ch 15 - Quia
... Marshall Nirenberg identified the codons that specify each amino acid. RNA molecules of only 1 nucleotide and of specific 3-base sequences were used to determine the amino acid encoded by each codon. The amino acids encoded by all 64 possible codons were determined. ...
... Marshall Nirenberg identified the codons that specify each amino acid. RNA molecules of only 1 nucleotide and of specific 3-base sequences were used to determine the amino acid encoded by each codon. The amino acids encoded by all 64 possible codons were determined. ...
The Nature of Genes The Nature of Genes The Nature of Genes The
... Gene expression requires the participation of multiple types of RNA: messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the information from DNA that encodes proteins ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is a structural component of the ribosome transfer RNA (tRNA) carries amino acids to the ribosome for translation ...
... Gene expression requires the participation of multiple types of RNA: messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the information from DNA that encodes proteins ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is a structural component of the ribosome transfer RNA (tRNA) carries amino acids to the ribosome for translation ...
SBI4U Translation
... • The anticodons of some tRNAs recognize more than one codon • This is possible because the rules for base pairing between the third base of the codon and anticodon are relaxed (called the wobble hypothesis) – At the wobble position, U on the anticodon can bind with A or G in the third position of a ...
... • The anticodons of some tRNAs recognize more than one codon • This is possible because the rules for base pairing between the third base of the codon and anticodon are relaxed (called the wobble hypothesis) – At the wobble position, U on the anticodon can bind with A or G in the third position of a ...
lecture 5
... - The process of decoding the information content of an mRNA into a linear sequence of linked amino acids is called translation. Translation requires the interaction of mRNA, charged tRNAs, ribosomes, and a large number of proteins (factors) that facilitate the initiation, elongation, and terminatio ...
... - The process of decoding the information content of an mRNA into a linear sequence of linked amino acids is called translation. Translation requires the interaction of mRNA, charged tRNAs, ribosomes, and a large number of proteins (factors) that facilitate the initiation, elongation, and terminatio ...
From Gene to Protein
... The central dogma of molecular biology information flows in one direction when genes are expressed ...
... The central dogma of molecular biology information flows in one direction when genes are expressed ...
Genes chapt15
... • Elongation of translation involves the addition of amino acids: – a charged tRNA binds to the A site if its anticodon is complementary to the codon at the A site – peptidyl transferase forms a peptide ...
... • Elongation of translation involves the addition of amino acids: – a charged tRNA binds to the A site if its anticodon is complementary to the codon at the A site – peptidyl transferase forms a peptide ...
Translation
... 6. once enough of the message has been read, another ribosome can attach through the initiation process and start translating the same message 7. A total of 4 high energy phosphates are used for each amino acid added to the chain ...
... 6. once enough of the message has been read, another ribosome can attach through the initiation process and start translating the same message 7. A total of 4 high energy phosphates are used for each amino acid added to the chain ...
chapter 18 - rci.rutgers.edu
... the stomach, and then by trypsin, chymotrypsin, and other proteases in the small intestine. Essentially all protein consumed orally is broken down to amino acids, which is why money spent on most "enzyme pills" (like Superoxide Dismutase) is wasted. ...
... the stomach, and then by trypsin, chymotrypsin, and other proteases in the small intestine. Essentially all protein consumed orally is broken down to amino acids, which is why money spent on most "enzyme pills" (like Superoxide Dismutase) is wasted. ...
Application Sheet: DNA - NETZSCH Thermal Analysis
... of molecules called bases and it is the sequence of these ...
... of molecules called bases and it is the sequence of these ...
Biology 102 Lecture 12: From DNA to Proteins
... Some genes can be spliced together in multiple ways ...
... Some genes can be spliced together in multiple ways ...
Pipe Cleaner Protein
... 1. Create a DNA strand with 42 nucleotide bases ◦ Must start with the DNA - TAC ...
... 1. Create a DNA strand with 42 nucleotide bases ◦ Must start with the DNA - TAC ...
Chapter 17 Molecular Genetics
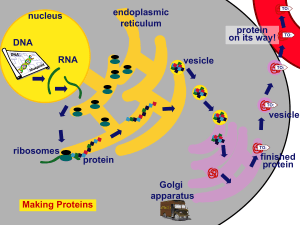
... Protein is synthesized on a mRNA template. – This process is called translation. – The genetic information contained in the DNA molecule is transferred to messenger RNA. – Messenger RNA molecules carry this information to the cytoplasm, where proteins are synthesized. – Messenger RNA serves as a tem ...
... Protein is synthesized on a mRNA template. – This process is called translation. – The genetic information contained in the DNA molecule is transferred to messenger RNA. – Messenger RNA molecules carry this information to the cytoplasm, where proteins are synthesized. – Messenger RNA serves as a tem ...
Coding for Amino Acids and Proteins
... 5. Have each group figure out their base sequence by simply matching, in order, their candy bar’s simple ingredients. 6. Use the base sequence to determine the amino acid sequence, such as CAA codes for glutamine (peanuts). 7. Lead the students to understand this is how each cell’s ribosome uses the ...
... 5. Have each group figure out their base sequence by simply matching, in order, their candy bar’s simple ingredients. 6. Use the base sequence to determine the amino acid sequence, such as CAA codes for glutamine (peanuts). 7. Lead the students to understand this is how each cell’s ribosome uses the ...
DNA Code problerm
... C. The entire molecule has encoded information for protein synthesis. D. In the condensed form, it is transcriptionally inactive. E. It must be unpackaged before it can be transcribed into RNA. ...
... C. The entire molecule has encoded information for protein synthesis. D. In the condensed form, it is transcriptionally inactive. E. It must be unpackaged before it can be transcribed into RNA. ...
D5 Phylogeny and systematics – summary of mark
... phylogeny / evolutionary history of a species / relationship between species can be determined; proteins analysed for amino acid sequences; more similar the amino acid sequence, the more closely related the species are; eg cytochrome C / hemoglobin / chlorophyll / other valid example; DNA / mitochon ...
... phylogeny / evolutionary history of a species / relationship between species can be determined; proteins analysed for amino acid sequences; more similar the amino acid sequence, the more closely related the species are; eg cytochrome C / hemoglobin / chlorophyll / other valid example; DNA / mitochon ...
Slide 1
... where the protein will get made • tRNA(transfer RNA) will bring specific amino acids to the mRNA and those a.a. will join together to make a specific protein that was coded for by the order of the ATGC’s in the original DNA strand. ...
... where the protein will get made • tRNA(transfer RNA) will bring specific amino acids to the mRNA and those a.a. will join together to make a specific protein that was coded for by the order of the ATGC’s in the original DNA strand. ...
Pre-post test questions
... You would need to translate the sequence into amino acids and then align the two sequences to see which amino acids had changed. Translation would start at the start codon (ATG). This question addresses bioinformatics and translation and the difficult concept of where translation starts. 15. Indivi ...
... You would need to translate the sequence into amino acids and then align the two sequences to see which amino acids had changed. Translation would start at the start codon (ATG). This question addresses bioinformatics and translation and the difficult concept of where translation starts. 15. Indivi ...
Biology Genetics Unit: Online Activities 1.) Go to the link: http://learn
... A.) Click the “Next” button on the bottom right hand side of the white box. B.) How does the cell know to make a certain protein? ___________________________________________________________________________ C.) How is the gene, as part of the DNA, able to be read? ____________________________________ ...
... A.) Click the “Next” button on the bottom right hand side of the white box. B.) How does the cell know to make a certain protein? ___________________________________________________________________________ C.) How is the gene, as part of the DNA, able to be read? ____________________________________ ...
SI Worksheet 11
... 7. A sequence of pictures of polypeptides synthesis shows a ribosome holding two transfer RNAs. One tRNA has a polypeptide chain attached to it, the other tRNA has a single amino acid attaches to it. What does the next picture show? a. the polypeptide chain moves over and bonds to the single amino a ...
... 7. A sequence of pictures of polypeptides synthesis shows a ribosome holding two transfer RNAs. One tRNA has a polypeptide chain attached to it, the other tRNA has a single amino acid attaches to it. What does the next picture show? a. the polypeptide chain moves over and bonds to the single amino a ...
Evidences of Evolution
... • an organism’s evolutionary past • a common ancestor with species that have similar structures that are still functioning ...
... • an organism’s evolutionary past • a common ancestor with species that have similar structures that are still functioning ...
Lecture notes 1 - University of Washington
... covalently attached to a sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) but without the phosphate group. A nucleotide consists of a nitrogenous base, a sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) and one to three phosphate groups. nucleoside = sugar + base. nucleotide = sugar + base + phosphate. 2.1.4. Amino acids 2.1.5. Peptide ...
... covalently attached to a sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) but without the phosphate group. A nucleotide consists of a nitrogenous base, a sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) and one to three phosphate groups. nucleoside = sugar + base. nucleotide = sugar + base + phosphate. 2.1.4. Amino acids 2.1.5. Peptide ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.