1.6 General age and tectonic setting of the Arabian Shield
... late Mesozoic to Cenozoic rocks that reflect the history of Red Sea rifting and marginal uplift. These include thick epiclastic successions of sandstone, siltstone, and periodic conglomerates, a thick evaporite sequence, and minor volcanic rocks. As in the Arabian Platform, the total thickness of se ...
... late Mesozoic to Cenozoic rocks that reflect the history of Red Sea rifting and marginal uplift. These include thick epiclastic successions of sandstone, siltstone, and periodic conglomerates, a thick evaporite sequence, and minor volcanic rocks. As in the Arabian Platform, the total thickness of se ...
- Earthdoc
... exploration are discussed. Pools associated with the rifts and grabens exhibit profound effect of tectonics. In Barmer Cambay basin, all the pools are trending parallel to the basin forming faults, indicating that the deposition of source rocks, reservoir rocks as well as trapping mechanism are cont ...
... exploration are discussed. Pools associated with the rifts and grabens exhibit profound effect of tectonics. In Barmer Cambay basin, all the pools are trending parallel to the basin forming faults, indicating that the deposition of source rocks, reservoir rocks as well as trapping mechanism are cont ...
topic_4_5 - Earth and Environmental Sciences
... movement of the Indian continental plate into Eurasia. The following link leads to an animation of the motion of India relative to Eurasia and Africa, reconstructed on the basis of oceanic and continental paleomagnetic data: http://earth.leeds.ac.uk/dynamicearth/himalayas/india/anim ation.htm As you ...
... movement of the Indian continental plate into Eurasia. The following link leads to an animation of the motion of India relative to Eurasia and Africa, reconstructed on the basis of oceanic and continental paleomagnetic data: http://earth.leeds.ac.uk/dynamicearth/himalayas/india/anim ation.htm As you ...
7.0 GEOLOGIC SETTING 7.1 Regional Geologic Setting 7.2
... Figure 7-1, Regional geology, and Figure 7-2, Regional stratigraphy). Also included in the Intermediate Series are extensive metamorphosed felsic, mafic volcanic and volcaniclastic rocks. These rocks are postEburnean (i.e., younger than 1,800 million years) and are cut by basic dikes. The original d ...
... Figure 7-1, Regional geology, and Figure 7-2, Regional stratigraphy). Also included in the Intermediate Series are extensive metamorphosed felsic, mafic volcanic and volcaniclastic rocks. These rocks are postEburnean (i.e., younger than 1,800 million years) and are cut by basic dikes. The original d ...
Field Guide Seattle to CRB
... About 2 million years ago, a cooling global temperature provided conditions in the Northern Hemisphere favorable for the creation of great mile-thick sheets of moving ice called glaciers. Thus began the Pleistocene Ice Age. In western North America, glaciers flowed south out of Canada, damming river ...
... About 2 million years ago, a cooling global temperature provided conditions in the Northern Hemisphere favorable for the creation of great mile-thick sheets of moving ice called glaciers. Thus began the Pleistocene Ice Age. In western North America, glaciers flowed south out of Canada, damming river ...
Glossary a - Teacher Friendly Guides
... a geologic time period that extends from 359 to 299 million years ago. It is divided into two subperiods, the Mississippian and the Pennsylvanian. By the Carboniferous, terrestrial life had become well established. The name Carboniferous means "coal-bearing," and it is during this time that many of ...
... a geologic time period that extends from 359 to 299 million years ago. It is divided into two subperiods, the Mississippian and the Pennsylvanian. By the Carboniferous, terrestrial life had become well established. The name Carboniferous means "coal-bearing," and it is during this time that many of ...
The Geology of Antarctica
... these terranes, which occur around the coast of the EAS, the ArchaeanPalaeoproterozoic geological histories are largely intact. The principal examples of such terranes are the Napier Complex of Enderby Land, the Grunehogna Craton of western Dronning Maud Land, the Vestfold Block of Prydz Bay, and th ...
... these terranes, which occur around the coast of the EAS, the ArchaeanPalaeoproterozoic geological histories are largely intact. The principal examples of such terranes are the Napier Complex of Enderby Land, the Grunehogna Craton of western Dronning Maud Land, the Vestfold Block of Prydz Bay, and th ...
Plate Tectonics
... Although plate tectonics is a relatively young idea in comparison with unifying theories from other sciences (e.g., law of gravity, theory of evolution), some of the basic observations that represent the foundation of the theory were made many centuries ago when the first maps of the Atlantic Ocean ...
... Although plate tectonics is a relatively young idea in comparison with unifying theories from other sciences (e.g., law of gravity, theory of evolution), some of the basic observations that represent the foundation of the theory were made many centuries ago when the first maps of the Atlantic Ocean ...
Earth Sciences 089G MIDTERM EXAMINATION MARKING KEY Part
... Part 4. Short Essays (Answer two of the following) Select two of the following questions and prepare short essay responses using the examination booklet provided. Your answers should be written in complete sentences and be as detailed as possible, including definitions of relevant general concepts a ...
... Part 4. Short Essays (Answer two of the following) Select two of the following questions and prepare short essay responses using the examination booklet provided. Your answers should be written in complete sentences and be as detailed as possible, including definitions of relevant general concepts a ...
Sorting - HCC Learning Web
... • Rounding results from abrasion against other particles and grain impact during transport. • Very well rounded sand grains suggest that a sand may have been recycled from older sandstones. ...
... • Rounding results from abrasion against other particles and grain impact during transport. • Very well rounded sand grains suggest that a sand may have been recycled from older sandstones. ...
MSWord file
... Part 4. Short Essays (Answer two of the following) Select two of the following questions and prepare short essay responses using the examination booklet provided. Your answers should be written in complete sentences and be as detailed as possible, including definitions of relevant general concepts a ...
... Part 4. Short Essays (Answer two of the following) Select two of the following questions and prepare short essay responses using the examination booklet provided. Your answers should be written in complete sentences and be as detailed as possible, including definitions of relevant general concepts a ...
Ore Bin / Oregon Geology magazine / journal
... abundance of coarse sediment, with foreset bedding and crossbeddi ng. Besides coal, it includes shallow-water marine and brackish-water fossils which are indicative of a deltaic environment. The sediment was apparently transported by an ancestral Yaquina River from highland areas of older rocks east ...
... abundance of coarse sediment, with foreset bedding and crossbeddi ng. Besides coal, it includes shallow-water marine and brackish-water fossils which are indicative of a deltaic environment. The sediment was apparently transported by an ancestral Yaquina River from highland areas of older rocks east ...
end of course earth science
... copyright owner. Commonwealth of Virginia public school educators may photocopy or print any portion of these Released Tests for educational purposes without requesting permission. All others should direct their requests to the Commonwealth of Virginia Department of Education at (804) 225-2102, Divi ...
... copyright owner. Commonwealth of Virginia public school educators may photocopy or print any portion of these Released Tests for educational purposes without requesting permission. All others should direct their requests to the Commonwealth of Virginia Department of Education at (804) 225-2102, Divi ...
Geologic Time - Kean University
... time, the much longer interval that occurred before the evolution of organisms with hard skeletons suitable for preservation. The oldest known rock that was deposited in water is nearly four billion years old and is found along the west coast of Greenland. These rocks contain the key chemical elemen ...
... time, the much longer interval that occurred before the evolution of organisms with hard skeletons suitable for preservation. The oldest known rock that was deposited in water is nearly four billion years old and is found along the west coast of Greenland. These rocks contain the key chemical elemen ...
Geologic Time
... time, the much longer interval that occurred before the evolution of organisms with hard skeletons suitable for preservation. The oldest known rock that was deposited in water is nearly four billion years old and is found along the west coast of Greenland. These rocks contain the key chemical elemen ...
... time, the much longer interval that occurred before the evolution of organisms with hard skeletons suitable for preservation. The oldest known rock that was deposited in water is nearly four billion years old and is found along the west coast of Greenland. These rocks contain the key chemical elemen ...
Carter`s piece - Texas Master Naturalist
... solid layer of limestone? Remember that when this layer of strata was initially is microcrystalline deposited it was a fine calcium carbonate mud. Only after burial and lithification did it ...
... solid layer of limestone? Remember that when this layer of strata was initially is microcrystalline deposited it was a fine calcium carbonate mud. Only after burial and lithification did it ...
CHAPTER 10_Deep Time..
... Why is there a difference? ANS: The oldest rocks on Earth are about 4 billion years old. Meteorites are as ancient as 4.57 billion years old; this is likely the age of formation of the entire Solar System (including Earth) given the orbital characteristics of the planets. No Earth rocks are likely t ...
... Why is there a difference? ANS: The oldest rocks on Earth are about 4 billion years old. Meteorites are as ancient as 4.57 billion years old; this is likely the age of formation of the entire Solar System (including Earth) given the orbital characteristics of the planets. No Earth rocks are likely t ...
Moray and Caithness - Scottish Natural Heritage
... Before 29,000 years ago. There were prolonged cold glacial periods separated by shorter, warmer interludes. ...
... Before 29,000 years ago. There were prolonged cold glacial periods separated by shorter, warmer interludes. ...
The Hadean-Archaean Environment
... events have highly existed throughout geological time and with them the opportunity for evolution of more extreme thermophiles. Life cannot function at temperatures where water is solid. However, life likely arose in or around rocks rather than photosynthetically at the surface (Gaucher et al. 2010) ...
... events have highly existed throughout geological time and with them the opportunity for evolution of more extreme thermophiles. Life cannot function at temperatures where water is solid. However, life likely arose in or around rocks rather than photosynthetically at the surface (Gaucher et al. 2010) ...
PDF - Rosemont EIS
... movements throughout the Paleozoic Era are recorded hy a marine sequence whose continuity is interrupted by several disconformities. Strong vertical movementa, largely on faults, 0ccurred at intervals from the Triassic to the Early Cretaceous; two stocke were injected into the rocks of the area, at ...
... movements throughout the Paleozoic Era are recorded hy a marine sequence whose continuity is interrupted by several disconformities. Strong vertical movementa, largely on faults, 0ccurred at intervals from the Triassic to the Early Cretaceous; two stocke were injected into the rocks of the area, at ...
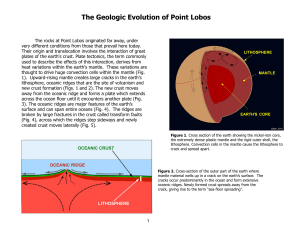
Geologic Evolution of Point Lobos
... Pacific and North American Plates, a volcano spewed lava (“basaltic andesite”) over what would become the Monterey Peninsula. Radiometric dating places the time of eruption at 27 million years ago, during the Oligocene Epoch (Fig. 18). At that time, the Eocene canyon fill and the Cretaceous granodio ...
... Pacific and North American Plates, a volcano spewed lava (“basaltic andesite”) over what would become the Monterey Peninsula. Radiometric dating places the time of eruption at 27 million years ago, during the Oligocene Epoch (Fig. 18). At that time, the Eocene canyon fill and the Cretaceous granodio ...
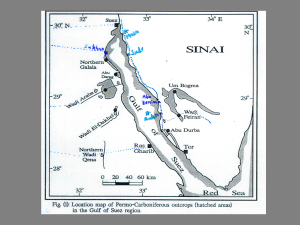
Abu Darag Formation
... about 10 kms south of Ain Sukhna. This formation could be subdivided into three members as follows (KORA & MANSOUR 1992). ...
... about 10 kms south of Ain Sukhna. This formation could be subdivided into three members as follows (KORA & MANSOUR 1992). ...
Some Geology Basics
... Sedimentary rocks make up only a small percentage of the crust, but sediments and sedimentary rocks cover most of the planet’s surfaces and sea floor. Sedimentary rocks may contain some of the igneous rock-forming minerals (especially quartz), but the process of weathering tends to break the mineral ...
... Sedimentary rocks make up only a small percentage of the crust, but sediments and sedimentary rocks cover most of the planet’s surfaces and sea floor. Sedimentary rocks may contain some of the igneous rock-forming minerals (especially quartz), but the process of weathering tends to break the mineral ...
Chapter 30. The Sediments of the Continental Margin
... steeply seaward (see Figure 7.3). The more steeply dipping strata are believed to have formed by either sea level changes, changes in sediment supply, or subsidence.7,8 The shallowest strata on seismic profiles are generally parallel with the surface of the continental shelf, slope, and rise.9 The d ...
... steeply seaward (see Figure 7.3). The more steeply dipping strata are believed to have formed by either sea level changes, changes in sediment supply, or subsidence.7,8 The shallowest strata on seismic profiles are generally parallel with the surface of the continental shelf, slope, and rise.9 The d ...
The Geology of Grahamstown: the Regional Setting
... very considerable period of time, from about 400 million years ago up until today. The rocks can be grouped into three main divisions: 1. The oldest rocks belong to the Cape Supergroup, which constitutes the major part of the Cape Fold Belt. This is a belt of deformed rocks that runs approximately w ...
... very considerable period of time, from about 400 million years ago up until today. The rocks can be grouped into three main divisions: 1. The oldest rocks belong to the Cape Supergroup, which constitutes the major part of the Cape Fold Belt. This is a belt of deformed rocks that runs approximately w ...
Geological history of Earth
The geological history of Earth follows the major events in Earth's past based on the geologic time scale, a system of chronological measurement based on the study of the planet's rock layers (stratigraphy). Earth formed about 4.54 billion years ago by accretion from the solar nebula, a disk-shaped mass of dust and gas left over from the formation of the Sun, which also created the rest of the Solar System.Earth was initially molten due to extreme volcanism and frequent collisions with other bodies. Eventually, the outer layer of the planet cooled to form a solid crust when water began accumulating in the atmosphere. The Moon formed soon afterwards, possibly as the result of a Mars-sized object with about 10% of the Earth's mass impacting the planet in a glancing blow. Some of this object's mass merged with the Earth, significantly altering its internal composition, and a portion was ejected into space. Some of the material survived to form an orbiting moon. Outgassing and volcanic activity produced the primordial atmosphere. Condensing water vapor, augmented by ice delivered from comets, produced the oceans.As the surface continually reshaped itself over hundreds of millions of years, continents formed and broke apart. They migrated across the surface, occasionally combining to form a supercontinent. Roughly 750 million years ago, the earliest-known supercontinent Rodinia, began to break apart. The continents later recombined to form Pannotia, 600 to 540 million years ago, then finally Pangaea, which broke apart 180 million years ago.The present pattern of ice ages began about 40 million years ago, then intensified at the end of the Pliocene. The polar regions have since undergone repeated cycles of glaciation and thaw, repeating every 40,000–100,000 years. The last glacial period of the current ice age ended about 10,000 years ago.