Hot spot activity and the break-up of Pangea (PDF
... overlying plate. This is, of course, not quite correct; the plate is moving over a relatively stationary mantle plume expressed by a hot spot. Nevertheless, the term makes it somewhat easier to describe the geodynamic process. 3.1. Late Triassic — 220 Ma (Fig. 3) At this stage the Bouvet hot spot wa ...
... overlying plate. This is, of course, not quite correct; the plate is moving over a relatively stationary mantle plume expressed by a hot spot. Nevertheless, the term makes it somewhat easier to describe the geodynamic process. 3.1. Late Triassic — 220 Ma (Fig. 3) At this stage the Bouvet hot spot wa ...
ONE THE PLATE TECTONICS REVOLUTION
... sometimes witnessed—but could not begin to explain—the earthquakes, volcanoes, and storms that provided such compelling and unfathomable displays of power. Such ideas were also consistent with, indeed almost a consequence of, prevailing Western beliefs in a world inexorably shaped by catastrophic bi ...
... sometimes witnessed—but could not begin to explain—the earthquakes, volcanoes, and storms that provided such compelling and unfathomable displays of power. Such ideas were also consistent with, indeed almost a consequence of, prevailing Western beliefs in a world inexorably shaped by catastrophic bi ...
Field Trip to the Fall Zone, Cape Fear River, Raven Rock State Park
... be directly addressed by EarthScope and related research. These questions include, but are not limited to the assembly, structure, and evolution of the lithosphere of the eastern U.S., the dynamic flow of the underlying asthenosphere, Appalachian orogenesis, post-Appalachian rift initiation and evol ...
... be directly addressed by EarthScope and related research. These questions include, but are not limited to the assembly, structure, and evolution of the lithosphere of the eastern U.S., the dynamic flow of the underlying asthenosphere, Appalachian orogenesis, post-Appalachian rift initiation and evol ...
Sample Chapter 2 - Investigating Geologic Questions
... samples, even from depths of several kilometers. This and later drilling revealed that layers of salt hundreds to thousands of meters thick were within the sediments on the seafloor. Surprisingly, the drilling also encountered sands that show evidence of being deposited by wind. From these and other ...
... samples, even from depths of several kilometers. This and later drilling revealed that layers of salt hundreds to thousands of meters thick were within the sediments on the seafloor. Surprisingly, the drilling also encountered sands that show evidence of being deposited by wind. From these and other ...
View PDF - Cengage
... and metamorphosed volcanic and sedimentary rocks intruded by large bodies of granitic rocks. This complex assemblage represents the tectonic creation and convergence of volcanic island arcs, similar to the modern volcanic archipelagoes of the western Pacific Ocean such as Japan and the Philippians ( ...
... and metamorphosed volcanic and sedimentary rocks intruded by large bodies of granitic rocks. This complex assemblage represents the tectonic creation and convergence of volcanic island arcs, similar to the modern volcanic archipelagoes of the western Pacific Ocean such as Japan and the Philippians ( ...
Amherst County Public Schools Earth Science Curriculum Pacing
... The student will investigate and understand the origin and evolution of the atmosphere and the interrelationship of geologic processes, biologic processes, and human activities on its composition and dynamics. Key concepts include a) scientific evidence for atmospheric composition changes over geolo ...
... The student will investigate and understand the origin and evolution of the atmosphere and the interrelationship of geologic processes, biologic processes, and human activities on its composition and dynamics. Key concepts include a) scientific evidence for atmospheric composition changes over geolo ...
Lower Jurassic Mudstones and Limestones
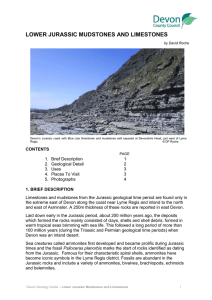
... Lower Jurassic limestones and mudstones are found only in the extreme east of Devon near Lyme Regis and Axminster. Approximately 250m thickness of strata are recorded in east Devon consisting mainly of thinly interbedded sequences of mudstones and limestones. Eastwards, in neighbouring Dorset and in ...
... Lower Jurassic limestones and mudstones are found only in the extreme east of Devon near Lyme Regis and Axminster. Approximately 250m thickness of strata are recorded in east Devon consisting mainly of thinly interbedded sequences of mudstones and limestones. Eastwards, in neighbouring Dorset and in ...
Geologic Timeline for the eastern Beartooth Mountains
... General information about the Precambrian rocks of the Beartooth Mtns Archean rocks are exposed in the Wyoming Province in the cores of mountain ranges uplifted during the Laramide Orogeny (Fig. 1). Archean rocks in the eastern and central Beartooth Mountains, Bighorn Mountains, and samples from dee ...
... General information about the Precambrian rocks of the Beartooth Mtns Archean rocks are exposed in the Wyoming Province in the cores of mountain ranges uplifted during the Laramide Orogeny (Fig. 1). Archean rocks in the eastern and central Beartooth Mountains, Bighorn Mountains, and samples from dee ...
Unit 1 The Ocean Basins
... open the Once and Future Oceans view. This view shows the present locations of today’s continents and oceans. However, the continents and oceans have not always been in these locations, nor will they be in the future. In this investigation, you will trace the movements of three continents from 750 m ...
... open the Once and Future Oceans view. This view shows the present locations of today’s continents and oceans. However, the continents and oceans have not always been in these locations, nor will they be in the future. In this investigation, you will trace the movements of three continents from 750 m ...
The geological story of Pennsylvania
... viously stated, however, the dragging action of convection continued to move the plates, causing them to collide. The behavior of the plates when they collide is largely controlled by the type of crust on the plate. There are two main types of crust: continental crust, which is mostly composed of hi ...
... viously stated, however, the dragging action of convection continued to move the plates, causing them to collide. The behavior of the plates when they collide is largely controlled by the type of crust on the plate. There are two main types of crust: continental crust, which is mostly composed of hi ...
California terranes
... nomenclature (e.g., nappe, block, thrust fault, allochthon, ophiolite) in order to enhance the precision of the discussion. The principal terrane-related tectonic events for California and surroundings include the following. 1. Rifting of the western North American margin occurred during the latest ...
... nomenclature (e.g., nappe, block, thrust fault, allochthon, ophiolite) in order to enhance the precision of the discussion. The principal terrane-related tectonic events for California and surroundings include the following. 1. Rifting of the western North American margin occurred during the latest ...
Geology Background booklet
... A lesser threat to southwest Oregon is volcanic eruption. The Cascade Mountains, which lie just east of the Bear Creek valley, but actually extend all the way from California to Canada, are volcanically active. While the Cascade volcanoes are relatively quiet right now, they have been more or less c ...
... A lesser threat to southwest Oregon is volcanic eruption. The Cascade Mountains, which lie just east of the Bear Creek valley, but actually extend all the way from California to Canada, are volcanically active. While the Cascade volcanoes are relatively quiet right now, they have been more or less c ...
Geology of the Rogue Valley
... Geology is the study of the earth’s rocks and the processes that affect them. Geologists study the earth in many different ways. Some geologists locate new rock quarries and mineral deposits, while others study rocks in an effort to locate energy reserves including gas, oil, and coal. Another import ...
... Geology is the study of the earth’s rocks and the processes that affect them. Geologists study the earth in many different ways. Some geologists locate new rock quarries and mineral deposits, while others study rocks in an effort to locate energy reserves including gas, oil, and coal. Another import ...
Thematic Article Tethyan ophiolites and Pangea break-up
... have formed as an incipient opening of a new ocean, the Eastern Mesozoic Tethys or ‘Neotethys’, which, during the Triassic, began to separate Gondwana (Adria Promontory) from Laurasia. The location of the western termination of this oceanic basin is uncertain, although several lines of evidence indi ...
... have formed as an incipient opening of a new ocean, the Eastern Mesozoic Tethys or ‘Neotethys’, which, during the Triassic, began to separate Gondwana (Adria Promontory) from Laurasia. The location of the western termination of this oceanic basin is uncertain, although several lines of evidence indi ...
Heterogeneous Growth and Dissolution of Sillimanite
... Archean rocks exposed in the eastern and central Beartooth Mountains, Bighorn Mountains, and samples from deep-drill cores in eastern Wyoming and Montana are dominantly Late Archean granitoids, members of the tonalite-trondhjemitegranodiorite suite, with inclusions of older supracrustal rocks preser ...
... Archean rocks exposed in the eastern and central Beartooth Mountains, Bighorn Mountains, and samples from deep-drill cores in eastern Wyoming and Montana are dominantly Late Archean granitoids, members of the tonalite-trondhjemitegranodiorite suite, with inclusions of older supracrustal rocks preser ...
The Geology of Crowders Mountain State Park, North Carolina – A
... prospects or other geologic features. To produce a geologic map, a geologist systematically walks and/or drives the subject area looking for rock outcrop, other geologic material, evidence for faults, and active and former mines and prospects. The geologic map is the fundamental starting point in un ...
... prospects or other geologic features. To produce a geologic map, a geologist systematically walks and/or drives the subject area looking for rock outcrop, other geologic material, evidence for faults, and active and former mines and prospects. The geologic map is the fundamental starting point in un ...
Classification of Sedimentary Rocks
... 2) Stratigraphers try to trace these layers over (often by looking at the sequence of layers or again by using fossil assemblages. 3) Using these sciences together, geologists can date or find fossils, locate petroleum bearing rocks (and areas where petroleum is trapped) ...
... 2) Stratigraphers try to trace these layers over (often by looking at the sequence of layers or again by using fossil assemblages. 3) Using these sciences together, geologists can date or find fossils, locate petroleum bearing rocks (and areas where petroleum is trapped) ...
the cretaceous sanfranciscan basin, eastern plateau of
... cobbles of quartzite, with lenses of red sandstones associated. Directional structures like imbrication of clasts and cross-bedding in sands and gravels also indicate sense of paleoflow approximately from south to north. This conglomerate seems to have a low diamond content. Tompkins and Gonzaga (19 ...
... cobbles of quartzite, with lenses of red sandstones associated. Directional structures like imbrication of clasts and cross-bedding in sands and gravels also indicate sense of paleoflow approximately from south to north. This conglomerate seems to have a low diamond content. Tompkins and Gonzaga (19 ...
Evidence for iceberg armadas from East Antarctica
... cores in the northwest part of the Ross Ice Shelf taken by the ANDRILL program show 38 cycles of advance and retreat of the West Antarctic ice sheet over the last 5 Ma (Naish, et al., 2009). Glacial sediments of the Lambert Graben indicate at least four retreats of the ice sheet several hundred kms ...
... cores in the northwest part of the Ross Ice Shelf taken by the ANDRILL program show 38 cycles of advance and retreat of the West Antarctic ice sheet over the last 5 Ma (Naish, et al., 2009). Glacial sediments of the Lambert Graben indicate at least four retreats of the ice sheet several hundred kms ...
A Geological Tour Information Guide
... foreground, resembles five fingers or knuckles of a hand extending into the ocean, and is an excellent example of how rocks of different origin and composition react differently to the mechanical and chemical weathering agents of the atmosphere and ocean. For reference purposes (Fig. 5), if one face ...
... foreground, resembles five fingers or knuckles of a hand extending into the ocean, and is an excellent example of how rocks of different origin and composition react differently to the mechanical and chemical weathering agents of the atmosphere and ocean. For reference purposes (Fig. 5), if one face ...
THE GEOLOGICAL STORY OF PENNSYLVANIA Educational Series 4
... viously stated, however, the dragging action of convection continued to move the plates, causing them to collide. The behavior of the plates when they collide is largely controlled by the type of crust on the plate. There are two main types of crust: continental crust, which is mostly composed of hi ...
... viously stated, however, the dragging action of convection continued to move the plates, causing them to collide. The behavior of the plates when they collide is largely controlled by the type of crust on the plate. There are two main types of crust: continental crust, which is mostly composed of hi ...
Unconformity-Associated U - Ministry of Energy and Mines
... and regional fault zones that intersect the unconformity may be important features. Generally found close to basement granitic rocks with a high U clarke. GENETIC ...
... and regional fault zones that intersect the unconformity may be important features. Generally found close to basement granitic rocks with a high U clarke. GENETIC ...
The Ocean Bottom
... produced in place by chemical reactions in seawater or within the upper sediment Volcanogenic sediment produced from the ejections of volcanic eruptions Cosmogenic sediments produced from cosmic debris that constantly bombards the Earth ...
... produced in place by chemical reactions in seawater or within the upper sediment Volcanogenic sediment produced from the ejections of volcanic eruptions Cosmogenic sediments produced from cosmic debris that constantly bombards the Earth ...
Short Course in Basic Geology Gregory A. Miles This short course
... a jigsaw puzzle. Although there was little or no scientific evidence available, it was proposed that the continents had been joined together at some time in the past. a. In the early 20th Century, Alfred Wegener proposed an idea called continental drift. Wegener: fit the continents together into o ...
... a jigsaw puzzle. Although there was little or no scientific evidence available, it was proposed that the continents had been joined together at some time in the past. a. In the early 20th Century, Alfred Wegener proposed an idea called continental drift. Wegener: fit the continents together into o ...
Geological history of Earth
The geological history of Earth follows the major events in Earth's past based on the geologic time scale, a system of chronological measurement based on the study of the planet's rock layers (stratigraphy). Earth formed about 4.54 billion years ago by accretion from the solar nebula, a disk-shaped mass of dust and gas left over from the formation of the Sun, which also created the rest of the Solar System.Earth was initially molten due to extreme volcanism and frequent collisions with other bodies. Eventually, the outer layer of the planet cooled to form a solid crust when water began accumulating in the atmosphere. The Moon formed soon afterwards, possibly as the result of a Mars-sized object with about 10% of the Earth's mass impacting the planet in a glancing blow. Some of this object's mass merged with the Earth, significantly altering its internal composition, and a portion was ejected into space. Some of the material survived to form an orbiting moon. Outgassing and volcanic activity produced the primordial atmosphere. Condensing water vapor, augmented by ice delivered from comets, produced the oceans.As the surface continually reshaped itself over hundreds of millions of years, continents formed and broke apart. They migrated across the surface, occasionally combining to form a supercontinent. Roughly 750 million years ago, the earliest-known supercontinent Rodinia, began to break apart. The continents later recombined to form Pannotia, 600 to 540 million years ago, then finally Pangaea, which broke apart 180 million years ago.The present pattern of ice ages began about 40 million years ago, then intensified at the end of the Pliocene. The polar regions have since undergone repeated cycles of glaciation and thaw, repeating every 40,000–100,000 years. The last glacial period of the current ice age ended about 10,000 years ago.