Neogene tilting of crustal panels near Wrangell, Alaska
... tilt angle is 88 or half of the required 168 Neogene tilt indicated by the paleomagnetic and structural geologic observations from the mafic dikes. Paleozoic rocks of the Alexander terrane on Prince of Wales Island have very low metamorphic grade at the northwest corner of the island. Metamorphic gr ...
... tilt angle is 88 or half of the required 168 Neogene tilt indicated by the paleomagnetic and structural geologic observations from the mafic dikes. Paleozoic rocks of the Alexander terrane on Prince of Wales Island have very low metamorphic grade at the northwest corner of the island. Metamorphic gr ...
It is my opinion that the Earth is very nob le and admirable ••• and if it
... The other solid planets and smaller worlds have much more ancient surfaces and this tells us two things that we could not learn from the Earth itself. One is that violent and gigantic impacts were common in the early days of the Solar system as the larger bodies swept up and devoured the smaller ob ...
... The other solid planets and smaller worlds have much more ancient surfaces and this tells us two things that we could not learn from the Earth itself. One is that violent and gigantic impacts were common in the early days of the Solar system as the larger bodies swept up and devoured the smaller ob ...
Document
... and different kinds of rocks record different kinds of history. Metamorphic rocks, which have been subjected to high temperatures and high pressures, carry a record of events deep in the Earth's crust, and thus they are critical for understanding the origins of deformed mountain belts like the Alps, ...
... and different kinds of rocks record different kinds of history. Metamorphic rocks, which have been subjected to high temperatures and high pressures, carry a record of events deep in the Earth's crust, and thus they are critical for understanding the origins of deformed mountain belts like the Alps, ...
Chapter 6 - Sedimentary Rock
... but it must be used with caution because the same geometry may be found in more than one environment can be modified by sediment compaction during lithification and by erosion and deformation ...
... but it must be used with caution because the same geometry may be found in more than one environment can be modified by sediment compaction during lithification and by erosion and deformation ...
Offshore Somalia: crustal structure and implications
... central attenuated crust. However, break-up of Somalia and the Madagascar-Seychelles-India (MSI) block occurred in the Early Jurassic (Bossellini, 1992), as the separation axis was E-W, such that the MSI Block drifted due-south. The western margin of this transform movement was controlled by the N-S ...
... central attenuated crust. However, break-up of Somalia and the Madagascar-Seychelles-India (MSI) block occurred in the Early Jurassic (Bossellini, 1992), as the separation axis was E-W, such that the MSI Block drifted due-south. The western margin of this transform movement was controlled by the N-S ...
Focus on Learning - earthjay science
... work for a very long time. Thus, to understand ancient rocks, we must first understand present-day processes and their results. This idea is commonly stated as the present is the key to the past. Prior to Hutton’s Theory of the Earth, no one had effectively demonstrated that geological processes can ...
... work for a very long time. Thus, to understand ancient rocks, we must first understand present-day processes and their results. This idea is commonly stated as the present is the key to the past. Prior to Hutton’s Theory of the Earth, no one had effectively demonstrated that geological processes can ...
The Geologic Enigma of the Red Sea Rift
... (1985) state that a model where the oceanic-continental boundary might be 35 km inland from the coast and 8 km from the Precambrian shield satisfies all the geological and geophysical measurements. The implication from their model is that little continental crustal extension took place and the decou ...
... (1985) state that a model where the oceanic-continental boundary might be 35 km inland from the coast and 8 km from the Precambrian shield satisfies all the geological and geophysical measurements. The implication from their model is that little continental crustal extension took place and the decou ...
Non-ideal Subduction
... Late Devonian / Early Mississippian Antler Orogeny. Above: the sheared and folded deep water sediments of the distal (far west, deep sea) Antler marine basin thrust over and placed on top of the shallow water deposits of the con&nental margin. It is uncertain what process caused these deep wate ...
... Late Devonian / Early Mississippian Antler Orogeny. Above: the sheared and folded deep water sediments of the distal (far west, deep sea) Antler marine basin thrust over and placed on top of the shallow water deposits of the con&nental margin. It is uncertain what process caused these deep wate ...
Dunbar Geology Walk - Edinburgh Geological Society
... The path continues to Belhaven Point, where you can see another small outcrop of volcanic rock. The Point marks a major transition on the coast, going west from here there is no more volcanic rock until you reach St Baldred’s Cradle on the other side of the Tyne Estuary. Instead, this area is domina ...
... The path continues to Belhaven Point, where you can see another small outcrop of volcanic rock. The Point marks a major transition on the coast, going west from here there is no more volcanic rock until you reach St Baldred’s Cradle on the other side of the Tyne Estuary. Instead, this area is domina ...
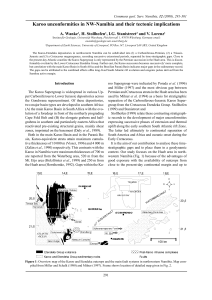
Wanke et al_Karoo unconformities
... al., 1999). In these areas, however, both the Carboniferous-Permian and the Cretaceous sequences are either entirely missing or only thinly developed. Karoo stratigraphy and depositional environments of the Huab area The lowermost stratigraphic unit of the Karoo Supergroup in the Huab outcrop area i ...
... al., 1999). In these areas, however, both the Carboniferous-Permian and the Cretaceous sequences are either entirely missing or only thinly developed. Karoo stratigraphy and depositional environments of the Huab area The lowermost stratigraphic unit of the Karoo Supergroup in the Huab outcrop area i ...
Geologic Time - Tulane University
... that fossils that were contained in the rock could also be used to determine relative age. It was soon recognized that some fossils of once living organisms only occurred in very old rocks and others only occurred in younger rocks. Furthermore, some fossils were only found within a limited range of ...
... that fossils that were contained in the rock could also be used to determine relative age. It was soon recognized that some fossils of once living organisms only occurred in very old rocks and others only occurred in younger rocks. Furthermore, some fossils were only found within a limited range of ...
SGES 1302 Lecture16
... Wheathering, which is a set of physical, chemical and biological processes that breaks rock into smaller particles while some dissolved into solution. Gravity and erosion agents remove the products of weathering and carry them into a new location where they are deposited. These small pieces of rock ...
... Wheathering, which is a set of physical, chemical and biological processes that breaks rock into smaller particles while some dissolved into solution. Gravity and erosion agents remove the products of weathering and carry them into a new location where they are deposited. These small pieces of rock ...
Chapter 9 - Ocean Circulation
... • Geologic data shows that sea level has risen and fallen many times, sometimes 100s meters. • Some are associated with mass extinctions. • Sea levels are currently rising, and have been since the end of the last ice age Ice Ages of the Pleistocene Epoch • The peak of the last glaciation stage (call ...
... • Geologic data shows that sea level has risen and fallen many times, sometimes 100s meters. • Some are associated with mass extinctions. • Sea levels are currently rising, and have been since the end of the last ice age Ice Ages of the Pleistocene Epoch • The peak of the last glaciation stage (call ...
THE ORIGIN AND GROWTH OF CONTINENTS 1 Geophysical
... is sedimentary. Ewing and Nafe (1963) conclude from the observed hickening near volcanic islands that it is in part volcanic. The question is of interest for the age of the ocean basins, total amount of sedimentation; rates of erosion and geochemical belance calculations generally. However, the atte ...
... is sedimentary. Ewing and Nafe (1963) conclude from the observed hickening near volcanic islands that it is in part volcanic. The question is of interest for the age of the ocean basins, total amount of sedimentation; rates of erosion and geochemical belance calculations generally. However, the atte ...
Fethard
... This is a mostly undulating land surface. There are higher elevations along the northern boundary at the contact with the Duncannon Group but even these are not very significant. Elevations are mostly below 100m OD. The highest elevation is in the east of the body at Forth Mountain, which is at 237m ...
... This is a mostly undulating land surface. There are higher elevations along the northern boundary at the contact with the Duncannon Group but even these are not very significant. Elevations are mostly below 100m OD. The highest elevation is in the east of the body at Forth Mountain, which is at 237m ...
Episodic nature of continental arc activity since 750 Ma - Cin
... oceanic plate subducts beneath another oceanic plate. Continental arcs, such as the present-day Andes or Cretaceous North American Cordilleran arcs, form when oceanic plates subduct beneath continental plates (Fig. 1a). Because of greater crustal thickness at continental arcs, magmatic differentiati ...
... oceanic plate subducts beneath another oceanic plate. Continental arcs, such as the present-day Andes or Cretaceous North American Cordilleran arcs, form when oceanic plates subduct beneath continental plates (Fig. 1a). Because of greater crustal thickness at continental arcs, magmatic differentiati ...
Outline 4: Sedimentary Rocks
... Time Units • Time can be separated into “pure” time and “rock” time. Rock time is divided into time stratigraphic units. • Time stratigraphic units sometimes parallel formation boundaries, but often they cross formation boundaries. ...
... Time Units • Time can be separated into “pure” time and “rock” time. Rock time is divided into time stratigraphic units. • Time stratigraphic units sometimes parallel formation boundaries, but often they cross formation boundaries. ...
Sedimentary Rocks
... Time Units • Time can be separated into “pure” time and “rock” time. Rock time is divided into time stratigraphic units. • Time stratigraphic units sometimes parallel formation boundaries, but often they cross formation boundaries. ...
... Time Units • Time can be separated into “pure” time and “rock” time. Rock time is divided into time stratigraphic units. • Time stratigraphic units sometimes parallel formation boundaries, but often they cross formation boundaries. ...
Contents - King Island Natural Resource Management Group
... deposited by a series of pulses of suspended sediment known as turbidity currents. Such beds are sometimes referred to as turbidites. Mapping out the whole formation at Surprise Bay shows it to be at least 4 kilometres thick: it was evidently deposited in a deep, continually and slowly subsiding, ma ...
... deposited by a series of pulses of suspended sediment known as turbidity currents. Such beds are sometimes referred to as turbidites. Mapping out the whole formation at Surprise Bay shows it to be at least 4 kilometres thick: it was evidently deposited in a deep, continually and slowly subsiding, ma ...
What is the meaning of ophiolites? - Creation Ministries International
... mantle] onto continents remains one of the great mysteries of plate tectonics—how does ophiolitic material with a density of 3.0–3.3 g/cm3 rise from its natural depths of ≥2.5 km beneath the ocean surface to elevations more than 1 km above sea level on continents with densities of 2.7–2.8 g/cm3?’10 ...
... mantle] onto continents remains one of the great mysteries of plate tectonics—how does ophiolitic material with a density of 3.0–3.3 g/cm3 rise from its natural depths of ≥2.5 km beneath the ocean surface to elevations more than 1 km above sea level on continents with densities of 2.7–2.8 g/cm3?’10 ...
f.y.b.a geography
... Geography is one of the important subjects of understanding the spatial science of the earth in relation with the components of physical and human aspects. Physical Geography as a science studies the earth’s surface and its characteristics representing spatial relationships and varying regional patt ...
... Geography is one of the important subjects of understanding the spatial science of the earth in relation with the components of physical and human aspects. Physical Geography as a science studies the earth’s surface and its characteristics representing spatial relationships and varying regional patt ...
Chapter 3 Palaeozoic Sedimentary Rocks
... The Lok Ma Chau Formation comprises two members; the older Mai Po Member consisting of metamorphosed siltstone, fine-grained sandstone and carbonaceous siltstone, and the younger Tai Shek Mo Member consisting of metamorphosed sandstone and conglomerate. The rocks exposed at Tsz Kan Chau have been as ...
... The Lok Ma Chau Formation comprises two members; the older Mai Po Member consisting of metamorphosed siltstone, fine-grained sandstone and carbonaceous siltstone, and the younger Tai Shek Mo Member consisting of metamorphosed sandstone and conglomerate. The rocks exposed at Tsz Kan Chau have been as ...
Seafloor Spreading notes guide 2015
... (rocks /magma?) seeps up to the crust where it cools, solidifies, and forms new (seafloor/ mountain ranges?). Underwater volcanoes are found here. 7. This colder and denser seafloor (rises/ sinks?) and continues to form ridges. 8. There are two things that provide evidence/proof of seafloor spreadin ...
... (rocks /magma?) seeps up to the crust where it cools, solidifies, and forms new (seafloor/ mountain ranges?). Underwater volcanoes are found here. 7. This colder and denser seafloor (rises/ sinks?) and continues to form ridges. 8. There are two things that provide evidence/proof of seafloor spreadin ...
BCS311 Module 3
... landscape in Figure 3.2b. that follows. Glacial till is virtually absent although boulders carried by glaciers have been deposited on the rock surface. Mountain ranges are located along the uplifted eastern margin of the Canadian Shield: the Torngat Mountains in Labrador and the Davis Highlands of B ...
... landscape in Figure 3.2b. that follows. Glacial till is virtually absent although boulders carried by glaciers have been deposited on the rock surface. Mountain ranges are located along the uplifted eastern margin of the Canadian Shield: the Torngat Mountains in Labrador and the Davis Highlands of B ...
Geological history of Earth
The geological history of Earth follows the major events in Earth's past based on the geologic time scale, a system of chronological measurement based on the study of the planet's rock layers (stratigraphy). Earth formed about 4.54 billion years ago by accretion from the solar nebula, a disk-shaped mass of dust and gas left over from the formation of the Sun, which also created the rest of the Solar System.Earth was initially molten due to extreme volcanism and frequent collisions with other bodies. Eventually, the outer layer of the planet cooled to form a solid crust when water began accumulating in the atmosphere. The Moon formed soon afterwards, possibly as the result of a Mars-sized object with about 10% of the Earth's mass impacting the planet in a glancing blow. Some of this object's mass merged with the Earth, significantly altering its internal composition, and a portion was ejected into space. Some of the material survived to form an orbiting moon. Outgassing and volcanic activity produced the primordial atmosphere. Condensing water vapor, augmented by ice delivered from comets, produced the oceans.As the surface continually reshaped itself over hundreds of millions of years, continents formed and broke apart. They migrated across the surface, occasionally combining to form a supercontinent. Roughly 750 million years ago, the earliest-known supercontinent Rodinia, began to break apart. The continents later recombined to form Pannotia, 600 to 540 million years ago, then finally Pangaea, which broke apart 180 million years ago.The present pattern of ice ages began about 40 million years ago, then intensified at the end of the Pliocene. The polar regions have since undergone repeated cycles of glaciation and thaw, repeating every 40,000–100,000 years. The last glacial period of the current ice age ended about 10,000 years ago.