Notes - people.vcu.edu
... The frameshift experiment gave the overall nature of the code but did nothing to tell us which specific triplet codons coded for which specific amino acids. Indeed, Crick despaired of cracking the code, knowing of no way to proceed. Ironically, the same year the frameshift experiment was completed, ...
... The frameshift experiment gave the overall nature of the code but did nothing to tell us which specific triplet codons coded for which specific amino acids. Indeed, Crick despaired of cracking the code, knowing of no way to proceed. Ironically, the same year the frameshift experiment was completed, ...
Text S13.
... Due to the substantial per-codon variability of ribosomal densities, we pooled different codons together to estimate the effect size of each factor concerned. These analyses were first conducted within each gene to avoid estimating translation initiation rates. The median or mean value among all gen ...
... Due to the substantial per-codon variability of ribosomal densities, we pooled different codons together to estimate the effect size of each factor concerned. These analyses were first conducted within each gene to avoid estimating translation initiation rates. The median or mean value among all gen ...
Protein Synthesis - BLI-Research-SynBio-2016-session-2
... MAJOR PLAYERS IN TRANSCRIPTION RNA polymerase- complex of enzymes with 2 functions: • Unwind DNA sequence • Produce primary transcript by stringing together the chain of RNA nucleotides ...
... MAJOR PLAYERS IN TRANSCRIPTION RNA polymerase- complex of enzymes with 2 functions: • Unwind DNA sequence • Produce primary transcript by stringing together the chain of RNA nucleotides ...
Study and engineering of gene function: mutagenesis
... • New amino acid = new functional group • Alter or enhance protein function (rational design) • Chemically modify protein following synthesis (chemical derivitization) – Probe protein structure, function – Modify protein in vivo, add labels and monitor protein localization, movement, dynamics in liv ...
... • New amino acid = new functional group • Alter or enhance protein function (rational design) • Chemically modify protein following synthesis (chemical derivitization) – Probe protein structure, function – Modify protein in vivo, add labels and monitor protein localization, movement, dynamics in liv ...
Genetic Code Activity
... using tRNAs to translate genetic information in mRNA. BI5. a. Students know the general structures and functions of DNA, RNA, and protein. Objectives: SWBAT… Understand the general pathway by which ribosomes make proteins. Resources: http://www.johnkyrk.com/DNAtranslation.html http://www-cla ...
... using tRNAs to translate genetic information in mRNA. BI5. a. Students know the general structures and functions of DNA, RNA, and protein. Objectives: SWBAT… Understand the general pathway by which ribosomes make proteins. Resources: http://www.johnkyrk.com/DNAtranslation.html http://www-cla ...
DNA Deoxyribonucleic Acid
... language: DNA and RNA are written in the language of nucleotides ...
... language: DNA and RNA are written in the language of nucleotides ...
Protein Synthesis: Transcription and Translation
... 2. mRNA made from DNA. 3. mRNA leaves nucleus and enters ribosome. 4. tRNA reads mRNA from “start” to “stop” 5. As tRNA reads mRNA, it brings the correct amino acids. DNA makes mRNA (complement) mRNA matches up with tRNA (complement) tRNA brings amino acid Chains of amino acids can make prot ...
... 2. mRNA made from DNA. 3. mRNA leaves nucleus and enters ribosome. 4. tRNA reads mRNA from “start” to “stop” 5. As tRNA reads mRNA, it brings the correct amino acids. DNA makes mRNA (complement) mRNA matches up with tRNA (complement) tRNA brings amino acid Chains of amino acids can make prot ...
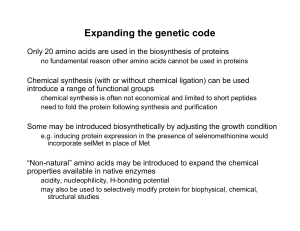
Non-natural amino acid
... – there is a certain amount of promiscuity – differentiating similar amino acids is chemically difficult—e.g. Val and Ile differ by a single ...
... – there is a certain amount of promiscuity – differentiating similar amino acids is chemically difficult—e.g. Val and Ile differ by a single ...
BHS 150.1 – Biochemistry II Date: 2/8/2013, 2sndhalf Notetaker: Kim
... 12. Ascorbate in the aqueous is needed by the cornea for which two of the following functions: antioxidant properties collagen synthesis 13. A missense mutation occurs when the: amino acid sequence changes 14. During fasting, what are some possible sources of carbons for gluconeogenesis: amino acids ...
... 12. Ascorbate in the aqueous is needed by the cornea for which two of the following functions: antioxidant properties collagen synthesis 13. A missense mutation occurs when the: amino acid sequence changes 14. During fasting, what are some possible sources of carbons for gluconeogenesis: amino acids ...
Basic Bioinformatics Laboratory
... acid sequence of each organism (in a one letter code – for interpretation of the code go to http://wwwchem.csustan.edu/chem4400/code.htm 5. Choose one of the comparisons (with at least five organisms) and using the human as a base, count the number of amino acid differences for the other organisms. ...
... acid sequence of each organism (in a one letter code – for interpretation of the code go to http://wwwchem.csustan.edu/chem4400/code.htm 5. Choose one of the comparisons (with at least five organisms) and using the human as a base, count the number of amino acid differences for the other organisms. ...
Basics of Molecular Biology
... other proteins and with DNA molecules. The inference of protein structure is closely related to the inference of protein ...
... other proteins and with DNA molecules. The inference of protein structure is closely related to the inference of protein ...
How DNA Controls the Workings of the Cell
... diabetes has a defective DNA sequence that codes for the making of the insulin protein. Suppose a person has a mutation in their DNA and the first triplet for the insulin gene reads T A T but the normal gene reads T A G. a. What amino acid does the mutant DNA and the normal DNA code for and will the ...
... diabetes has a defective DNA sequence that codes for the making of the insulin protein. Suppose a person has a mutation in their DNA and the first triplet for the insulin gene reads T A T but the normal gene reads T A G. a. What amino acid does the mutant DNA and the normal DNA code for and will the ...
Document
... 13. Several forms of RNA or ______________________ help change DNA code into proteins. 14. Because it is so similar to ______________________, RNA can serve as a temporary copy of a DNA sequence. 15. The “factory” that assembles proteins is known as a(n) ______________________. 16. A mirror-like cop ...
... 13. Several forms of RNA or ______________________ help change DNA code into proteins. 14. Because it is so similar to ______________________, RNA can serve as a temporary copy of a DNA sequence. 15. The “factory” that assembles proteins is known as a(n) ______________________. 16. A mirror-like cop ...
DIR RD 4C-2
... Name ______________________________ Class___________________Date__________________ ...
... Name ______________________________ Class___________________Date__________________ ...
Chapter 3 LEAP Biology practice Test
... What is “R”? A chemical group that determines prop of each of the 20 amino acids used to make proteins What is a peptide bond? Bond created when Amino Acid monomers are linked together in a dehydration reaction, Joining Carboxyl group of one Amino Acid to the Amino group of the next amino acid What ...
... What is “R”? A chemical group that determines prop of each of the 20 amino acids used to make proteins What is a peptide bond? Bond created when Amino Acid monomers are linked together in a dehydration reaction, Joining Carboxyl group of one Amino Acid to the Amino group of the next amino acid What ...
mRNA - Decatur ISD
... Carries amino acids to ribosome Contains an “anticodon” of nitrogen bases Anticodons use complementary bond with codons Less tRNA’s than codons, so one tRNA may bind with more than one codon. • Supports the degenerate code • “Wobble” hypothesis: anticodon with U in third position can bind to A or G ...
... Carries amino acids to ribosome Contains an “anticodon” of nitrogen bases Anticodons use complementary bond with codons Less tRNA’s than codons, so one tRNA may bind with more than one codon. • Supports the degenerate code • “Wobble” hypothesis: anticodon with U in third position can bind to A or G ...
The chemical basis of heredity Nucleic acid
... molecules that consist of pentose and one of Nitrogen base called (nucleoside) and the sugar linked with nitrogen base by the (Glycosidic) bond .the nucleoside will be linkage with the phosphate group by the phosphate bond in order to consist ...
... molecules that consist of pentose and one of Nitrogen base called (nucleoside) and the sugar linked with nitrogen base by the (Glycosidic) bond .the nucleoside will be linkage with the phosphate group by the phosphate bond in order to consist ...
The control of complexity in the human genome
... sequence of DNA that codes for a protein contiguous stretch of DNA, contains many genes double helix of base pairs A, C, T, G A – T, G - C ribosomal, messenger, transfer (U for T) discovered structure DNA discovered transforming principle of DNA blender experiment sequence of amino acids, selected b ...
... sequence of DNA that codes for a protein contiguous stretch of DNA, contains many genes double helix of base pairs A, C, T, G A – T, G - C ribosomal, messenger, transfer (U for T) discovered structure DNA discovered transforming principle of DNA blender experiment sequence of amino acids, selected b ...
Introduction to 9th Grade Biology
... Steroid ring structure • The common structural feature of steroids is that their molecules contain the following ring skeleton. ...
... Steroid ring structure • The common structural feature of steroids is that their molecules contain the following ring skeleton. ...
The Molecules of Life
... Primary is based on the sequence of amino acids in the chain Secondary is based on H-bonding between amino acids in the chain Tertiary is based on other interactions (hydrophobic and hydrophilic interactions, covalent, and non-covalent bonds) Quaternary is based on the various interactions between t ...
... Primary is based on the sequence of amino acids in the chain Secondary is based on H-bonding between amino acids in the chain Tertiary is based on other interactions (hydrophobic and hydrophilic interactions, covalent, and non-covalent bonds) Quaternary is based on the various interactions between t ...
Kids Building Bricks - Johnston County Schools
... • There is a total of 20 amino acids, but there are only 4 nitrogen bases… • So, how many bases must be grouped together for at least 20 possible combinations? –1 base = 41 = 4 –2 bases = 42 = 16 –3 bases = 43 = 64 ...
... • There is a total of 20 amino acids, but there are only 4 nitrogen bases… • So, how many bases must be grouped together for at least 20 possible combinations? –1 base = 41 = 4 –2 bases = 42 = 16 –3 bases = 43 = 64 ...
WLHS / AP Bio / Monson
... 1) Explain (or use a sketch/diagram) how Hershey & Chase used radioactively labeled viruses to show that DNA, not protein, is the genetic material. 2) Briefly explain the function of each protein / enzyme listed below: A) Helicase B) Single stranded binding proteins C) Topoisomerase (see text p. 314 ...
... 1) Explain (or use a sketch/diagram) how Hershey & Chase used radioactively labeled viruses to show that DNA, not protein, is the genetic material. 2) Briefly explain the function of each protein / enzyme listed below: A) Helicase B) Single stranded binding proteins C) Topoisomerase (see text p. 314 ...
3.1 Review PBS
... What is a mutation? How does a change in the DNA code affect the shape of a protein? • A mutation is change in one base (point mutation) or bases (frameshift mutation due to addition or deletion of base) of DNA. • This can change the codon, which then can change the amino acid(s). • If an amino aci ...
... What is a mutation? How does a change in the DNA code affect the shape of a protein? • A mutation is change in one base (point mutation) or bases (frameshift mutation due to addition or deletion of base) of DNA. • This can change the codon, which then can change the amino acid(s). • If an amino aci ...
Table 1 The Essential Amino Acids and Their Plant Sources
... converting one type of amino X X acid into another. There are 9 Tryptophan X Methionine amino acids that we cannot X synthesize, and they are called essential amino acids because it is essential that we have these in our diet. Animal sources of protein such as meat, milk, or eggs contain all the ess ...
... converting one type of amino X X acid into another. There are 9 Tryptophan X Methionine amino acids that we cannot X synthesize, and they are called essential amino acids because it is essential that we have these in our diet. Animal sources of protein such as meat, milk, or eggs contain all the ess ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.