Searching for the “Secret of Life”
... the base pairs No T (thymine) so when it reads the nucleotide A on DNA it matches it with U (Uracil). ...
... the base pairs No T (thymine) so when it reads the nucleotide A on DNA it matches it with U (Uracil). ...
Unit 5 Test Review 14-15
... 19. __________ is the genetic material found in each cell in your body. One segment of this molecule is called a _______________. Every gene expresses itself as a _________________. Many proteins put together make up all of your _____________________. ...
... 19. __________ is the genetic material found in each cell in your body. One segment of this molecule is called a _______________. Every gene expresses itself as a _________________. Many proteins put together make up all of your _____________________. ...
013368718X_CH04_047
... 15. Mutations are important to the evolution of a species because they A. happen over the long period of time that evolution requires. B. cut out and replace damaged or useless genes. C. are a source of genetic variability. D. accelerate the transcription rate of DNA. 16. Cancer is the product of a ...
... 15. Mutations are important to the evolution of a species because they A. happen over the long period of time that evolution requires. B. cut out and replace damaged or useless genes. C. are a source of genetic variability. D. accelerate the transcription rate of DNA. 16. Cancer is the product of a ...
Characterization of AtAAP1 function in amino acid uptake by the root
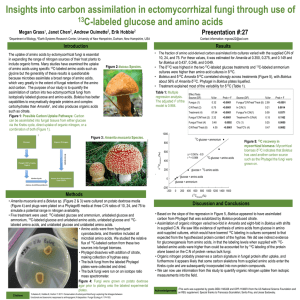
... in supplied C:N. We saw little evidence of synthesis of amino acids from glucose in amino acid-supplied cultures, which would have lowered 13C labeling in cultures compared to that expected from the hypothesized protein content of the hyphae. We did see indirect evidence for gluconeogenesis from ami ...
... in supplied C:N. We saw little evidence of synthesis of amino acids from glucose in amino acid-supplied cultures, which would have lowered 13C labeling in cultures compared to that expected from the hypothesized protein content of the hyphae. We did see indirect evidence for gluconeogenesis from ami ...
Genetics Quiz – 18 October 2005
... crosses its DNA with its homologous pair. One set of these crossed over chromosomes is packaged into each haploid daughter cell (sperm/egg). True 5. the chromosomes are made of deoxyribose nucleic acid that exists as chromatin (fuzzy in appearance) in the Interphase nucleus True 6. DNA is made up of ...
... crosses its DNA with its homologous pair. One set of these crossed over chromosomes is packaged into each haploid daughter cell (sperm/egg). True 5. the chromosomes are made of deoxyribose nucleic acid that exists as chromatin (fuzzy in appearance) in the Interphase nucleus True 6. DNA is made up of ...
Biochemistry of Cells - Warren County Public Schools
... make proteins The process is called condensation or dehydration Peptide bonds form to hold the amino acids together ...
... make proteins The process is called condensation or dehydration Peptide bonds form to hold the amino acids together ...
Lecture7
... • In human genome, ~3% of DNA sequence is genes • Lot of “junk” DNA between genes, and even inside genes (between exons). • Gene prediction must deal with this. ...
... • In human genome, ~3% of DNA sequence is genes • Lot of “junk” DNA between genes, and even inside genes (between exons). • Gene prediction must deal with this. ...
Genetic Changes = Mutations
... 6. cancer … uncontrolled cell division 7. Point mutation: a change in a single N-base pair in DNA a. End result: a change in ONE of the amino acids in the sequence b. THE DOG BIT THE CAT c. THE DOG BIT THE CAR (each word is representing an amino acid. The whole sentence represents a protein d. Sickl ...
... 6. cancer … uncontrolled cell division 7. Point mutation: a change in a single N-base pair in DNA a. End result: a change in ONE of the amino acids in the sequence b. THE DOG BIT THE CAT c. THE DOG BIT THE CAR (each word is representing an amino acid. The whole sentence represents a protein d. Sickl ...
Transcription and Translation
... • http://www.phschool.com/science/biology _place/biocoach/translation/term.html • Release factors function in termination ( RF1 and 3) • GTP is required for energy • The termination or stop codon enters the A site( UAA, UAG, UGA) • Recognized by the ribosome ...
... • http://www.phschool.com/science/biology _place/biocoach/translation/term.html • Release factors function in termination ( RF1 and 3) • GTP is required for energy • The termination or stop codon enters the A site( UAA, UAG, UGA) • Recognized by the ribosome ...
Molecules of Life---Whoa! - Rimac-Science-Web
... Levels of Organization • Proteins can have 4 different structural levels of organization. • Primary Structure: is the sequence of its amino acids. • Secondary Structure: the folding or coiling of a peptide chain. Typically done ...
... Levels of Organization • Proteins can have 4 different structural levels of organization. • Primary Structure: is the sequence of its amino acids. • Secondary Structure: the folding or coiling of a peptide chain. Typically done ...
DNA Biology
... Applying Your Knowledge If the mRNA sequence for codons 5, 6, and 7 of a protein is 5’-AAG-AUU-GGA-3’, what is the amino acid sequence in the protein? ...
... Applying Your Knowledge If the mRNA sequence for codons 5, 6, and 7 of a protein is 5’-AAG-AUU-GGA-3’, what is the amino acid sequence in the protein? ...
Jeopardy Review 2013
... transcribed onto mRNA, and eventually translated into a protein. The protein is the phenotype (expression of the ...
... transcribed onto mRNA, and eventually translated into a protein. The protein is the phenotype (expression of the ...
Document
... Structure and Function All amino acids are identical in the amino and carboxyl groups. Any amino acid can be joined to any other amino acid by a peptide bond formed between these amino and carboxyl groups. Amino acids differ from each other in a side chain called the R-groups, which have a range of ...
... Structure and Function All amino acids are identical in the amino and carboxyl groups. Any amino acid can be joined to any other amino acid by a peptide bond formed between these amino and carboxyl groups. Amino acids differ from each other in a side chain called the R-groups, which have a range of ...
3. Organic Compounds
... molecules such as heme. After the polypeptides are synthesized by the cell, they spontaneously fold up into a characteristic conformation which allows them to be active. The proper shape is essential for active proteins. For most proteins, the amino acids sequence itself is all that is needed to get ...
... molecules such as heme. After the polypeptides are synthesized by the cell, they spontaneously fold up into a characteristic conformation which allows them to be active. The proper shape is essential for active proteins. For most proteins, the amino acids sequence itself is all that is needed to get ...
4/20 & 4/21 - 7th Grade Agenda
... 2nd Step: Hypothesis • Hypothesis is a possible expl_______ anations for a set of observation or answer to a scientific question ...
... 2nd Step: Hypothesis • Hypothesis is a possible expl_______ anations for a set of observation or answer to a scientific question ...
Glossary Protein
... fluid balance maintenance of the proper types and amounts of fluid in each compartment of the body fluids. gene expression the process by which a cell converts the genetic code into RNA and protein. hemoglobin the globular protein of the red blood cells that carries oxygen from the lungs to the cell ...
... fluid balance maintenance of the proper types and amounts of fluid in each compartment of the body fluids. gene expression the process by which a cell converts the genetic code into RNA and protein. hemoglobin the globular protein of the red blood cells that carries oxygen from the lungs to the cell ...
Biochemistry of Cells - Doral Academy Preparatory
... •Blood sugar level is controlled by a protein called insulin •Insulin causes the liver to uptake and store excess sugar as Glycogen The cell membrane also contains proteins Receptor proteins help cells recognize other cells ...
... •Blood sugar level is controlled by a protein called insulin •Insulin causes the liver to uptake and store excess sugar as Glycogen The cell membrane also contains proteins Receptor proteins help cells recognize other cells ...
Unit 3 Biotechnology
... • Cloning of a mule – Idaho Gem: first clone from the horse family; first clone of a hybrid animal incapable of reproduction – What is the significance of this and other cloning ...
... • Cloning of a mule – Idaho Gem: first clone from the horse family; first clone of a hybrid animal incapable of reproduction – What is the significance of this and other cloning ...
Proteins*
... More than 2 linked together are called polypeptides polypeptides can be thousands of amino acids long ...
... More than 2 linked together are called polypeptides polypeptides can be thousands of amino acids long ...
Proteinler - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... cleaves at COOH end of Lys and Arg cleaves at COOH end of Phe, Tyr, Trp ...
... cleaves at COOH end of Lys and Arg cleaves at COOH end of Phe, Tyr, Trp ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.