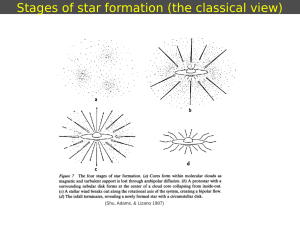
Stages of star formation (the classical view)
... High-mass star-forming regions are farther than low-mass. The closest is the Orion molecular cloud, at 500 pc (compared with Taurus at 140 pc) ...
... High-mass star-forming regions are farther than low-mass. The closest is the Orion molecular cloud, at 500 pc (compared with Taurus at 140 pc) ...
Chapter 15 The Formation of Planetary Systems
... Jupiter and an orbital period of 6 years. You can see why it has taken so long to discover planets in Jupiter-like orbits: You have to observe for at least one orbital period. It takes six years for this planet to orbit just once, and observers usually demand more than one orbit for confirmation. Th ...
... Jupiter and an orbital period of 6 years. You can see why it has taken so long to discover planets in Jupiter-like orbits: You have to observe for at least one orbital period. It takes six years for this planet to orbit just once, and observers usually demand more than one orbit for confirmation. Th ...
Chapter 15 The Formation of Planetary Systems
... Jupiter and an orbital period of 6 years. You can see why it has taken so long to discover planets in Jupiter-like orbits: You have to observe for at least one orbital period. It takes six years for this planet to orbit just once, and observers usually demand more than one orbit for confirmation. Th ...
... Jupiter and an orbital period of 6 years. You can see why it has taken so long to discover planets in Jupiter-like orbits: You have to observe for at least one orbital period. It takes six years for this planet to orbit just once, and observers usually demand more than one orbit for confirmation. Th ...
Deployment of the Hobby-Eberly Telescope wide
... the telescope correctly aligned. The WFC is a four-mirror design with two concave 1 meter diameter mirrors, one concave 0.9 meter diameter mirror, and one convex 0.23 m diameter mirror. The corrector is designed for feeding optical fibers at f/3.65 to minimize focal ratio degradation, and so the chi ...
... the telescope correctly aligned. The WFC is a four-mirror design with two concave 1 meter diameter mirrors, one concave 0.9 meter diameter mirror, and one convex 0.23 m diameter mirror. The corrector is designed for feeding optical fibers at f/3.65 to minimize focal ratio degradation, and so the chi ...
スライド タイトルなし - X-ray Astronomy Group at ISAS
... absorption of a single X-ray photon. The small heat capacities and low temperature lead to very small fluctuations, resulting in higher energy resolution compared to ordinary semiconductor devices. The XRS can resolve very small energy differences of X-ray photons. ...
... absorption of a single X-ray photon. The small heat capacities and low temperature lead to very small fluctuations, resulting in higher energy resolution compared to ordinary semiconductor devices. The XRS can resolve very small energy differences of X-ray photons. ...
Manual - TUM
... receives to much light during an exposure, it will saturate. Saturation is when a pixel’s counting value exceeds 215 , in which case the image cannot be used, if the saturated pixels are within the object of interest. Be mindful of this when taking your images: do not allow pixels of your object of ...
... receives to much light during an exposure, it will saturate. Saturation is when a pixel’s counting value exceeds 215 , in which case the image cannot be used, if the saturated pixels are within the object of interest. Be mindful of this when taking your images: do not allow pixels of your object of ...
Direct Imaging of Exoplanets - American Museum of Natural History
... science, so each of them is valuable. Radial velocity has been very successful in measuring masses and periods of planets with masses greater than several Earths and in short-period orbits. Transits have been valuable in measuring the diameters and periods of giant planets, and in combined-light mod ...
... science, so each of them is valuable. Radial velocity has been very successful in measuring masses and periods of planets with masses greater than several Earths and in short-period orbits. Transits have been valuable in measuring the diameters and periods of giant planets, and in combined-light mod ...
The IAU Changes our Solar System: Pluto Demoted
... exceptionally elliptical and erratic with wide variances in its distance from the Sun during its orbital rotation. In fact, between January 1979 and February 1999, Pluto’s orbit was actually within the orbit of Neptune, making Neptune the outermost planet of our solar system for those years. All of ...
... exceptionally elliptical and erratic with wide variances in its distance from the Sun during its orbital rotation. In fact, between January 1979 and February 1999, Pluto’s orbit was actually within the orbit of Neptune, making Neptune the outermost planet of our solar system for those years. All of ...
P7 Further Physics
... Astronomers often use the “parsec” to describe galactic distances. A parsec is roughly 3¼ light years. Angles involved in parallax measurements are often very small and are measured in seconds of an arc (arcseconds). A second of an arc is 1/60th of a minute of an arc, which is 1/60th of a degree. In ...
... Astronomers often use the “parsec” to describe galactic distances. A parsec is roughly 3¼ light years. Angles involved in parallax measurements are often very small and are measured in seconds of an arc (arcseconds). A second of an arc is 1/60th of a minute of an arc, which is 1/60th of a degree. In ...
Supermassive black holes
... younger, more metal rich and orbit in the same orientation, excepting some up and down motion ...
... younger, more metal rich and orbit in the same orientation, excepting some up and down motion ...
11 01 04 Portable M Class Astro
... multiple spherical mirrors—the Hobby-Eberly and South African Large Telescope (SALT)— utilize multiple spherical surface, hexagon shaped mirrors to form 11 meter telescopes that were built at a fraction of the cost of the 10 meter Keck telescopes. Of course there are no free lunches, and because lig ...
... multiple spherical mirrors—the Hobby-Eberly and South African Large Telescope (SALT)— utilize multiple spherical surface, hexagon shaped mirrors to form 11 meter telescopes that were built at a fraction of the cost of the 10 meter Keck telescopes. Of course there are no free lunches, and because lig ...
Workshop Summary & Discussion
... continuum for studies of short time scale objects such as first cores and transitional disks (Momose) • Unbiased survey in both spatial and frequency domains to probe the origin of stars and planets (Yamamoto) • CCAT will have a similar point source sensitivity with ALMA at 350 um and more sensitive ...
... continuum for studies of short time scale objects such as first cores and transitional disks (Momose) • Unbiased survey in both spatial and frequency domains to probe the origin of stars and planets (Yamamoto) • CCAT will have a similar point source sensitivity with ALMA at 350 um and more sensitive ...
Potential for Life on the Terrestrial Planets
... close-in planets). But exoplanets which are discovered by transits can be re-observed by the Doppler method so that their mass can also be determined if the precision is above the current signal threshold. The discovery of CoRoT-7b, the first small rocky exoplanet with measured radius and mass (Lége ...
... close-in planets). But exoplanets which are discovered by transits can be re-observed by the Doppler method so that their mass can also be determined if the precision is above the current signal threshold. The discovery of CoRoT-7b, the first small rocky exoplanet with measured radius and mass (Lége ...
Building large telescopes. I- Refractors.
... The next two big refractors were also built by the Clarks. In 1880 the Clark firm was given a contract to build a 36-inch (91 cm) objective and photographic corrector. The lens with a focal length of 17.6 m was finished in 1885 but the photographic corrector (33-inch, 84 cm) was only completed in 18 ...
... The next two big refractors were also built by the Clarks. In 1880 the Clark firm was given a contract to build a 36-inch (91 cm) objective and photographic corrector. The lens with a focal length of 17.6 m was finished in 1885 but the photographic corrector (33-inch, 84 cm) was only completed in 18 ...
Exploring the Universe
... QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
... QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
P7 Further Physics : Observing the Universe
... © University of York (UYSEG) and the Nuffield Foundation • This page may be copied solely for use in the purchaser’s school or college ...
... © University of York (UYSEG) and the Nuffield Foundation • This page may be copied solely for use in the purchaser’s school or college ...
Imaging Uranus
... the planet. Most of our detailed knowledge of Uranus and in stratospheric emission as a function of longitude.8,9 It is its satellites comes from the Voyager mission. The spaceclear then that Uranus is indeed an active world, and that the craft approached the planet pole on and flew over the equaact ...
... the planet. Most of our detailed knowledge of Uranus and in stratospheric emission as a function of longitude.8,9 It is its satellites comes from the Voyager mission. The spaceclear then that Uranus is indeed an active world, and that the craft approached the planet pole on and flew over the equaact ...
observing the universe
... A galaxy is an assembly of between a billion (109) and a hundred billion (1011) stars. There is often a large amount of dust and gas intermingled, all held together by gravity. The Sun and Earth are in the Milky Way Galaxy. Galaxies have many different characteristics, but the easiest way to classif ...
... A galaxy is an assembly of between a billion (109) and a hundred billion (1011) stars. There is often a large amount of dust and gas intermingled, all held together by gravity. The Sun and Earth are in the Milky Way Galaxy. Galaxies have many different characteristics, but the easiest way to classif ...
EQUIPMENT
... GRBs are the biggest bangs since the Big Bang. They are so luminous that they can be observed with relatively small telescopes, even if very far away. However, they fade quickly, often lasting only minutes. Consequently, PROMPT was built to be fast, not big. In 2005, UNC undergraduate Josh Haislip a ...
... GRBs are the biggest bangs since the Big Bang. They are so luminous that they can be observed with relatively small telescopes, even if very far away. However, they fade quickly, often lasting only minutes. Consequently, PROMPT was built to be fast, not big. In 2005, UNC undergraduate Josh Haislip a ...
Seeds of a Tychonic Revolution: Telescopic Observations of the
... scattered throughout space, so such a pair must be in line-of-sight alignment. However, at the distances implied by Mareo's hypothesis, these two stars should exhibit parallax if the Earth is moving, and the difference between the parallaxes of the two stars (differential parallax) must greatly exce ...
... scattered throughout space, so such a pair must be in line-of-sight alignment. However, at the distances implied by Mareo's hypothesis, these two stars should exhibit parallax if the Earth is moving, and the difference between the parallaxes of the two stars (differential parallax) must greatly exce ...
Here - Amateur Observers` Society of New York
... Aurorae borealis (or the Northern Lights) are caused by streams of solar particles striking the upper atmosphere and causing it to glow. Best in dark skies. Small bodies left over from the birth of the solar system, comets are usually quite faint and require a medium to large size telescope to obser ...
... Aurorae borealis (or the Northern Lights) are caused by streams of solar particles striking the upper atmosphere and causing it to glow. Best in dark skies. Small bodies left over from the birth of the solar system, comets are usually quite faint and require a medium to large size telescope to obser ...
Spitzer Space Telescope

The Spitzer Space Telescope (SST), formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF), is an infrared space observatory launched in 2003. It is the fourth and final of the NASA Great Observatories program.The planned mission period was to be 2.5 years with a pre-launch expectation that the mission could extend to five or slightly more years until the onboard liquid helium supply was exhausted. This occurred on 15 May 2009. Without liquid helium to cool the telescope to the very low temperatures needed to operate, most of the instruments are no longer usable. However, the two shortest-wavelength modules of the IRAC camera are still operable with the same sensitivity as before the cryogen was exhausted, and will continue to be used in the Spitzer Warm Mission. All Spitzer data, from both the primary and warm phases, are archived at the Infrared Science Archive (IRSA).In keeping with NASA tradition, the telescope was renamed after its successful demonstration of operation, on 18 December 2003. Unlike most telescopes that are named after famous deceased astronomers by a board of scientists, the new name for SIRTF was obtained from a contest open to the general public.The contest led to the telescope being named in honor of astronomer Lyman Spitzer, who had promoted the concept of space telescopes in the 1940s. Spitzer wrote a 1946 report for RAND Corporation describing the advantages of an extraterrestrial observatory and how it could be realized with available or upcoming technology. He has been cited for his pioneering contributions to rocketry and astronomy, as well as ""his vision and leadership in articulating the advantages and benefits to be realized from the Space Telescope Program.""The US$800 million Spitzer was launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, on a Delta II 7920H ELV rocket, Monday, 25 August 2003 at 13:35:39 UTC-5 (EDT).It follows a heliocentric instead of geocentric orbit, trailing and drifting away from Earth's orbit at approximately 0.1 astronomical unit per year (a so-called ""earth-trailing"" orbit). The primary mirror is 85 centimeters (33 in) in diameter, f/12, made of beryllium and is cooled to 5.5 K (−449.77 °F). The satellite contains three instruments that allow it to perform astronomical imaging and photometry from 3 to 180 micrometers, spectroscopy from 5 to 40 micrometers, and spectrophotometry from 5 to 100 micrometers.