Spectral fingerprinting student project
... scientists may soon be hot on its trail. In 1995, the first planet around another sun-like star was discovered by astronomers using Doppler detection—a method that scientists have used to reveal Saturn-sized (or larger) planets close to their parent suns. Today, astronomers know of more than 100 can ...
... scientists may soon be hot on its trail. In 1995, the first planet around another sun-like star was discovered by astronomers using Doppler detection—a method that scientists have used to reveal Saturn-sized (or larger) planets close to their parent suns. Today, astronomers know of more than 100 can ...
The ExOoS Mission - Extraterrestrial Octopus on Steroids
... The targets will be selected very carefully to get the highest chance for the mission to find life. Therefore the planet and the star have both to full fill certain criteria. First of all, the planet has to orbit its star in the habitable zone. The habitable zone is defined as the area in which wate ...
... The targets will be selected very carefully to get the highest chance for the mission to find life. Therefore the planet and the star have both to full fill certain criteria. First of all, the planet has to orbit its star in the habitable zone. The habitable zone is defined as the area in which wate ...
Here
... Good Review Questions, Chapter 3 4. What are the three major functions of a telescope? 12. Why must astronomers use satellites and Earth-orbiting observatories to study the heavens at X-ray wavelengths? 13. What is a blackbody? What does it mean to say that a star appears almost like a black body? ...
... Good Review Questions, Chapter 3 4. What are the three major functions of a telescope? 12. Why must astronomers use satellites and Earth-orbiting observatories to study the heavens at X-ray wavelengths? 13. What is a blackbody? What does it mean to say that a star appears almost like a black body? ...
Document
... one half to two thirds of the way out. The disk is very thin— 2 per cent of its width—like a phonograph record, CD, or DVD. It contains all the young stars and interstellar gas and dust, as well as some old stars. The disk is slightly warped at its ends, perhaps by interaction with our satellite gal ...
... one half to two thirds of the way out. The disk is very thin— 2 per cent of its width—like a phonograph record, CD, or DVD. It contains all the young stars and interstellar gas and dust, as well as some old stars. The disk is slightly warped at its ends, perhaps by interaction with our satellite gal ...
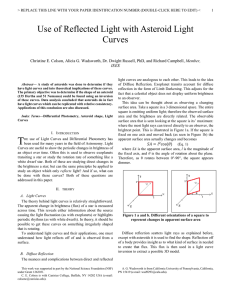
Use of Reflected Light with Asteroid Light Curves
... Here, I n is the intensity of a light ray normal to a plane and I θ is the intensity θ degrees from the normal. This shows that as light bends further from the normal, intensity decreases (i.e. a large θ makes light dimmer). D. YORP Effect One important contribution towards some asteroid’s rotation ...
... Here, I n is the intensity of a light ray normal to a plane and I θ is the intensity θ degrees from the normal. This shows that as light bends further from the normal, intensity decreases (i.e. a large θ makes light dimmer). D. YORP Effect One important contribution towards some asteroid’s rotation ...
What, and Why, is the International Astronomical Union?
... (founder of Yerkes, Mt. Wilson, and Palomar Observatories) was the prime mover. They met at least once, at Mt. Wilson in 1910, discussing, among other issues, how to standardize measurements of solar rotation made from different sites, so that real variations across the sun and with time could be id ...
... (founder of Yerkes, Mt. Wilson, and Palomar Observatories) was the prime mover. They met at least once, at Mt. Wilson in 1910, discussing, among other issues, how to standardize measurements of solar rotation made from different sites, so that real variations across the sun and with time could be id ...
chapter 26 instructor notes
... These are a group of strongly interacting galaxies that are bluer in colour than isolated galaxies, presumably because of the presence of recently-created hot young stars. Larson and Tinsley (1972) argued that the tidal interaction with another galaxy has induced star formation, although the resulti ...
... These are a group of strongly interacting galaxies that are bluer in colour than isolated galaxies, presumably because of the presence of recently-created hot young stars. Larson and Tinsley (1972) argued that the tidal interaction with another galaxy has induced star formation, although the resulti ...
astronomy discovery tour to india
... The site has been found to be good (about 150 cloud free nights per year) for astronomical observations. The specifications for surface finish of the telescope mirrors has been one-tenth of 589 nm line of sodium so that the telescope can be effectively used for imaging studies at both optical and in ...
... The site has been found to be good (about 150 cloud free nights per year) for astronomical observations. The specifications for surface finish of the telescope mirrors has been one-tenth of 589 nm line of sodium so that the telescope can be effectively used for imaging studies at both optical and in ...
A Search for Exozodiacal Dust and Faint Companions near Sirius
... faint companions in our images. If there were a low-mass companion orbiting Sirius at 4.2 AU, we could not detect it because it would lie in the saturated parts of our images. However, we did survey a large fraction of the space where a companion orbiting Sirius B might be found, and we could have d ...
... faint companions in our images. If there were a low-mass companion orbiting Sirius at 4.2 AU, we could not detect it because it would lie in the saturated parts of our images. However, we did survey a large fraction of the space where a companion orbiting Sirius B might be found, and we could have d ...
Custom Solutions Catalog
... the carrier lens so that the optic center of the ocular lens is 11mm below the top of the carrier lens. They are laterally decentered to the patient’s PD and have a standard drilling angle of inclination of 20º upward from the horizontal plane. Any position or angle, however, can be special-ordered. ...
... the carrier lens so that the optic center of the ocular lens is 11mm below the top of the carrier lens. They are laterally decentered to the patient’s PD and have a standard drilling angle of inclination of 20º upward from the horizontal plane. Any position or angle, however, can be special-ordered. ...
Galaxies – Island universes
... cluster. If they’re big enough to identify as having eaten several galaxies, we call them “central dominant” or “cannibal galaxies” … ...
... cluster. If they’re big enough to identify as having eaten several galaxies, we call them “central dominant” or “cannibal galaxies” … ...
Science and the Universe - Wayne State University Physics and
... hypotheses needed to explain these Some observational facts are very well understood, but others remain “mysterious” Typically, new ideas are difficult to test either because the amount of data is small, or because they require observations that are difficult based on current technology 29 Jun 2005 ...
... hypotheses needed to explain these Some observational facts are very well understood, but others remain “mysterious” Typically, new ideas are difficult to test either because the amount of data is small, or because they require observations that are difficult based on current technology 29 Jun 2005 ...
Publisher: Emily Barrosse Acquisitions Editor: Kelley Tyner
... them. www Its infrared camera provided views of different aspects of some of the planetary nebulae (Fig. 13–4). The remaining part of the star in the center is the star’s exposed hot core, which reaches temperatures of 100,000 K and so appears bluish. It is known as the “central star of the planetar ...
... them. www Its infrared camera provided views of different aspects of some of the planetary nebulae (Fig. 13–4). The remaining part of the star in the center is the star’s exposed hot core, which reaches temperatures of 100,000 K and so appears bluish. It is known as the “central star of the planetar ...
Which planet has never been orbited or flown past by a
... galaxies and cosmology, for which there are numerous HST images to exemplify the concepts. • My particular favorites are the Hubble Deep Field and Ultra Deep Field. • But since we’ve dispensed with Bob, I leave incorporating these into your class as an exercise for the reader. Dr. C. Renee James N ...
... galaxies and cosmology, for which there are numerous HST images to exemplify the concepts. • My particular favorites are the Hubble Deep Field and Ultra Deep Field. • But since we’ve dispensed with Bob, I leave incorporating these into your class as an exercise for the reader. Dr. C. Renee James N ...
Astronomy - Troop 179
... b. Describe the similarities and differences of several types of astronomical telescopes. c. Explain the purposes of at least three instruments used with astronomical telescopes. 4. Do the following: Material is covered during the program and the scout will be required to describe the appropriate in ...
... b. Describe the similarities and differences of several types of astronomical telescopes. c. Explain the purposes of at least three instruments used with astronomical telescopes. 4. Do the following: Material is covered during the program and the scout will be required to describe the appropriate in ...
lab 11 only - Penn State University
... spherical cloud of stars that surrounds the entire galaxy). The halo is much larger than the bulge. Our Milky Way Galaxy is made up of mostly stars, gas, and dust. The dust blocks out light from distant stars, and makes it hard to see a lot of the galaxy, especially the bulge and parts of the disk. ...
... spherical cloud of stars that surrounds the entire galaxy). The halo is much larger than the bulge. Our Milky Way Galaxy is made up of mostly stars, gas, and dust. The dust blocks out light from distant stars, and makes it hard to see a lot of the galaxy, especially the bulge and parts of the disk. ...
Goal: To understand the structure and makeup of our own Milky Way
... Hydrogen you are looking at is moving away from us (away because the wavelength is increased) at 1400 km/s. • By using this we can map our the homes, and our galaxy. • Everything in our galaxy orbits around the center of our galaxy – so we have one really big system. ...
... Hydrogen you are looking at is moving away from us (away because the wavelength is increased) at 1400 km/s. • By using this we can map our the homes, and our galaxy. • Everything in our galaxy orbits around the center of our galaxy – so we have one really big system. ...
19. Our Galaxy 19.1 The Milky Way Revealed Our goals for learning
... • What is the significance of a rotation curve that is flat at large distances from the galactic center? • The Milky Way’s flat rotation curve implies that the matter associated with our galaxy extends to large distances from the center. A rotation curve is a plot of the orbital speed of stars or ga ...
... • What is the significance of a rotation curve that is flat at large distances from the galactic center? • The Milky Way’s flat rotation curve implies that the matter associated with our galaxy extends to large distances from the center. A rotation curve is a plot of the orbital speed of stars or ga ...
October 2005 NSTAR - North Houston Astronomy Club
... When a massive star reaches the end of its life, it can explode into a supernova rivaling the brilliance of an entire galaxy. What’s left of the star fades in weeks, but its outer layers expand through space as a turbulent cloud of gases. Astronomers see beautiful remnants from past supernovas all a ...
... When a massive star reaches the end of its life, it can explode into a supernova rivaling the brilliance of an entire galaxy. What’s left of the star fades in weeks, but its outer layers expand through space as a turbulent cloud of gases. Astronomers see beautiful remnants from past supernovas all a ...
Refracting vs Reflecting Telescopes
... • uses ten dedicated, 25-meter telescopes spanning 5351 miles across the United States • the largest VLBI array that operates all year round as both an astronomical and geodesy instrument. Global VLBI • Combination of the EVN and VLBA Space Very Long Baseline Interferometry (SVLBI) •dedicated VLBI p ...
... • uses ten dedicated, 25-meter telescopes spanning 5351 miles across the United States • the largest VLBI array that operates all year round as both an astronomical and geodesy instrument. Global VLBI • Combination of the EVN and VLBA Space Very Long Baseline Interferometry (SVLBI) •dedicated VLBI p ...
HAT-P-7: A RETROGRADE OR POLAR ORBIT, AND A THIRD BODY
... Department of Physics, and Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA 02139, USA 2 Institute for Astronomy, University of Hawaii, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA 3 Department of Astronomy, University of California, Mail Code 3411, Berkeley, CA 9 ...
... Department of Physics, and Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA 02139, USA 2 Institute for Astronomy, University of Hawaii, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA 3 Department of Astronomy, University of California, Mail Code 3411, Berkeley, CA 9 ...
Solar Physics, Space Weather, and Wide-field X-ray
... “space weather” ranges from disruption of our space communication systems to astronaut health hazards to power grid overloads and blackouts. The National Oceanic & Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and NASA are cooperating on a Solar X-ray Imager (SXI) program intended to allow NOAA to monitor and p ...
... “space weather” ranges from disruption of our space communication systems to astronaut health hazards to power grid overloads and blackouts. The National Oceanic & Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and NASA are cooperating on a Solar X-ray Imager (SXI) program intended to allow NOAA to monitor and p ...
Spitzer Space Telescope

The Spitzer Space Telescope (SST), formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF), is an infrared space observatory launched in 2003. It is the fourth and final of the NASA Great Observatories program.The planned mission period was to be 2.5 years with a pre-launch expectation that the mission could extend to five or slightly more years until the onboard liquid helium supply was exhausted. This occurred on 15 May 2009. Without liquid helium to cool the telescope to the very low temperatures needed to operate, most of the instruments are no longer usable. However, the two shortest-wavelength modules of the IRAC camera are still operable with the same sensitivity as before the cryogen was exhausted, and will continue to be used in the Spitzer Warm Mission. All Spitzer data, from both the primary and warm phases, are archived at the Infrared Science Archive (IRSA).In keeping with NASA tradition, the telescope was renamed after its successful demonstration of operation, on 18 December 2003. Unlike most telescopes that are named after famous deceased astronomers by a board of scientists, the new name for SIRTF was obtained from a contest open to the general public.The contest led to the telescope being named in honor of astronomer Lyman Spitzer, who had promoted the concept of space telescopes in the 1940s. Spitzer wrote a 1946 report for RAND Corporation describing the advantages of an extraterrestrial observatory and how it could be realized with available or upcoming technology. He has been cited for his pioneering contributions to rocketry and astronomy, as well as ""his vision and leadership in articulating the advantages and benefits to be realized from the Space Telescope Program.""The US$800 million Spitzer was launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, on a Delta II 7920H ELV rocket, Monday, 25 August 2003 at 13:35:39 UTC-5 (EDT).It follows a heliocentric instead of geocentric orbit, trailing and drifting away from Earth's orbit at approximately 0.1 astronomical unit per year (a so-called ""earth-trailing"" orbit). The primary mirror is 85 centimeters (33 in) in diameter, f/12, made of beryllium and is cooled to 5.5 K (−449.77 °F). The satellite contains three instruments that allow it to perform astronomical imaging and photometry from 3 to 180 micrometers, spectroscopy from 5 to 40 micrometers, and spectrophotometry from 5 to 100 micrometers.