How Things Go Wrong
... Show student Overhead 1 and tell them, “There are many types of mutations: Point mutations: A single nucleotide base being changed. This type of mutation can affect a gene’s protein production in several ways. Missense Mutation: A point mutation that results in a single amino acid change in a protei ...
... Show student Overhead 1 and tell them, “There are many types of mutations: Point mutations: A single nucleotide base being changed. This type of mutation can affect a gene’s protein production in several ways. Missense Mutation: A point mutation that results in a single amino acid change in a protei ...
Genetics Learning Goals
... Score 4: Student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications of the learning goal(s) and can reconstruct and apply their knowledge from limited information: A/B4) Describe important discoveries that led to today’s model of DNA structure and explain how the development of the DNA model exhibits ...
... Score 4: Student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications of the learning goal(s) and can reconstruct and apply their knowledge from limited information: A/B4) Describe important discoveries that led to today’s model of DNA structure and explain how the development of the DNA model exhibits ...
CHAPTER 27
... of elimination or fixation would probably be quite variable. These alleles are acted upon by natural selection. As environmental conditions change, the degree to which natural selection would favor beneficial alleles and eliminate deleterious alleles would also change. For example, natural selection ...
... of elimination or fixation would probably be quite variable. These alleles are acted upon by natural selection. As environmental conditions change, the degree to which natural selection would favor beneficial alleles and eliminate deleterious alleles would also change. For example, natural selection ...
Differences between DNA and RNA • Ribonucleic acid is similar to
... those hydroxyl groups have been removed. ...
... those hydroxyl groups have been removed. ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... – Hydrophobicity is likely to allow exposed hydrophobic side chains of nascent polypeptide to slide through easily ...
... – Hydrophobicity is likely to allow exposed hydrophobic side chains of nascent polypeptide to slide through easily ...
Organic Chemistry Notes Powerpoint
... Saturated vs. Unsaturated Saturated means that all the carbon bonds are taken. They are solid at room temperature and bad for you. Unsaturated means that there is at least one double bond with the carbon. They are liquid at room temp. and are better for you. ...
... Saturated vs. Unsaturated Saturated means that all the carbon bonds are taken. They are solid at room temperature and bad for you. Unsaturated means that there is at least one double bond with the carbon. They are liquid at room temp. and are better for you. ...
lect3
... 1. Starch: made in plants; stores energy 2. Glycogen: made in animals; stores energy 3. Cellulose: undigestible polysaccharide made in ...
... 1. Starch: made in plants; stores energy 2. Glycogen: made in animals; stores energy 3. Cellulose: undigestible polysaccharide made in ...
Unti 8-9 - DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis
... Score 4: Student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications of the learning goal(s) and can reconstruct and apply their knowledge from limited information: A/B4) Describe important discoveries that led to today’s model of DNA structure and explain how the development of the DNA model exhibits ...
... Score 4: Student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications of the learning goal(s) and can reconstruct and apply their knowledge from limited information: A/B4) Describe important discoveries that led to today’s model of DNA structure and explain how the development of the DNA model exhibits ...
ANTH 2301 - Week 4 DNA
... Regulatory genes don t code for proteins but do regulate development (7%) ...
... Regulatory genes don t code for proteins but do regulate development (7%) ...
hemp seed: the most nutritionally complete food source in the world
... availability of the amino acids necessary to make specific proteins. The body needs the necessary kinds of amino acids in sufficient quantity in order to make proteins such as the globulins. Proper quantities of the right kinds may not be available to the body much of the time. So even though the bo ...
... availability of the amino acids necessary to make specific proteins. The body needs the necessary kinds of amino acids in sufficient quantity in order to make proteins such as the globulins. Proper quantities of the right kinds may not be available to the body much of the time. So even though the bo ...
Tinkering with the Biochemistry of Life: Viruses, Prions, and Peptide
... Like DNA, PNA has sequences of nucleic acid bases, but backbone is composed of glycine amino acid residues and ethyl amine units, instead of ribose and phosphate. ...
... Like DNA, PNA has sequences of nucleic acid bases, but backbone is composed of glycine amino acid residues and ethyl amine units, instead of ribose and phosphate. ...
Transcription
... initially synthesized‐‐a cut‐and‐paste job called RNA splicing. The average length of a transcription unit along a eukaryotic DNA molecule is about 8,000 nucleotides, so the primary RNA transcript is also that long. But it takes only about 1,200 nucleotides to code for an average‐sized protein of ...
... initially synthesized‐‐a cut‐and‐paste job called RNA splicing. The average length of a transcription unit along a eukaryotic DNA molecule is about 8,000 nucleotides, so the primary RNA transcript is also that long. But it takes only about 1,200 nucleotides to code for an average‐sized protein of ...
File - Wk 1-2
... beta-oxidation, amino acid breakdown, TCA cycle and electron transport chain. For each, include the cellular location, the major organs in which each pathway is active and the effect of starvation or flux of substrates through the pathway. 4. Outline how chemical energy released from the oxidation o ...
... beta-oxidation, amino acid breakdown, TCA cycle and electron transport chain. For each, include the cellular location, the major organs in which each pathway is active and the effect of starvation or flux of substrates through the pathway. 4. Outline how chemical energy released from the oxidation o ...
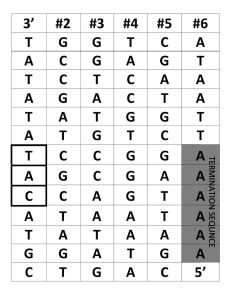
Just One Nucleotide! Exploring the Effects of Random
... messenger RNA and turns it into a linear sequence of amino acids covalently joined by peptide bonds. It really is a translation from one code, nucleotide sequence, to another code, amino acid sequence. 1. Name the three different types of RNA. Mention their functions. Messenger RNA (mRNA) – copy of ...
... messenger RNA and turns it into a linear sequence of amino acids covalently joined by peptide bonds. It really is a translation from one code, nucleotide sequence, to another code, amino acid sequence. 1. Name the three different types of RNA. Mention their functions. Messenger RNA (mRNA) – copy of ...
Similarity
... were known, they were able to determine stretches of amino acids that could serve to form an a-helix or a bsheet. These amino acids are called helix formers or sheet formers and can have different strengths for forming their structures. Once these nucleation sites are determined, adjacent amino acid ...
... were known, they were able to determine stretches of amino acids that could serve to form an a-helix or a bsheet. These amino acids are called helix formers or sheet formers and can have different strengths for forming their structures. Once these nucleation sites are determined, adjacent amino acid ...
Alignment scoring statistics and scoring matrices
... and by the pair exchange frequency->mutation probability score • Relative mutability = chance that the amino acid will change (Dayhoff used # times observed to change) • Pair exchange frequency = fraction of Phe->Tyr/all Phe mutations • Normalize to a sum of 1% probability of any amino acid change, ...
... and by the pair exchange frequency->mutation probability score • Relative mutability = chance that the amino acid will change (Dayhoff used # times observed to change) • Pair exchange frequency = fraction of Phe->Tyr/all Phe mutations • Normalize to a sum of 1% probability of any amino acid change, ...
Final Review Answer Key - Mercer Island School District
... 17. Two cats both have long whiskers. They have the same phenotype for this trait. If long whiskers is a recessive trait they must also have the same genotype. However, if long whiskers is a dominant trait, they could have either a homozygous dominant or heterozygous genotype. 18. Describe what a P ...
... 17. Two cats both have long whiskers. They have the same phenotype for this trait. If long whiskers is a recessive trait they must also have the same genotype. However, if long whiskers is a dominant trait, they could have either a homozygous dominant or heterozygous genotype. 18. Describe what a P ...
Unit VII: Genetics
... Matches the codon to an anticodon on tRNA Ribosome reads next codon and brings in next tRNA with matching anticodon Since tRNA is attached to Amino Acids – two amino acids are located next to each other This proximity allows the ____________________ Makes a peptide Repeats until mRNA says stop ...
... Matches the codon to an anticodon on tRNA Ribosome reads next codon and brings in next tRNA with matching anticodon Since tRNA is attached to Amino Acids – two amino acids are located next to each other This proximity allows the ____________________ Makes a peptide Repeats until mRNA says stop ...
amino acids - El Camino College
... Each type has a distinctive sequence of amino acids which determines both its specialized ___________ and its unique ___________. • number, weight B) length, mass C) structure, function D) charge, pH 4. Nucleic acids: A) are the energy source for our bodies. B) act on other molecules, breaking them ...
... Each type has a distinctive sequence of amino acids which determines both its specialized ___________ and its unique ___________. • number, weight B) length, mass C) structure, function D) charge, pH 4. Nucleic acids: A) are the energy source for our bodies. B) act on other molecules, breaking them ...
48x36 Poster Template
... A patient has two pathogenic mutations in the acid α-glucosidase gene, one on each chromosome. Basically, the nature of the mutations in the acid α-glucosidase gene and the combination of mutant alleles determine the level of residual lysosomal acid αglucosidase activity and primarily the clinical p ...
... A patient has two pathogenic mutations in the acid α-glucosidase gene, one on each chromosome. Basically, the nature of the mutations in the acid α-glucosidase gene and the combination of mutant alleles determine the level of residual lysosomal acid αglucosidase activity and primarily the clinical p ...
Ion exchange chromatography File
... groups become loosely associated with Na+ and Clions of the opposite charge. These loosely bound ions are called mobile counter-ions. ...
... groups become loosely associated with Na+ and Clions of the opposite charge. These loosely bound ions are called mobile counter-ions. ...
Genetic Engineering Essay Handout
... couple's having children, stating that cystic fibrosis is a serious disease that usually shortens an individual's life span. On the other hand, great advances have been made in research, and people with cystic fibrosis are now living longer lives of a higher quality than ever before. In addition, it ...
... couple's having children, stating that cystic fibrosis is a serious disease that usually shortens an individual's life span. On the other hand, great advances have been made in research, and people with cystic fibrosis are now living longer lives of a higher quality than ever before. In addition, it ...
Unit 6B Learning Targets
... ii. Addition of a GTP cap iii. Excision of introns c. Translation of the mRNA occurs in the cytoplasm on the ribosome. d. In prokaryotic organisms, transcription is coupled to translation of the message. Translation involves energy and many steps, including initiation, elongation, and termination. i ...
... ii. Addition of a GTP cap iii. Excision of introns c. Translation of the mRNA occurs in the cytoplasm on the ribosome. d. In prokaryotic organisms, transcription is coupled to translation of the message. Translation involves energy and many steps, including initiation, elongation, and termination. i ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.