Light: The Cosmic Messenger
... • Why do we put telescopes into space? – Forms of light other than radio and visible do not pass through Earth’s atmosphere. – Also, much sharper images are possible because there is no turbulence. ...
... • Why do we put telescopes into space? – Forms of light other than radio and visible do not pass through Earth’s atmosphere. – Also, much sharper images are possible because there is no turbulence. ...
April 2015 - Southern Astronomical Society
... been shown to be insubstantial — passing through itself as well as everything else. A study of data returned from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope and the ESA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory has found dark matter does not slow down when it collides with itself. This is significant as it shows the ghostly s ...
... been shown to be insubstantial — passing through itself as well as everything else. A study of data returned from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope and the ESA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory has found dark matter does not slow down when it collides with itself. This is significant as it shows the ghostly s ...
Autoguiding - Thrush Observatory
... no more difficult or complicated than using an off-axis guider if one follows a few simple rules. • The most fundamental mistake is to attempt to mount the guide scope directly to the primary tube. A guide scope is just too heavy and will bend the main tube in all sorts of random ways when in use. • ...
... no more difficult or complicated than using an off-axis guider if one follows a few simple rules. • The most fundamental mistake is to attempt to mount the guide scope directly to the primary tube. A guide scope is just too heavy and will bend the main tube in all sorts of random ways when in use. • ...
2. Chapter 11
... To be considered a planet, a body must orbit one or more stars, be large enough that its own gravity holds it in a spherical shape, and be the only body occupying the orbital path. Large distances keep our solar neighbourhood’s family of eight planets well separated from each other (Figure 11.9). In ...
... To be considered a planet, a body must orbit one or more stars, be large enough that its own gravity holds it in a spherical shape, and be the only body occupying the orbital path. Large distances keep our solar neighbourhood’s family of eight planets well separated from each other (Figure 11.9). In ...
February 2013 - astronomy for beginners
... Ursa Major showing Mizar, imaged by Richard Fleet At the centre of the three stars forming the handle of the Plough is a famous naked eye double star Mizar and Alcor its companion. Viewed through powerful binoculars or a telescope Mizar is seen to be a double star itself. When the light from the two ...
... Ursa Major showing Mizar, imaged by Richard Fleet At the centre of the three stars forming the handle of the Plough is a famous naked eye double star Mizar and Alcor its companion. Viewed through powerful binoculars or a telescope Mizar is seen to be a double star itself. When the light from the two ...
Toward a revival of Stellar Intensity Interferometry
... Intensity Interferometer does not rely on actual light interference, instead, the mutual degree of coherence is obtained from the measurement of the degree of correlation between the fluctuations of intensity recorded with a quadratic detector at different telescopes. The principal component of the ...
... Intensity Interferometer does not rely on actual light interference, instead, the mutual degree of coherence is obtained from the measurement of the degree of correlation between the fluctuations of intensity recorded with a quadratic detector at different telescopes. The principal component of the ...
to get the file
... the sun in a mere five minutes after the first picture •The solution to the transmittance problem was to attach a variable polarizing lens to the telescope ...
... the sun in a mere five minutes after the first picture •The solution to the transmittance problem was to attach a variable polarizing lens to the telescope ...
memphis astronomical society short course in astronomy 2015
... day, explaining the concept with a sketch. Be able to define declination and right ascension. Know what precession is, and its two principal results as seen in the sky. ...
... day, explaining the concept with a sketch. Be able to define declination and right ascension. Know what precession is, and its two principal results as seen in the sky. ...
Galaxies, Cosmology and the Accelera`ng Universe
... – Average distance between stars is about 12 6mes the size of the Solar System – The night sky there contains more than a million stars brighter than Sirius, the brightest star in our sky ...
... – Average distance between stars is about 12 6mes the size of the Solar System – The night sky there contains more than a million stars brighter than Sirius, the brightest star in our sky ...
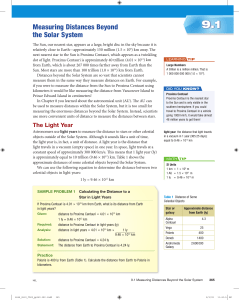
Measuring Distances Beyond the Solar System
... next nearest star to the Sun is Proxima Centauri, which appears as a twinkling dot of light. Proxima Centauri is approximately 40 trillion (4.01 × 1013) km from Earth, which is about 267 000 times farther away from Earth than the Sun. Most stars are more than 100 trillion (1.0 × 1014) km from Earth. ...
... next nearest star to the Sun is Proxima Centauri, which appears as a twinkling dot of light. Proxima Centauri is approximately 40 trillion (4.01 × 1013) km from Earth, which is about 267 000 times farther away from Earth than the Sun. Most stars are more than 100 trillion (1.0 × 1014) km from Earth. ...
DAY AND NIGHT, SEASONS
... temperature is too high. Organisms would require energy stores to keep them going through these times. ...
... temperature is too high. Organisms would require energy stores to keep them going through these times. ...
Functional Fields of Bioptic: implications for driving
... the eye minus half the angular size of the optical field of view.” (true if ocular at the eye) – Feinbloom, 1977. ...
... the eye minus half the angular size of the optical field of view.” (true if ocular at the eye) – Feinbloom, 1977. ...
DTU 8e Chap 3 Light and Telescopes
... Very sharp radio images are produced with arrays of radio telescopes linked together in a technique called interferometry. ...
... Very sharp radio images are produced with arrays of radio telescopes linked together in a technique called interferometry. ...
Cepheid Calibration
... The apparent brightness of a light source varies inversely as the square of its distance. In other words, if the distance between an observer and a light source is doubled, the light source will appear four times as faint to the observer. Astronomers can use this inverse square law to estimate dist ...
... The apparent brightness of a light source varies inversely as the square of its distance. In other words, if the distance between an observer and a light source is doubled, the light source will appear four times as faint to the observer. Astronomers can use this inverse square law to estimate dist ...
Milky Way Galaxy
... The galaxy NGC 7742 is an otherwise normal spiral galaxy except for its extraordinarily bright nucleus that outshines the rest of the galaxy. Such galaxies, i.e. spirals with extremely bright nuclei, form a class of active galaxies known as Seyfert galaxies. ...
... The galaxy NGC 7742 is an otherwise normal spiral galaxy except for its extraordinarily bright nucleus that outshines the rest of the galaxy. Such galaxies, i.e. spirals with extremely bright nuclei, form a class of active galaxies known as Seyfert galaxies. ...
Special Protein in Zebrafish May Lead to Full Spinal
... Zebrafish and humans share a lot of proteincoding genes such as CTGF. Our CTGF proteins are nearly 90 percent similar to that of the zebrafish. When human CTGFs were added to zebrafish injuries, they even boosted the regeneration. It also appears that the second half of the protein does wonders as ...
... Zebrafish and humans share a lot of proteincoding genes such as CTGF. Our CTGF proteins are nearly 90 percent similar to that of the zebrafish. When human CTGFs were added to zebrafish injuries, they even boosted the regeneration. It also appears that the second half of the protein does wonders as ...
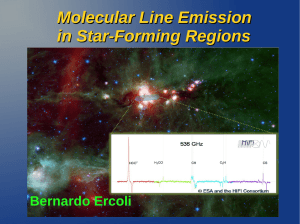
Molecular Line Emission in Star
... velocity of the emitting source. Velocities are usually calculated respect to the Local Standard of Rest (LSR), an ideal point in rotation around the Galactic centre as far as the Sun. The relationship between velocity and frequency is: ...
... velocity of the emitting source. Velocities are usually calculated respect to the Local Standard of Rest (LSR), an ideal point in rotation around the Galactic centre as far as the Sun. The relationship between velocity and frequency is: ...
PanEOS A first data characterization
... In the context of an agreement between Laboratório Nacional de Astrofı́sica (LNA) and the Russian Space Agency ROSCOSMOS an “Optical-Electronic Complex for Detection and Measurement of the Movement Parameters of Space Debris” (OEC DSD), also known as “PanEOS” (abbreviation to be used throughout thi ...
... In the context of an agreement between Laboratório Nacional de Astrofı́sica (LNA) and the Russian Space Agency ROSCOSMOS an “Optical-Electronic Complex for Detection and Measurement of the Movement Parameters of Space Debris” (OEC DSD), also known as “PanEOS” (abbreviation to be used throughout thi ...
PDF - WM Keck Observatory
... • How do the observatories and the science that occurs on Maunakea directly affect people as individuals? ANSWER: The observatories impact local people directly in many ways, including educational outreach, com ...
... • How do the observatories and the science that occurs on Maunakea directly affect people as individuals? ANSWER: The observatories impact local people directly in many ways, including educational outreach, com ...
Slide 1
... The camera is general purpose detector with a universal face-plate for attachment to various ...
... The camera is general purpose detector with a universal face-plate for attachment to various ...
it now and get started on your discovery
... astronaut until she realized her near-sighted vision and fear of small spaces didn’t fit well with the astronaut job description. So, she decided to go to graduate school and became the first African American woman to earn an Astronomy Ph.D. from the University of Michigan. In addition to her work o ...
... astronaut until she realized her near-sighted vision and fear of small spaces didn’t fit well with the astronaut job description. So, she decided to go to graduate school and became the first African American woman to earn an Astronomy Ph.D. from the University of Michigan. In addition to her work o ...
Slide 1
... small fraction of an arm sitting between two larger arms. 99% of the stars we see in the sky are in this spur. ...
... small fraction of an arm sitting between two larger arms. 99% of the stars we see in the sky are in this spur. ...
ORBITAL MOTION
... Stage 3. At densities of 1011 cm-3 and within a radius of 1014 cm the gas becomes opaque to the dust radiation even at 300microns. The energy released is trapped and the temperature rises. As the temperature ascends, the opacity also ascends. The core suddenly switches from isothermal to adiabatic. ...
... Stage 3. At densities of 1011 cm-3 and within a radius of 1014 cm the gas becomes opaque to the dust radiation even at 300microns. The energy released is trapped and the temperature rises. As the temperature ascends, the opacity also ascends. The core suddenly switches from isothermal to adiabatic. ...
Jia-Rui C. Cook 818-354-0850 Jet Propulsion Laboratory
... by some other unknown component. Long, dark lines are fractures in the crust, some of which are more than 3,000 kilometers (1,850 miles) long. Image credit: NASA/JPL/University of Arizona › Full image and caption April 04, 2013 A new paper led by a NASA researcher shows that hydrogen peroxide is abu ...
... by some other unknown component. Long, dark lines are fractures in the crust, some of which are more than 3,000 kilometers (1,850 miles) long. Image credit: NASA/JPL/University of Arizona › Full image and caption April 04, 2013 A new paper led by a NASA researcher shows that hydrogen peroxide is abu ...
Aryabhatta Research Institute of Observational Sciences
... CCD cameras, imaging polarimeter, three channel fast photometer and an optical multichannel analyzer. ARIES also has two 15-cm reflectors equipped with Hα , Ca II K and CN filters and CCD cameras for carrying out observations of solar activities with a time resolution of up to 25 millisecond. For op ...
... CCD cameras, imaging polarimeter, three channel fast photometer and an optical multichannel analyzer. ARIES also has two 15-cm reflectors equipped with Hα , Ca II K and CN filters and CCD cameras for carrying out observations of solar activities with a time resolution of up to 25 millisecond. For op ...
Spitzer Space Telescope

The Spitzer Space Telescope (SST), formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF), is an infrared space observatory launched in 2003. It is the fourth and final of the NASA Great Observatories program.The planned mission period was to be 2.5 years with a pre-launch expectation that the mission could extend to five or slightly more years until the onboard liquid helium supply was exhausted. This occurred on 15 May 2009. Without liquid helium to cool the telescope to the very low temperatures needed to operate, most of the instruments are no longer usable. However, the two shortest-wavelength modules of the IRAC camera are still operable with the same sensitivity as before the cryogen was exhausted, and will continue to be used in the Spitzer Warm Mission. All Spitzer data, from both the primary and warm phases, are archived at the Infrared Science Archive (IRSA).In keeping with NASA tradition, the telescope was renamed after its successful demonstration of operation, on 18 December 2003. Unlike most telescopes that are named after famous deceased astronomers by a board of scientists, the new name for SIRTF was obtained from a contest open to the general public.The contest led to the telescope being named in honor of astronomer Lyman Spitzer, who had promoted the concept of space telescopes in the 1940s. Spitzer wrote a 1946 report for RAND Corporation describing the advantages of an extraterrestrial observatory and how it could be realized with available or upcoming technology. He has been cited for his pioneering contributions to rocketry and astronomy, as well as ""his vision and leadership in articulating the advantages and benefits to be realized from the Space Telescope Program.""The US$800 million Spitzer was launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, on a Delta II 7920H ELV rocket, Monday, 25 August 2003 at 13:35:39 UTC-5 (EDT).It follows a heliocentric instead of geocentric orbit, trailing and drifting away from Earth's orbit at approximately 0.1 astronomical unit per year (a so-called ""earth-trailing"" orbit). The primary mirror is 85 centimeters (33 in) in diameter, f/12, made of beryllium and is cooled to 5.5 K (−449.77 °F). The satellite contains three instruments that allow it to perform astronomical imaging and photometry from 3 to 180 micrometers, spectroscopy from 5 to 40 micrometers, and spectrophotometry from 5 to 100 micrometers.