Advances in the Treatment of Erectile Dysfunction
... erectile tissue. Further investigation of the neurotransmission involved in penile erection, hormone actions involved in this response, and biochemical signal transduction processes within the erectile tissue represent major areas of scientific pursuit. Current objectives scientifically are to ident ...
... erectile tissue. Further investigation of the neurotransmission involved in penile erection, hormone actions involved in this response, and biochemical signal transduction processes within the erectile tissue represent major areas of scientific pursuit. Current objectives scientifically are to ident ...
Basics of Anatomy.pub
... The Nervous System: Neurons, Networks and the Human Brain (GPM0041) Begins by examining the structure and func on of neurons; res ng, ac on and post-synap c poten als; and reflexes and neural networks. The peripheral, soma c, autonomic, sympathe c and parasympathe c nervous systems are introduced ...
... The Nervous System: Neurons, Networks and the Human Brain (GPM0041) Begins by examining the structure and func on of neurons; res ng, ac on and post-synap c poten als; and reflexes and neural networks. The peripheral, soma c, autonomic, sympathe c and parasympathe c nervous systems are introduced ...
D. Brain
... hands). This progresses to infantile behavior….they will often talk about their “past”….what they can remember. ...
... hands). This progresses to infantile behavior….they will often talk about their “past”….what they can remember. ...
Unit 2, the Brain
... Parts of a Neuron Cell Body: Life support center of the neuron. Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches ...
... Parts of a Neuron Cell Body: Life support center of the neuron. Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches ...
NervousSystem2
... etc., take place within the CNS itself. They are mechanisms of interneurons, a part of, and have their effect on, interneuronal circuitry within the CNS. By having excitatory and inhibitory neurons, the interneuronal circuitry modulates the wave of afferent excitation and brings about the variable c ...
... etc., take place within the CNS itself. They are mechanisms of interneurons, a part of, and have their effect on, interneuronal circuitry within the CNS. By having excitatory and inhibitory neurons, the interneuronal circuitry modulates the wave of afferent excitation and brings about the variable c ...
Endocrine glands
... • Autonomic nervous system (ANS) - division of the PNS consisting of nerves that control all of the involuntary muscles, organs, and glands sensory pathway nerves coming from the sensory organs to the CNS consisting of sensory neurons. – Sympathetic division (fight-or-flight system) - part of the AN ...
... • Autonomic nervous system (ANS) - division of the PNS consisting of nerves that control all of the involuntary muscles, organs, and glands sensory pathway nerves coming from the sensory organs to the CNS consisting of sensory neurons. – Sympathetic division (fight-or-flight system) - part of the AN ...
Central Nervous System
... Medulla oblongata - dictates all life functions including: heart rate, breathing, and reflex actions. ...
... Medulla oblongata - dictates all life functions including: heart rate, breathing, and reflex actions. ...
Neuron Stations
... halves sticking out. Take the 2 halves and twist them together into a single extension. Axons send information received from the neuron to the next neuron in its path. Axons can be as long as 3 meters and information can travel as fast as 100 meters/second (224 miles/hour). Q3: What else can travel ...
... halves sticking out. Take the 2 halves and twist them together into a single extension. Axons send information received from the neuron to the next neuron in its path. Axons can be as long as 3 meters and information can travel as fast as 100 meters/second (224 miles/hour). Q3: What else can travel ...
The Brain*s Two Hemispheres
... For example: A person with Wernicke’s Area damage would be able to recognize the individual parts of a computer (monitor, mouse, keyboard, etc.) but not understand that these parts, together, create a ...
... For example: A person with Wernicke’s Area damage would be able to recognize the individual parts of a computer (monitor, mouse, keyboard, etc.) but not understand that these parts, together, create a ...
DRUG RECEPTOR AND PHARMCODYNAMICS
... response to drug that is noxious and unintended and that occurs at dose used in man for prophylaxis, diagnosis or therapy of a disease, or for the modification of physiological function”. (1)Side effects In the range of therapeutic doses, the drug effects, which are not related to the current therap ...
... response to drug that is noxious and unintended and that occurs at dose used in man for prophylaxis, diagnosis or therapy of a disease, or for the modification of physiological function”. (1)Side effects In the range of therapeutic doses, the drug effects, which are not related to the current therap ...
Michael J. Fisher, MD – Research Investment
... pediatric training at Children's Hospital in Boston. He then did fellowships in pediatric hematology/oncology and pediatric neuro-oncology at CHOP, and has been on staff at CHOP since that time. His research focuses on identifying new treatments and novel biomarkers (particularly using new imaging m ...
... pediatric training at Children's Hospital in Boston. He then did fellowships in pediatric hematology/oncology and pediatric neuro-oncology at CHOP, and has been on staff at CHOP since that time. His research focuses on identifying new treatments and novel biomarkers (particularly using new imaging m ...
Brain Lecture - Scott County Schools
... The Nervous System • A. The Central Nervous System – 1. Also known as the CNS – 2. It consist of the brain and the spinal cord – 3. Cerebrospinal Fluid (CFS) is a a liquid similar to blood serum found in the ventricles of the brain and in the central canal of the spinal cord – 4. The Blood-Brain Ba ...
... The Nervous System • A. The Central Nervous System – 1. Also known as the CNS – 2. It consist of the brain and the spinal cord – 3. Cerebrospinal Fluid (CFS) is a a liquid similar to blood serum found in the ventricles of the brain and in the central canal of the spinal cord – 4. The Blood-Brain Ba ...
The Science of Psychology
... • Resting potential - the state of the neuron when not firing a neural impulse. • Action potential - the release of the neural impulse • All-or-none - referring to the fact that a neuron either fires completely or does not fire at all. ...
... • Resting potential - the state of the neuron when not firing a neural impulse. • Action potential - the release of the neural impulse • All-or-none - referring to the fact that a neuron either fires completely or does not fire at all. ...
Nervous System Development Inner Cell Mass of Blastocyst Inner
... overlying skin. If closure does not occur normally, nervous system may remain exposed (“open NTD”). • In other cases the neural tube may not be exposed to the surface (“closed NTD”), but the spinal vertebrae and skin surrounding the spine may not be completely normal. ...
... overlying skin. If closure does not occur normally, nervous system may remain exposed (“open NTD”). • In other cases the neural tube may not be exposed to the surface (“closed NTD”), but the spinal vertebrae and skin surrounding the spine may not be completely normal. ...
Slide ()
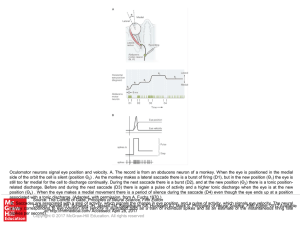
... Oculomotor neurons signal eye position and velocity. A. The record is from an abducens neuron of a monkey. When the eye is positioned in the medial side of the orbit the cell is silent (position Θ0) . As the monkey makes a lateral saccade there is a burst of firing (D1), but in the new position (Θ1) ...
... Oculomotor neurons signal eye position and velocity. A. The record is from an abducens neuron of a monkey. When the eye is positioned in the medial side of the orbit the cell is silent (position Θ0) . As the monkey makes a lateral saccade there is a burst of firing (D1), but in the new position (Θ1) ...
Neural Networks
... known as the Generalised Delta Rule (GDR), or more commonly, the Back Propagation (BP) algorithm ...
... known as the Generalised Delta Rule (GDR), or more commonly, the Back Propagation (BP) algorithm ...
Toxicology
... Factors influencing toxicity: All these factors determine the drug/toxin bioavailability plasma concentration – time curves Drug eliminated from a single compartment by a first order process half life ~ 4hrs ...
... Factors influencing toxicity: All these factors determine the drug/toxin bioavailability plasma concentration – time curves Drug eliminated from a single compartment by a first order process half life ~ 4hrs ...
3A & 3B PowerPoint
... (like pushing the breaks). If the excitatory signals, minus the inhibitory signals exceed a minimum intensity, called the absolute threshold, then action potential is realized. ...
... (like pushing the breaks). If the excitatory signals, minus the inhibitory signals exceed a minimum intensity, called the absolute threshold, then action potential is realized. ...
test1short answer - answer key
... Electrophysiological and metabolic brain imaging techniques measure brain function, the activity of the living brain (2). Electrophysiological methods directly measure neurophysiological function though the electrical activity of the neurons (2). Metabolic brain imaging techniques indirectly measure ...
... Electrophysiological and metabolic brain imaging techniques measure brain function, the activity of the living brain (2). Electrophysiological methods directly measure neurophysiological function though the electrical activity of the neurons (2). Metabolic brain imaging techniques indirectly measure ...
It Wasn`t Like That When I Was a Teen!
... Heroin is a highly addictive drug derived from morphine. It is a “downer” or depressant that affects the brain’s pleasure systems and interferes with the brain’s ability to perceive pain. Potency: 5% in the 70’s – today – 50-80% pure Higher potency allows for snorting or smoking it to achieve ...
... Heroin is a highly addictive drug derived from morphine. It is a “downer” or depressant that affects the brain’s pleasure systems and interferes with the brain’s ability to perceive pain. Potency: 5% in the 70’s – today – 50-80% pure Higher potency allows for snorting or smoking it to achieve ...