- ORIGINS Space Telescope
... Origins Space Telescope: Cosmology and Reionization Joaquin Vieira (University of Illinois) for the Origins Space Telescope Science and Technology Definition Team ABSTRACT — The Origins Space Telescope (OST) is the mission concept for the Far-Infrared Surveyor, a study in development by NASA in prep ...
... Origins Space Telescope: Cosmology and Reionization Joaquin Vieira (University of Illinois) for the Origins Space Telescope Science and Technology Definition Team ABSTRACT — The Origins Space Telescope (OST) is the mission concept for the Far-Infrared Surveyor, a study in development by NASA in prep ...
Saturday Night Stargazing - Fort Wayne Astronomical Society
... naked eye is a part of our own Milky Way Galaxy. The thickest part of our galaxy can be seen in midwinter and mid-summer as a broad band of light stretching from north to south. Our Sun is just one of billions of stars contained within the Milky Way. ...
... naked eye is a part of our own Milky Way Galaxy. The thickest part of our galaxy can be seen in midwinter and mid-summer as a broad band of light stretching from north to south. Our Sun is just one of billions of stars contained within the Milky Way. ...
OLEARY_2004 - Armagh Observatory
... In order to use the telescope to time the eclipse of NN Ser, I used live sessions on the telescope to capture images of NN Ser during an eclipse. The Faulkes Telescope is equipped with a CCD camera. This contains a piece of silicon which detects light through the photoelectric effect, which causes i ...
... In order to use the telescope to time the eclipse of NN Ser, I used live sessions on the telescope to capture images of NN Ser during an eclipse. The Faulkes Telescope is equipped with a CCD camera. This contains a piece of silicon which detects light through the photoelectric effect, which causes i ...
The Planetarium Fleischmann Planetarium
... in our universe’s “birth-rate” over time. When the universe was young, massive galaxies were forming regularly, like baby bees in a bustling hive. In time, the universe bore fewer and fewer “offspring,” and newborn galaxies (white circles) matured into older ones more like our own Milky Way (spirals ...
... in our universe’s “birth-rate” over time. When the universe was young, massive galaxies were forming regularly, like baby bees in a bustling hive. In time, the universe bore fewer and fewer “offspring,” and newborn galaxies (white circles) matured into older ones more like our own Milky Way (spirals ...
OLEARY_2004_white
... In order to use the telescope to time the eclipse of NN Ser, I used live sessions on the telescope to capture images of NN Ser during an eclipse. The Faulkes Telescope is equipped with a CCD camera. This contains a piece of silicon which detects light through the photoelectric effect, which causes i ...
... In order to use the telescope to time the eclipse of NN Ser, I used live sessions on the telescope to capture images of NN Ser during an eclipse. The Faulkes Telescope is equipped with a CCD camera. This contains a piece of silicon which detects light through the photoelectric effect, which causes i ...
The Sky is Our Laboratory
... What percent of the total known Universe is our star (Sun)? Could there be anything faster than the speed of light? Are the laws of physics universal? Is it dark in space? Would a spaceship need headlights? What are the exact definitions of galaxy and cosmos? How are stars formed? Why do hottest sta ...
... What percent of the total known Universe is our star (Sun)? Could there be anything faster than the speed of light? Are the laws of physics universal? Is it dark in space? Would a spaceship need headlights? What are the exact definitions of galaxy and cosmos? How are stars formed? Why do hottest sta ...
imaging science in astronomy - RIT CIS
... phenomena in any given nebula, such objects demand a multiwavelength approach to imaging. A case in point is the young planetary nebula BD +30° 3639 (Fig. 10). This planetary nebula emits strongly at wavelengths ranging from radio through X ray. The Chandra X-ray image shows a region of X-ray emissi ...
... phenomena in any given nebula, such objects demand a multiwavelength approach to imaging. A case in point is the young planetary nebula BD +30° 3639 (Fig. 10). This planetary nebula emits strongly at wavelengths ranging from radio through X ray. The Chandra X-ray image shows a region of X-ray emissi ...
PRIMARY SOURCE from Starry Messenger
... reat indeed are the things which in this brief treatise I propose for observation and consideration by all students of nature. I say great, because of the excellence of the subject itself, the entirely unexpected and novel character of these things, and finally because of the instrument by means of w ...
... reat indeed are the things which in this brief treatise I propose for observation and consideration by all students of nature. I say great, because of the excellence of the subject itself, the entirely unexpected and novel character of these things, and finally because of the instrument by means of w ...
Exploring Space What’s Out There?
... celestial object that travels around a star • Orbit = the path that a celestial object takes around another object • Solar system = the sun and all the celestial objects that travel around it ...
... celestial object that travels around a star • Orbit = the path that a celestial object takes around another object • Solar system = the sun and all the celestial objects that travel around it ...
Cubs worksheet
... These planets are so far away from the Sun, that you’d have to go all the way into the Jodrell Bank Gardens to find them! (But don’t do this now!) 11. Are the planets in the Solar System spaced out evenly? ______________________________________________ The first four planets we came across were made ...
... These planets are so far away from the Sun, that you’d have to go all the way into the Jodrell Bank Gardens to find them! (But don’t do this now!) 11. Are the planets in the Solar System spaced out evenly? ______________________________________________ The first four planets we came across were made ...
Diffraction of Light - Flagstaff High School
... Opticks, that "Light is never known to follow crooked passages nor to bend into the shadow". This concept is consistent with the particle theory, which proposes that light particles must always travel in straight lines. ...
... Opticks, that "Light is never known to follow crooked passages nor to bend into the shadow". This concept is consistent with the particle theory, which proposes that light particles must always travel in straight lines. ...
Pressemitteilung - Micro
... technology - just as Galileo did 400 years ago, when he was the first to turn a telescope towards the sky. The telescope may help to answer some major scientific challenges of our time. Do other Earth-like planets exist that we could live and survive on? What are the characteristics of the first sta ...
... technology - just as Galileo did 400 years ago, when he was the first to turn a telescope towards the sky. The telescope may help to answer some major scientific challenges of our time. Do other Earth-like planets exist that we could live and survive on? What are the characteristics of the first sta ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
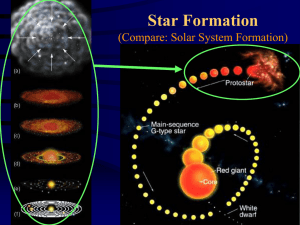
... • Main-sequence star; pressure from nuclear fusion and gravity are in balance – Duration ~ 10 billion years (much longer than all other stages combined) – Temperature ~ 15 million K at core, 6000 K at surface – Size ~ Sun ...
... • Main-sequence star; pressure from nuclear fusion and gravity are in balance – Duration ~ 10 billion years (much longer than all other stages combined) – Temperature ~ 15 million K at core, 6000 K at surface – Size ~ Sun ...
Long Ago and Far Away
... by Sheila Kannappan & Mary Kay Hemenway (The University of Texas at Austin) ...
... by Sheila Kannappan & Mary Kay Hemenway (The University of Texas at Austin) ...
Astronomy
... Two methods to detect planets are commonly used: the wobble method and the transit method. The wobble method is based on planets that are as massive as Jupiter. Massive planets pull on their stars, making them wobble like a large dog who walks its owner. You can often tell that a dog is walking it’s ...
... Two methods to detect planets are commonly used: the wobble method and the transit method. The wobble method is based on planets that are as massive as Jupiter. Massive planets pull on their stars, making them wobble like a large dog who walks its owner. You can often tell that a dog is walking it’s ...
Introduction to Telescopes
... astronomy by allowing scientists to get images of celestial objects too faint to be seen visually even with the biggest telescopes, so did the introduction of ‘charge-coupled devices’ (or CCDs) two decades ago. A CCD is a small electronic chip divided into a large number of little squares, so-called ...
... astronomy by allowing scientists to get images of celestial objects too faint to be seen visually even with the biggest telescopes, so did the introduction of ‘charge-coupled devices’ (or CCDs) two decades ago. A CCD is a small electronic chip divided into a large number of little squares, so-called ...
Progress of LiJET and Transit Search with Lijiang 2.4m Telescope
... To find systems with more than one giant planets ...
... To find systems with more than one giant planets ...
PHYS299B_Final_HudsonJustin
... a solar eclipse. The smaller dips in brightness is when the brighter star blocks out the light from the other star when passing in front of it. • From these curves, we can tell if stars follow the characteristics of an eclipsing binary or other types of variable stars. ...
... a solar eclipse. The smaller dips in brightness is when the brighter star blocks out the light from the other star when passing in front of it. • From these curves, we can tell if stars follow the characteristics of an eclipsing binary or other types of variable stars. ...
Space Test: Practice Questions and Answers 1. Who discovered
... A protostar is the first stage after a nebula. In a protostar hydrogen fusion has not yet started. 24. Describe the steady state theory? How was it different than the theory of the big bang? ...
... A protostar is the first stage after a nebula. In a protostar hydrogen fusion has not yet started. 24. Describe the steady state theory? How was it different than the theory of the big bang? ...
Jura et al. 2004 - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... template spectrum (Cohen et al 2003), and averaged the resulting spectra from corresponding nod positions. We plot the resulting spectra of our targets with IR excesses in Figure 1. Based upon comparisons of IRS spectra of non-variable calibration sources to ground-based, IRAS, and Spitzer IRAC flux ...
... template spectrum (Cohen et al 2003), and averaged the resulting spectra from corresponding nod positions. We plot the resulting spectra of our targets with IR excesses in Figure 1. Based upon comparisons of IRS spectra of non-variable calibration sources to ground-based, IRAS, and Spitzer IRAC flux ...
Planetary Nebula NGC 7027 Hubble Space Telescope
... image; the green and red, NICMOS exposures. The white is emission from the hot gas surrounding the central star; the red and pink represent emission from cool molecular hydrogen gas. I n effect, the colors represent the three layers in the material ejected by the dying star. Each layer depicts a cha ...
... image; the green and red, NICMOS exposures. The white is emission from the hot gas surrounding the central star; the red and pink represent emission from cool molecular hydrogen gas. I n effect, the colors represent the three layers in the material ejected by the dying star. Each layer depicts a cha ...
Homework 4
... 4. In figures 3.5 and 3.6 (pp. 74 and 75 in the text), the text shows what is called the “main sequence turnoff” for various open clusters (the text does not call it that, but astronomers use the term). How is the “main sequence turnoff” used to determine the age of an open cluster? ...
... 4. In figures 3.5 and 3.6 (pp. 74 and 75 in the text), the text shows what is called the “main sequence turnoff” for various open clusters (the text does not call it that, but astronomers use the term). How is the “main sequence turnoff” used to determine the age of an open cluster? ...
Spitzer Space Telescope

The Spitzer Space Telescope (SST), formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF), is an infrared space observatory launched in 2003. It is the fourth and final of the NASA Great Observatories program.The planned mission period was to be 2.5 years with a pre-launch expectation that the mission could extend to five or slightly more years until the onboard liquid helium supply was exhausted. This occurred on 15 May 2009. Without liquid helium to cool the telescope to the very low temperatures needed to operate, most of the instruments are no longer usable. However, the two shortest-wavelength modules of the IRAC camera are still operable with the same sensitivity as before the cryogen was exhausted, and will continue to be used in the Spitzer Warm Mission. All Spitzer data, from both the primary and warm phases, are archived at the Infrared Science Archive (IRSA).In keeping with NASA tradition, the telescope was renamed after its successful demonstration of operation, on 18 December 2003. Unlike most telescopes that are named after famous deceased astronomers by a board of scientists, the new name for SIRTF was obtained from a contest open to the general public.The contest led to the telescope being named in honor of astronomer Lyman Spitzer, who had promoted the concept of space telescopes in the 1940s. Spitzer wrote a 1946 report for RAND Corporation describing the advantages of an extraterrestrial observatory and how it could be realized with available or upcoming technology. He has been cited for his pioneering contributions to rocketry and astronomy, as well as ""his vision and leadership in articulating the advantages and benefits to be realized from the Space Telescope Program.""The US$800 million Spitzer was launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, on a Delta II 7920H ELV rocket, Monday, 25 August 2003 at 13:35:39 UTC-5 (EDT).It follows a heliocentric instead of geocentric orbit, trailing and drifting away from Earth's orbit at approximately 0.1 astronomical unit per year (a so-called ""earth-trailing"" orbit). The primary mirror is 85 centimeters (33 in) in diameter, f/12, made of beryllium and is cooled to 5.5 K (−449.77 °F). The satellite contains three instruments that allow it to perform astronomical imaging and photometry from 3 to 180 micrometers, spectroscopy from 5 to 40 micrometers, and spectrophotometry from 5 to 100 micrometers.