Reason 6: Protein Manufacture: Ribosomes are proof of
... molecules are involved? Although the cytoplasm contains water, proteins, carbohydrates, various ions, and assorted other molecules, proteins do most of the work. A typical bacterium requires more than 4,000 proteins for growth and reproduction. Not all of the proteins are made at the same time and s ...
... molecules are involved? Although the cytoplasm contains water, proteins, carbohydrates, various ions, and assorted other molecules, proteins do most of the work. A typical bacterium requires more than 4,000 proteins for growth and reproduction. Not all of the proteins are made at the same time and s ...
Chem of Life_Bio
... • Protein can be large complex molecules. Function of a protein depends on the Amino Acid sequence, shape and its ability to recognize and bind to some other molecule. ...
... • Protein can be large complex molecules. Function of a protein depends on the Amino Acid sequence, shape and its ability to recognize and bind to some other molecule. ...
Pantothenic Acid - Pure Encapsulations
... diarrhea. There is also one case of eosinophilic pleuropericardial effusion in a patient taking pantothenic acid 300 mg per day in combination with biotin 10 mg per day for 2 months. Consult your physician for more information. ...
... diarrhea. There is also one case of eosinophilic pleuropericardial effusion in a patient taking pantothenic acid 300 mg per day in combination with biotin 10 mg per day for 2 months. Consult your physician for more information. ...
Lesson Plan Template
... Base substitution is the simplest type of mutation where a nucleotide pair is replaced with a different nucleotide pair. There are four types of base substitution. One type is called transversion mutation. This happens when one purine (A,G) is swapped with a pyrimidine (C,T). The second type, transi ...
... Base substitution is the simplest type of mutation where a nucleotide pair is replaced with a different nucleotide pair. There are four types of base substitution. One type is called transversion mutation. This happens when one purine (A,G) is swapped with a pyrimidine (C,T). The second type, transi ...
DNA and RNA - davis.k12.ut.us
... you now have exposed nitrogen bases. Attach six mRNA nucleotides to your original DNA strand. Remember T (thymine) is replaced by U (uracil) when making RNA. Because mRNA is single stranded, it is only formed on one half of your DNA. Remove your mRNA strand from the DNA strand and put your DNA stran ...
... you now have exposed nitrogen bases. Attach six mRNA nucleotides to your original DNA strand. Remember T (thymine) is replaced by U (uracil) when making RNA. Because mRNA is single stranded, it is only formed on one half of your DNA. Remove your mRNA strand from the DNA strand and put your DNA stran ...
Genetic Engineering
... • Reich and his team explain in their study, published online in Nature. Different sections of the genome differ by different amounts, suggesting that they parted ways at different times. The divorce period between the two species, the data suggest, could have lasted a million years. The region bear ...
... • Reich and his team explain in their study, published online in Nature. Different sections of the genome differ by different amounts, suggesting that they parted ways at different times. The divorce period between the two species, the data suggest, could have lasted a million years. The region bear ...
Study Guide - Pierce College
... 29. Using a codon dictionary, show the relationship between DNA, mRNA, and tRNA sequences and amino acids by recognizing the sense sequences, codons, anticodons and amino acids in a 5 amino acid polypeptide. 30. Explain, with a specific example of DNA, how a mutation can result in a different polype ...
... 29. Using a codon dictionary, show the relationship between DNA, mRNA, and tRNA sequences and amino acids by recognizing the sense sequences, codons, anticodons and amino acids in a 5 amino acid polypeptide. 30. Explain, with a specific example of DNA, how a mutation can result in a different polype ...
DNA, RNA and Protein
... produce a new chain •Each new DNA helix contains one “old” and one “new” chain ...
... produce a new chain •Each new DNA helix contains one “old” and one “new” chain ...
Lecture 8 (9/18/14) Protein Folding
... where malaria is a problem, people's chances of survival actually increase if they carry sickle-cell trait (selection for the heterozygote). ...
... where malaria is a problem, people's chances of survival actually increase if they carry sickle-cell trait (selection for the heterozygote). ...
NUTRITIONAL REGULATIN OF GROWTH
... Dietary Protein Ruminants utilize microbial protein to satisfy part of protein requirements Amino acids synthesized to ammonia, CO2, and VFA’s (these are required for microbial protein growth)- degradation Nitrogen is the key for microbial protein satisfaction (NPN can be a source) ...
... Dietary Protein Ruminants utilize microbial protein to satisfy part of protein requirements Amino acids synthesized to ammonia, CO2, and VFA’s (these are required for microbial protein growth)- degradation Nitrogen is the key for microbial protein satisfaction (NPN can be a source) ...
m5zn_db523f23f00100a
... • What we come to know from human genome • The human genome contains 3164.7 million chemical nucleotide bases (A, C, T, and G). • The average gene consists of 3000 bases, but sizes vary greatly, with the largest known human gene being dystrophin at 2.4 million bases (a protein located mainly in mus ...
... • What we come to know from human genome • The human genome contains 3164.7 million chemical nucleotide bases (A, C, T, and G). • The average gene consists of 3000 bases, but sizes vary greatly, with the largest known human gene being dystrophin at 2.4 million bases (a protein located mainly in mus ...
Validation of an HPLC method for the determination of
... and detection in the visible region on an amino acid analyser. These analyses are reliable, but costly and time-consuming.9 The HPLC technique, combined with pre-column derivatisation of amino acids, has become a very important method for the analysis of amino acids.9 It should be emphasized that pr ...
... and detection in the visible region on an amino acid analyser. These analyses are reliable, but costly and time-consuming.9 The HPLC technique, combined with pre-column derivatisation of amino acids, has become a very important method for the analysis of amino acids.9 It should be emphasized that pr ...
Genetic Codes with No Dedicated Stop Codon: Context
... selection) (Yang, 2007). The hypothesis that UGA codons are translated was assessed experimentally in two ways: we determined that UGA codons are translated as tryptophan by protein mass spectrometry (Data S1D and S1E); using ribosome profiling we observe that ribosomes efficiently translate through ...
... selection) (Yang, 2007). The hypothesis that UGA codons are translated was assessed experimentally in two ways: we determined that UGA codons are translated as tryptophan by protein mass spectrometry (Data S1D and S1E); using ribosome profiling we observe that ribosomes efficiently translate through ...
Genetic Testing
... • The mapping of large number of families to MCPH5 locus and identification of common mutation in ASPM gene in families of Pakistani origin will enable us to formulate future strategies to control and prevent the disease to reduce the prevalence of MCPH in Pakistan. genetic counseling prenatal d ...
... • The mapping of large number of families to MCPH5 locus and identification of common mutation in ASPM gene in families of Pakistani origin will enable us to formulate future strategies to control and prevent the disease to reduce the prevalence of MCPH in Pakistan. genetic counseling prenatal d ...
Algorithms and a Software Application for the Discovery of Heparin
... the unwanted substances can easily be filtered out. Certain sequences or patterns of amino acids are known to have a high probability of binding to heparin. Thus, proteins that contain large numbers of these sequences of amino acids are more likely to bind to heparin. This research is focused on pro ...
... the unwanted substances can easily be filtered out. Certain sequences or patterns of amino acids are known to have a high probability of binding to heparin. Thus, proteins that contain large numbers of these sequences of amino acids are more likely to bind to heparin. This research is focused on pro ...
Designer Babies ? Fact or Fiction?
... So many genetic abnormalities that it would be impossible to screen for all of them. Only meaningful now because of background knowledge - such as family history ...
... So many genetic abnormalities that it would be impossible to screen for all of them. Only meaningful now because of background knowledge - such as family history ...
Three functionally diverged major structural proteins of white spot
... VP26 and VP24 are associated with the nucleocapsid and the remaining two with the envelope. Forty-one N-terminal amino acids of VP24 were determined biochemically allowing the identification of its gene (vp24) in the WSSV genome. Computer-assisted analysis revealed a striking similarity between WSSV ...
... VP26 and VP24 are associated with the nucleocapsid and the remaining two with the envelope. Forty-one N-terminal amino acids of VP24 were determined biochemically allowing the identification of its gene (vp24) in the WSSV genome. Computer-assisted analysis revealed a striking similarity between WSSV ...
Question 1
... possible to make variant enzymes which differ from the one above by a single amino acid substitution. (For example, Asp 78 could be replaced with tryptophan). You could use this technique to investigate the roles of each amino acid shown above. i) If you change Arg 31 to a lysine, would you predict ...
... possible to make variant enzymes which differ from the one above by a single amino acid substitution. (For example, Asp 78 could be replaced with tryptophan). You could use this technique to investigate the roles of each amino acid shown above. i) If you change Arg 31 to a lysine, would you predict ...
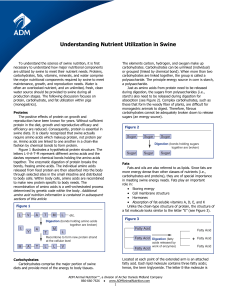
Nutrient Utilization in Swine
... Most information normally discusses excess nitrogen excretion as a result of overfeeding protein. However, deficiencies in one or more essential amino acids can also result in excess nitrogen excretion. To understand this process, one needs to have a basic understanding of how protein is formed. The ...
... Most information normally discusses excess nitrogen excretion as a result of overfeeding protein. However, deficiencies in one or more essential amino acids can also result in excess nitrogen excretion. To understand this process, one needs to have a basic understanding of how protein is formed. The ...
Linkage and Recombination
... Yes, changes in the DNA -- also known as mutations -- can cause these kinds of uncommon scenarios. In fact, there are documented cases where things like this have happened! Keep in mind, though, that mutations are very rare. Two O parents will get an O child nearly all of the time. But it is technic ...
... Yes, changes in the DNA -- also known as mutations -- can cause these kinds of uncommon scenarios. In fact, there are documented cases where things like this have happened! Keep in mind, though, that mutations are very rare. Two O parents will get an O child nearly all of the time. But it is technic ...
Chapter 1 Introduction
... explosive information is being provided at an unprecedented speed. Biochemistry is a window opening to the world of life science. Thus, the knowledge of biochemistry which involves the study of chemical molecules and reactions in living organisms, and the elucidations of the nature of live phenomeno ...
... explosive information is being provided at an unprecedented speed. Biochemistry is a window opening to the world of life science. Thus, the knowledge of biochemistry which involves the study of chemical molecules and reactions in living organisms, and the elucidations of the nature of live phenomeno ...
Gene Expression
... strand and attaches a "T" nucleotide to the RNA "A" nucleotide, etc, until the entire RNA strand has been paired with nucleotides. This is translation. Then the RNA strand is taken away, taken apart, and its nucleotides are recycled. The string of nucleotides that is left is then read in a different ...
... strand and attaches a "T" nucleotide to the RNA "A" nucleotide, etc, until the entire RNA strand has been paired with nucleotides. This is translation. Then the RNA strand is taken away, taken apart, and its nucleotides are recycled. The string of nucleotides that is left is then read in a different ...
Atomic Structure (Bohr or Planetary Model)
... proteins which in turn determines its biological function ...
... proteins which in turn determines its biological function ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.