What are mutations and how do they affect the production
... Aim 25: What are mutations and how do they affect the production of proteins? What is a Mutation? ...
... Aim 25: What are mutations and how do they affect the production of proteins? What is a Mutation? ...
Lecture#20
... p.2 of handout 3b Class I and Class II RS Three proteins, p38, p43,p18 co-purify with a multi-RS complex in eukaryotic systems. Those that co-purify are indicated by bold lines in the figure. Amino acids can be modified after they are attached to a tRNA, these are also indicated in the figure: one o ...
... p.2 of handout 3b Class I and Class II RS Three proteins, p38, p43,p18 co-purify with a multi-RS complex in eukaryotic systems. Those that co-purify are indicated by bold lines in the figure. Amino acids can be modified after they are attached to a tRNA, these are also indicated in the figure: one o ...
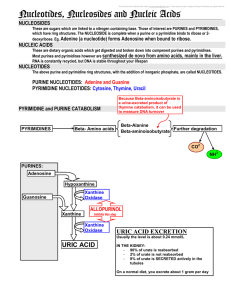
3 Nucleosides nucleotides and nucleic acids
... Extremely long nucleotide chains containing - ADENINE - GUANINE - THYMINE - CYTOSINE The double helix is held together by hudrogen bonds between the bases : - ADENINE BONDS TO THYMINE - GUANINE BONDS TO CYTOSINE A diploid human cell contains 46 chromosomes. Useful factoid to know. - EXONS are portio ...
... Extremely long nucleotide chains containing - ADENINE - GUANINE - THYMINE - CYTOSINE The double helix is held together by hudrogen bonds between the bases : - ADENINE BONDS TO THYMINE - GUANINE BONDS TO CYTOSINE A diploid human cell contains 46 chromosomes. Useful factoid to know. - EXONS are portio ...
Protein Folding and The Impact of Mutations
... When amino acids are assembled in a line to make a protein, they do not stay in an even, straight line. This is similar to a line at lunch sometimes… A couple might move closer to each other without leaving the line Two friends fighting might move away from each other That one kid who really lik ...
... When amino acids are assembled in a line to make a protein, they do not stay in an even, straight line. This is similar to a line at lunch sometimes… A couple might move closer to each other without leaving the line Two friends fighting might move away from each other That one kid who really lik ...
Cracking the Genetic Code
... ribosome, a peptide bond forms between the amino acids, beginning protein synthesis. The nascent protein chain is elongated by the subsequent binding of additional tRNAs and formation of a peptide bond between the incoming amino acid and the end of the growing chain. Although this general process wa ...
... ribosome, a peptide bond forms between the amino acids, beginning protein synthesis. The nascent protein chain is elongated by the subsequent binding of additional tRNAs and formation of a peptide bond between the incoming amino acid and the end of the growing chain. Although this general process wa ...
DNA Discovery, Structure, Replication, Transcription, Translation
... 31. What is labeled at J? 32. What is labeled at K? 33. What is labeled at L? 34. Explain what happens in translation. Include the role of mRNA, the ribosome, tRNA, amino acids, the start codon, mRNA codons, tRNA anti-codons ...
... 31. What is labeled at J? 32. What is labeled at K? 33. What is labeled at L? 34. Explain what happens in translation. Include the role of mRNA, the ribosome, tRNA, amino acids, the start codon, mRNA codons, tRNA anti-codons ...
File
... 9. Which organelle is responsible for producing lipids? 10. Which organelle breaks down long fatty acids? What is this process called? ...
... 9. Which organelle is responsible for producing lipids? 10. Which organelle breaks down long fatty acids? What is this process called? ...
Biological Macromolecules
... Primary structure is the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide (Usually read N-C) Secondary structures are localized folds or helices that form within a region of a polypeptide Tertiary structures are larger folding events that are stabilized by interactions between R groups Quaternary structure ...
... Primary structure is the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide (Usually read N-C) Secondary structures are localized folds or helices that form within a region of a polypeptide Tertiary structures are larger folding events that are stabilized by interactions between R groups Quaternary structure ...
Physical Properties of Amino Acids and Prediction of Secondary
... window centered at the position i whose accessibility state Si is calculated. The coefficients αj, βjk, and γjk are determined by minimizing the deviations of calculated accessibility states from actual ones for a training set. • Rj is an array of 19 zeros and a one representing the particular type ...
... window centered at the position i whose accessibility state Si is calculated. The coefficients αj, βjk, and γjk are determined by minimizing the deviations of calculated accessibility states from actual ones for a training set. • Rj is an array of 19 zeros and a one representing the particular type ...
The Molecules of Life Biochem! - Belle Vernon Area School District
... R group (thus the amino acids) are classified according to several criteria (two very important) Polar or nonpolar nature of the side chain Presence of an acidic or basic group in the side chain ...
... R group (thus the amino acids) are classified according to several criteria (two very important) Polar or nonpolar nature of the side chain Presence of an acidic or basic group in the side chain ...
Introduction to molecular biology
... Coding From DNA to protein is done by codons. There are three possibilities (starts with the first, the second or the third nucleotide in the sequence). We can use one strand (forward) or the other (reverse strand). Each of these six possbilities are called a reading frame. Only one of them is valid ...
... Coding From DNA to protein is done by codons. There are three possibilities (starts with the first, the second or the third nucleotide in the sequence). We can use one strand (forward) or the other (reverse strand). Each of these six possbilities are called a reading frame. Only one of them is valid ...
of a protein
... analysis of the relation between primary and 3D structures uncovers mechanisms of folding/unfolding/refolding of proteins sequence determination is a component of molecular pathology (searching for mutations that determines predisposition to various diseases – alterations in amino acid sequence may ...
... analysis of the relation between primary and 3D structures uncovers mechanisms of folding/unfolding/refolding of proteins sequence determination is a component of molecular pathology (searching for mutations that determines predisposition to various diseases – alterations in amino acid sequence may ...
Unit 08 - Lessons 1-3
... Amino acids are coded by mRNA base sequences. • translation - converts mRNA messages into a long chain of amino acids (polypeptide) • codon - (contained on the mRNA) - sequence of three nucleotides that codes for an amino acid codon for methionine (Met) ...
... Amino acids are coded by mRNA base sequences. • translation - converts mRNA messages into a long chain of amino acids (polypeptide) • codon - (contained on the mRNA) - sequence of three nucleotides that codes for an amino acid codon for methionine (Met) ...
Amino Acid Exporter: A Tool for the Next
... of why bacterial cells possess these transporters to export L-amino acids J Biotechnol Biomater ISSN:2155-952X JBTBM an open access journal ...
... of why bacterial cells possess these transporters to export L-amino acids J Biotechnol Biomater ISSN:2155-952X JBTBM an open access journal ...
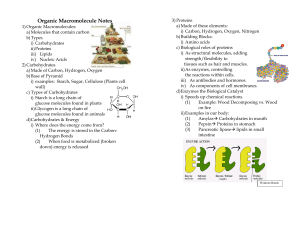
Organic Macromolecule Notes
... a) Made of these elements: i) Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen b) Building Blocks: i) Amino acids c) Biological roles of proteins i) As structural molecules, adding strength/flexibility to tissues such as hair and muscles. ii) As enzymes, controlling the reactions within cells. iii) As antibodies ...
... a) Made of these elements: i) Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen b) Building Blocks: i) Amino acids c) Biological roles of proteins i) As structural molecules, adding strength/flexibility to tissues such as hair and muscles. ii) As enzymes, controlling the reactions within cells. iii) As antibodies ...
amino acid , peptide and protein metabolism
... 1) Catabolism (protein, amino acid degradation) Excess AA excreted(Carbon skeleton, amino group) (2)Regulation of amino acid catabolism 3) Amino acid synthesis (Anabolism). essential and non essential amino acid. 4) Errors of protein metabolism and clinical significance ...
... 1) Catabolism (protein, amino acid degradation) Excess AA excreted(Carbon skeleton, amino group) (2)Regulation of amino acid catabolism 3) Amino acid synthesis (Anabolism). essential and non essential amino acid. 4) Errors of protein metabolism and clinical significance ...
S1.There are mutant tRNAs that act as nonsense and missense
... tRNA so that the anticodon recognizes a stop codon but inserts an amino acid at this site. A missense suppressor is a mutation in a tRNA gene that changes the anticodon so that it puts in the wrong amino acid at a normal codon that is not a stop codon. These mutant tRNAs are termed missense tRNAs. F ...
... tRNA so that the anticodon recognizes a stop codon but inserts an amino acid at this site. A missense suppressor is a mutation in a tRNA gene that changes the anticodon so that it puts in the wrong amino acid at a normal codon that is not a stop codon. These mutant tRNAs are termed missense tRNAs. F ...
Document
... tRNA so that the anticodon recognizes a stop codon but inserts an amino acid at this site. A missense suppressor is a mutation in a tRNA gene that changes the anticodon so that it puts in the wrong amino acid at a normal codon that is not a stop codon. These mutant tRNAs are termed missense tRNAs. F ...
... tRNA so that the anticodon recognizes a stop codon but inserts an amino acid at this site. A missense suppressor is a mutation in a tRNA gene that changes the anticodon so that it puts in the wrong amino acid at a normal codon that is not a stop codon. These mutant tRNAs are termed missense tRNAs. F ...
Pairwise Alignments Part 1
... V T + +L+ W+ QTKQDLELPKLAGTWHSMAMA-TNNISLMATLKAPLRVHITSLLPTPEDNLEIVLHRWEN 81 ...
... V T + +L+ W+ QTKQDLELPKLAGTWHSMAMA-TNNISLMATLKAPLRVHITSLLPTPEDNLEIVLHRWEN 81 ...
CH03_Lecture
... All animations will appear after viewing in Presentation Mode and playing each animation. Most animations will require the latest version of the Flash Player, which is available at http://get.adobe.com/flashplayer. ...
... All animations will appear after viewing in Presentation Mode and playing each animation. Most animations will require the latest version of the Flash Player, which is available at http://get.adobe.com/flashplayer. ...
Word Definition 1 non-Mendelian genetics rules
... genetic traits that are controlled by many genes 6 sex-linked gene a gene that is carried on the X or Y chromosome 7 carrier a person who has one dominant and one recessive allele for a trait 8 genetic disorder an abnormal condition that a person inherits through genes a genetic disorder that causes ...
... genetic traits that are controlled by many genes 6 sex-linked gene a gene that is carried on the X or Y chromosome 7 carrier a person who has one dominant and one recessive allele for a trait 8 genetic disorder an abnormal condition that a person inherits through genes a genetic disorder that causes ...
C h e m g u id e –... AMINO ACIDS: ACID-BASE BEHAVIOUR
... d) The overall charge on the ions produced in parts (b) and (c) can be investigated using electrophoresis. Describe how you would carry out simple electrophoresis on a solution containing one of these ions. e) The final result of the electrophoresis you have described will probably be a spot on a pi ...
... d) The overall charge on the ions produced in parts (b) and (c) can be investigated using electrophoresis. Describe how you would carry out simple electrophoresis on a solution containing one of these ions. e) The final result of the electrophoresis you have described will probably be a spot on a pi ...
Chapter 12 Test Review
... protein synthesis? Ribosome 24. Which type of RNA carries specific amino acids to the ribosome to be put in the correct sequence? tRNA 25. The process of DNA replication is necessary before a cell divides. 26. When DNA is replicated, the result is 2 identical strands of DNA. 27. In DNA, guanine pair ...
... protein synthesis? Ribosome 24. Which type of RNA carries specific amino acids to the ribosome to be put in the correct sequence? tRNA 25. The process of DNA replication is necessary before a cell divides. 26. When DNA is replicated, the result is 2 identical strands of DNA. 27. In DNA, guanine pair ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.