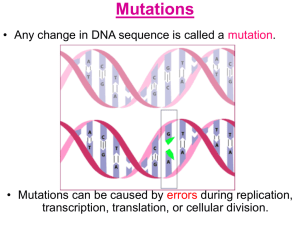
Mutations
... DNA polymerase proofreads the polymerisation step before proceeding to the next one Incorrect bases are removed by the 3’5’ exonuclease Some E. coli mutants with abnormally high mutation rates have an altered DNA polymerase II with lowered 3’5’ exonuclease activity ...
... DNA polymerase proofreads the polymerisation step before proceeding to the next one Incorrect bases are removed by the 3’5’ exonuclease Some E. coli mutants with abnormally high mutation rates have an altered DNA polymerase II with lowered 3’5’ exonuclease activity ...
To the protocol
... the blood stream. The active site of trypsin, as well as of any other enzyme, has two distinct functions; to bind the substrate in the active site, and to perform the catalysis. Trypsin has a preference to degrade peptides and proteins adjacent to basic amino acids, that is arginine or lysine. This ...
... the blood stream. The active site of trypsin, as well as of any other enzyme, has two distinct functions; to bind the substrate in the active site, and to perform the catalysis. Trypsin has a preference to degrade peptides and proteins adjacent to basic amino acids, that is arginine or lysine. This ...
4.2.1 Liver MS - Mrs Miller`s Blog
... long loop of Henlé or/ deep / wide, medulla ; very low water potential in medulla / AW ; A higher concentration of salts collecting duct more permeable to water ; large number of, water permeable channels / aquaporins, in collecting duct ; more sensitive to ADH / more ADH produced ; AVP ; e.g. other ...
... long loop of Henlé or/ deep / wide, medulla ; very low water potential in medulla / AW ; A higher concentration of salts collecting duct more permeable to water ; large number of, water permeable channels / aquaporins, in collecting duct ; more sensitive to ADH / more ADH produced ; AVP ; e.g. other ...
Gene Mutations
... change in the reading frame of a gene Sequences that encode proteins may lead to frameshift mutations changes in the reading frame Frameshift mutations generally have drastic effects on the phenotype Addition or removal of one or more amino acids may still affect the phenotype These mutation ...
... change in the reading frame of a gene Sequences that encode proteins may lead to frameshift mutations changes in the reading frame Frameshift mutations generally have drastic effects on the phenotype Addition or removal of one or more amino acids may still affect the phenotype These mutation ...
Vocabulary Quiz Key Terms
... of the unzipped double helix until the entire molecule has been replicated. The small segments of the lagging DNA strand. ...
... of the unzipped double helix until the entire molecule has been replicated. The small segments of the lagging DNA strand. ...
Distrofie muscolari dei cingoli
... Three mutations at two loci are necessary for pathogenesis in this pedigree, as the affected sibling (03) has three nonsense mutations (Q147X in BBS6, and Y24X and Q59X in BBS2) and the unaffected sibling (05) has two nonsense BBS2 mutations, but is wild-type for BBS6.. ...
... Three mutations at two loci are necessary for pathogenesis in this pedigree, as the affected sibling (03) has three nonsense mutations (Q147X in BBS6, and Y24X and Q59X in BBS2) and the unaffected sibling (05) has two nonsense BBS2 mutations, but is wild-type for BBS6.. ...
How Does DNA Determine the Traits of a SNORK? A Introduction: In
... Draw your Snork in the space below. Be creative! ...
... Draw your Snork in the space below. Be creative! ...
Human genetic disorders
... • The recessive allele causes three bases to be removed from on DNA molecule (mutation) ...
... • The recessive allele causes three bases to be removed from on DNA molecule (mutation) ...
doc
... are protected by negative feedback loops that help maintain homeostasis. D. Mars cooled faster than the Earth and therefore was a more habitable place for life earlier. Life arose first on Mars and traveled to Earth on meteorites E. Large glaciers and ice ages result from a runaway cold-house, where ...
... are protected by negative feedback loops that help maintain homeostasis. D. Mars cooled faster than the Earth and therefore was a more habitable place for life earlier. Life arose first on Mars and traveled to Earth on meteorites E. Large glaciers and ice ages result from a runaway cold-house, where ...
Part A: Amino Acids and Peptides
... Name one possible peptide sideproduct that would form if the protein simply activated both ends of the three amino acids shown above. ...
... Name one possible peptide sideproduct that would form if the protein simply activated both ends of the three amino acids shown above. ...
Chem331 Lect 5 Amino acids peptides
... Amino acids are zwitterions - a molecule with both a pos and neg charge All naturally occurring amino acids are optically active isomers, except glycine. L amino acids R-groups determine the functionality of the amino acids. All amino acids can be based on one of three basic groups, non-polar, uncha ...
... Amino acids are zwitterions - a molecule with both a pos and neg charge All naturally occurring amino acids are optically active isomers, except glycine. L amino acids R-groups determine the functionality of the amino acids. All amino acids can be based on one of three basic groups, non-polar, uncha ...
Nucleic Acids - University of California, Davis
... messenger RNA (mRNA, carries the information), transfer RNA (tRNA, brings the correct amino acid during synthesis), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA, major consituent of the ribosome, where protein synthesis occurs. ...
... messenger RNA (mRNA, carries the information), transfer RNA (tRNA, brings the correct amino acid during synthesis), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA, major consituent of the ribosome, where protein synthesis occurs. ...
Biochemistry Chp 3
... Lipids (CHO) 2x as many H as C, fewer O Proteins (CHONS) Nucleic Acids (CHONP) ...
... Lipids (CHO) 2x as many H as C, fewer O Proteins (CHONS) Nucleic Acids (CHONP) ...
11.3 Section Summary 6.3 – pages 296
... • A mutation may produce a new trait or it may result in a protein that does not work correctly. • Sometimes, the mutation results in a protein that is nonfunctional, and the embryo may not survive. ...
... • A mutation may produce a new trait or it may result in a protein that does not work correctly. • Sometimes, the mutation results in a protein that is nonfunctional, and the embryo may not survive. ...
Directed Reading 13
... ______ 9. Microspheres could not be considered true cells unless they could a. form cellular membranes. b. originate spontaneously in water. c. incorporate molecules and energy. d. pass their characteristics to offspring. ______10. Most scientists agree that double-stranded DNA evolved a. after RNA. ...
... ______ 9. Microspheres could not be considered true cells unless they could a. form cellular membranes. b. originate spontaneously in water. c. incorporate molecules and energy. d. pass their characteristics to offspring. ______10. Most scientists agree that double-stranded DNA evolved a. after RNA. ...
DNA Webquest - sciencewithskinner
... 2. List the RNA bases that pair up with the DNA nucleotides on the unzipped molecule during Transcription. DNA base A ...
... 2. List the RNA bases that pair up with the DNA nucleotides on the unzipped molecule during Transcription. DNA base A ...
PROTEIN-SYNTHESIS
... goes into the cytoplasm. mRNA will then attach itself to a ribosome. The strand of mRNA is then read in order to make protein. They are read 3 bases at a time. These bases are called codons. tRNA is the fetching puppy. It brings the amino acids to the ribosome to help make the protein. The 3 bases o ...
... goes into the cytoplasm. mRNA will then attach itself to a ribosome. The strand of mRNA is then read in order to make protein. They are read 3 bases at a time. These bases are called codons. tRNA is the fetching puppy. It brings the amino acids to the ribosome to help make the protein. The 3 bases o ...
Genetic Engineering
... taken from a human chromosome and inserted into a bacteria’s plasmid (a single ringed chromosome). This plasmid with the human insulin gene can then be used to produce insulin to treat certain forms of diabetes. This is one example of how genetic engineering techniques can be used to create pharmace ...
... taken from a human chromosome and inserted into a bacteria’s plasmid (a single ringed chromosome). This plasmid with the human insulin gene can then be used to produce insulin to treat certain forms of diabetes. This is one example of how genetic engineering techniques can be used to create pharmace ...
Macromolecules - Uplift Mighty Prep
... 1. What property do all Lipids share? 2. Name 3 examples of lipids in the body. 3. Why would we store excess energy as Fat, rather than carbohydrates? ...
... 1. What property do all Lipids share? 2. Name 3 examples of lipids in the body. 3. Why would we store excess energy as Fat, rather than carbohydrates? ...
Gene Mutations Worksheet
... Goals & Objectives: Students will be able to demonstrate how mutations change the amino acid sequence. Students will be able to explain the difference between mutations. Standards: CA Biology 4c. Students know that mutations in the DNA sequence of a gene may or may not affect the expression of the g ...
... Goals & Objectives: Students will be able to demonstrate how mutations change the amino acid sequence. Students will be able to explain the difference between mutations. Standards: CA Biology 4c. Students know that mutations in the DNA sequence of a gene may or may not affect the expression of the g ...
Macromolecules - Uplift Education
... 1. What property do all Lipids share? 2. Name 3 examples of lipids in the body. 3. Why would we store excess energy as Fat, rather than carbohydrates? ...
... 1. What property do all Lipids share? 2. Name 3 examples of lipids in the body. 3. Why would we store excess energy as Fat, rather than carbohydrates? ...
Protein Malnutrition - MSUD Family Support Group
... sustain life and to maintain growth in infants and children. It may involve protein, calories, minerals, or the co-factors for enzymes that we usually ingest as vitamins. Children can have a generalized lack of all nutrients, or a deficiency of a specific nutrient or group of nutrients. In most chil ...
... sustain life and to maintain growth in infants and children. It may involve protein, calories, minerals, or the co-factors for enzymes that we usually ingest as vitamins. Children can have a generalized lack of all nutrients, or a deficiency of a specific nutrient or group of nutrients. In most chil ...
Sequence Alignment - UTK-EECS
... primary structure — sequence of amino acids in the protein secondary structure — polypeptide chains folding into regular structures (i.e., ...
... primary structure — sequence of amino acids in the protein secondary structure — polypeptide chains folding into regular structures (i.e., ...
Who wants to be a Physiology Millionaire?
... C – enzymes are proteins D – All enzymes have the same Shape as substrate ...
... C – enzymes are proteins D – All enzymes have the same Shape as substrate ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.