or earlier versions of your text. Other resources used include Ahmad (2010) and Huffman’s (2010) Psychology in Action. Many slides & activities are adapted from the instructor’s manual. Images are from Google Images or the Instructor’s Manual. ...
Abstract Browser - The Journal of Neuroscience
... therefore important to individuals’ normal social functioning. Previous neuroimaging studies have highlighted the involvement of the insular and ventromedial prefrontal (vmPFC) cortices in representing norms. However, the necessity and dissociability of their involvement remain unclear. Using model- ...
... therefore important to individuals’ normal social functioning. Previous neuroimaging studies have highlighted the involvement of the insular and ventromedial prefrontal (vmPFC) cortices in representing norms. However, the necessity and dissociability of their involvement remain unclear. Using model- ...