C:\FrontPage Webs\Content\phy150fall03\Lectures\Lecture 10 Solar
... one estimates the age of the Earth and the solar system to be 4.6 ± 1 billion years old. This can be compared to the estimated time for the gravitational accretion process to form the solar system of 100,000 years. 2) The temperature within the gaseous nebula surrounding the forming sun determined w ...
... one estimates the age of the Earth and the solar system to be 4.6 ± 1 billion years old. This can be compared to the estimated time for the gravitational accretion process to form the solar system of 100,000 years. 2) The temperature within the gaseous nebula surrounding the forming sun determined w ...
23-4 - Fremont Peak Observatory
... on the Pluto debate. My initial reaction was one of puzzlement, since Pluto has been a planet ever since I first picked up an astronomy book 52 years ago. However, as I found out about 15 years ago, Ceres was also designated as a planet for over 40 years before it was reclassified as an asteroid. Ba ...
... on the Pluto debate. My initial reaction was one of puzzlement, since Pluto has been a planet ever since I first picked up an astronomy book 52 years ago. However, as I found out about 15 years ago, Ceres was also designated as a planet for over 40 years before it was reclassified as an asteroid. Ba ...
Steve Holmes - KWFN October 22 2012 speaker
... For example, the nearest star (Proxima Centauri) is 4.24 light-years away, meaning that it is 42 trillion km away from us. Other stars are thousands of light-years distant, for example Eta Carinae at 7500. These huge distances help convey the vastness of deep space and the size of the universe. They ...
... For example, the nearest star (Proxima Centauri) is 4.24 light-years away, meaning that it is 42 trillion km away from us. Other stars are thousands of light-years distant, for example Eta Carinae at 7500. These huge distances help convey the vastness of deep space and the size of the universe. They ...
Friends of the Planetarium Newsletter September
... billion kilometers from Earth, in a record eight years and eight months. New Horizons' milestone matched precisely the 25th anniversary of the historic encounter of NASA's Voyager 2 spacecraft with Neptune on Aug. 25, 1989. "It's a cosmic coincidence that connects one of NASA's iconic past outer sol ...
... billion kilometers from Earth, in a record eight years and eight months. New Horizons' milestone matched precisely the 25th anniversary of the historic encounter of NASA's Voyager 2 spacecraft with Neptune on Aug. 25, 1989. "It's a cosmic coincidence that connects one of NASA's iconic past outer sol ...
pptx format
... NEITHER cold or hot! Objects in sunlight heat up, objects in shadow cool down) One important cooled infrared space telescope is called WISE. This telescope has observed infrared radiation from many 10,000s of asteroids ...
... NEITHER cold or hot! Objects in sunlight heat up, objects in shadow cool down) One important cooled infrared space telescope is called WISE. This telescope has observed infrared radiation from many 10,000s of asteroids ...
Light and Telescopes - Otterbein University
... What is the focal length of the eyepiece? What is its magnification? Try to focus on an object. Describe the image. Is it upside down? If the telescope is on a mount: • How many axes does the mount have? Does it have a motor? What for? • Do you know how the mount is called? ...
... What is the focal length of the eyepiece? What is its magnification? Try to focus on an object. Describe the image. Is it upside down? If the telescope is on a mount: • How many axes does the mount have? Does it have a motor? What for? • Do you know how the mount is called? ...
Earth and Space Science - science
... • Space exploration has generated valuable knowledge but at enormous cost ...
... • Space exploration has generated valuable knowledge but at enormous cost ...
Homework #4 Astronomy 101 – Fall 2010 Due November 4, 11 a.m.
... Astronomy 101 – Fall 2010 Due November 4, 11 a.m. 1. Page 126, #14 Why not Hubble? Of the more than 200 extrasolar planets discovered, only one likely planet has ever been imaged by the Hubble Space Telescope. What limit’s Hubble’s ability to image planets around other stars? There are two main fact ...
... Astronomy 101 – Fall 2010 Due November 4, 11 a.m. 1. Page 126, #14 Why not Hubble? Of the more than 200 extrasolar planets discovered, only one likely planet has ever been imaged by the Hubble Space Telescope. What limit’s Hubble’s ability to image planets around other stars? There are two main fact ...
Astronomy Unit Test – Chapter 21
... 25. Predict what will happen when the sun runs out of fuel. 26. What is used to classify stars? 27. At which phase of the moon could a solar eclipse occur? 28. A star is twice as massive as the sun. How will its lifespan compare with the sun? 29. Some astronomers discover a galaxy that contains only ...
... 25. Predict what will happen when the sun runs out of fuel. 26. What is used to classify stars? 27. At which phase of the moon could a solar eclipse occur? 28. A star is twice as massive as the sun. How will its lifespan compare with the sun? 29. Some astronomers discover a galaxy that contains only ...
Quick Reference - Objects in the skies
... The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy 100,000–120,000 light-years in diameter, containing 200–400 billion stars. It is the galaxy that contains the Earth. The Milky Way appears like a band in the sky, is because it is a disk-shaped structure being viewed from inside. Minor Planet: A minor planet i ...
... The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy 100,000–120,000 light-years in diameter, containing 200–400 billion stars. It is the galaxy that contains the Earth. The Milky Way appears like a band in the sky, is because it is a disk-shaped structure being viewed from inside. Minor Planet: A minor planet i ...
Student Worksheet - Indiana University Astronomy
... young stellar objects and planetary systems. Dust is formed in the stellar winds blowing from old, evolved stars, and is ejected into the interstellar medium. Passing supernova shocks and ultraviolet radiation affect the dust grains, which collect into dusty clouds where new stars can form. Cosmic d ...
... young stellar objects and planetary systems. Dust is formed in the stellar winds blowing from old, evolved stars, and is ejected into the interstellar medium. Passing supernova shocks and ultraviolet radiation affect the dust grains, which collect into dusty clouds where new stars can form. Cosmic d ...
Astronomy work sheet
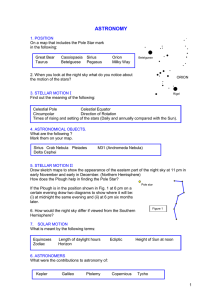
... Find out the distances of the planets of the Solar System from the Sun. How can you tell from the night sky which planets are closer to the Sun than the Earth? 11. ASTRONOMICAL TERMS What is meant by the following: Galaxy Magnitude Red Shift Black Hole ...
... Find out the distances of the planets of the Solar System from the Sun. How can you tell from the night sky which planets are closer to the Sun than the Earth? 11. ASTRONOMICAL TERMS What is meant by the following: Galaxy Magnitude Red Shift Black Hole ...
Diapositiva 1 - Yale University
... Another key reason for observing in the infrared is because life on Earth leaves its mark at these wavelengths. To see planets around nearby stars would require a telescope of roughly 30 metres in size and this is way beyond the current limits of technology. To overcome this limitation, Darwin wil ...
... Another key reason for observing in the infrared is because life on Earth leaves its mark at these wavelengths. To see planets around nearby stars would require a telescope of roughly 30 metres in size and this is way beyond the current limits of technology. To overcome this limitation, Darwin wil ...
ISM&Galaxy
... Blue light is scattered by dust more efficiently than red light, so dust seen in scattered light looks bluish. ...
... Blue light is scattered by dust more efficiently than red light, so dust seen in scattered light looks bluish. ...
Ultra High Precision X-ray Telescope Project - X
... Some Technical Consideration A normal incident telescope is easier than the grazing incident telescope. ...
... Some Technical Consideration A normal incident telescope is easier than the grazing incident telescope. ...
The Young Astronomers Newsletter Volume 22 Number 3 February
... There are 4 minor meteor showers in February with averages up to 3 per hour. The Centaurids are “southern hemisphere” showers with most of the observing reports, visual and radio, coming from Australia. From February 2nd through the 25th, the Alpha Centaurids and Beta Centaurids are only 8° apart wi ...
... There are 4 minor meteor showers in February with averages up to 3 per hour. The Centaurids are “southern hemisphere” showers with most of the observing reports, visual and radio, coming from Australia. From February 2nd through the 25th, the Alpha Centaurids and Beta Centaurids are only 8° apart wi ...
Ay 7A - Fall 2010 Section Worksheet 5 Telescopes
... 27 radio antennas on the Plains of San Agustin fifty miles west of Socorro, New Mexico. Each antenna is 25 meters (82 feet) in diameter. There are 4 array configurations : A array, with a maximum antenna separation of 36 km; B array – 10 km; C array – 3.6 km; and D array – 1 km. The VLA is an interf ...
... 27 radio antennas on the Plains of San Agustin fifty miles west of Socorro, New Mexico. Each antenna is 25 meters (82 feet) in diameter. There are 4 array configurations : A array, with a maximum antenna separation of 36 km; B array – 10 km; C array – 3.6 km; and D array – 1 km. The VLA is an interf ...
The MAS Winter Schedule February 21st: Membership Meeting at
... How hot? WASP-43b’s day side is hot enough of observing time on the Hubble Space Telescope to melt iron (2,700°F); the night side is much to obtain measurements of the planet over three “cooler”—at 900°F it would “only” melt lead. nearly consecutive orbits with Wide Field Camera Because heat is so p ...
... How hot? WASP-43b’s day side is hot enough of observing time on the Hubble Space Telescope to melt iron (2,700°F); the night side is much to obtain measurements of the planet over three “cooler”—at 900°F it would “only” melt lead. nearly consecutive orbits with Wide Field Camera Because heat is so p ...
An exceptional planetary system discovered in Cassiopeia by
... Under embargo until July the 30th (today), at 14:00 US EasterTime ...
... Under embargo until July the 30th (today), at 14:00 US EasterTime ...
Outline - March 16, 2010 Interstellar Medium (ISM) Why should you
... Center of a collapsing cloud becomes denser and hotter. The energy is gravitational. Half the gravitational energy goes into heating the collapsing clout, the other half escapes as light. The central object is called a “protostar”, and they are very bright! (Because they have very large radii.) ...
... Center of a collapsing cloud becomes denser and hotter. The energy is gravitational. Half the gravitational energy goes into heating the collapsing clout, the other half escapes as light. The central object is called a “protostar”, and they are very bright! (Because they have very large radii.) ...
astronomy timeline
... H.C. van de Hulst predicts 21 cm line of interstellar hydrogen. van de Hulst calculated that interstellar hydrogen atoms emit a spectral line at a wavelength of 21 cm in the radio part of the spectrum. He suggested that it would be possible to detect the 21 cm line using radio telescopes. p. 462463, ...
... H.C. van de Hulst predicts 21 cm line of interstellar hydrogen. van de Hulst calculated that interstellar hydrogen atoms emit a spectral line at a wavelength of 21 cm in the radio part of the spectrum. He suggested that it would be possible to detect the 21 cm line using radio telescopes. p. 462463, ...
Spitzer Space Telescope

The Spitzer Space Telescope (SST), formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF), is an infrared space observatory launched in 2003. It is the fourth and final of the NASA Great Observatories program.The planned mission period was to be 2.5 years with a pre-launch expectation that the mission could extend to five or slightly more years until the onboard liquid helium supply was exhausted. This occurred on 15 May 2009. Without liquid helium to cool the telescope to the very low temperatures needed to operate, most of the instruments are no longer usable. However, the two shortest-wavelength modules of the IRAC camera are still operable with the same sensitivity as before the cryogen was exhausted, and will continue to be used in the Spitzer Warm Mission. All Spitzer data, from both the primary and warm phases, are archived at the Infrared Science Archive (IRSA).In keeping with NASA tradition, the telescope was renamed after its successful demonstration of operation, on 18 December 2003. Unlike most telescopes that are named after famous deceased astronomers by a board of scientists, the new name for SIRTF was obtained from a contest open to the general public.The contest led to the telescope being named in honor of astronomer Lyman Spitzer, who had promoted the concept of space telescopes in the 1940s. Spitzer wrote a 1946 report for RAND Corporation describing the advantages of an extraterrestrial observatory and how it could be realized with available or upcoming technology. He has been cited for his pioneering contributions to rocketry and astronomy, as well as ""his vision and leadership in articulating the advantages and benefits to be realized from the Space Telescope Program.""The US$800 million Spitzer was launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, on a Delta II 7920H ELV rocket, Monday, 25 August 2003 at 13:35:39 UTC-5 (EDT).It follows a heliocentric instead of geocentric orbit, trailing and drifting away from Earth's orbit at approximately 0.1 astronomical unit per year (a so-called ""earth-trailing"" orbit). The primary mirror is 85 centimeters (33 in) in diameter, f/12, made of beryllium and is cooled to 5.5 K (−449.77 °F). The satellite contains three instruments that allow it to perform astronomical imaging and photometry from 3 to 180 micrometers, spectroscopy from 5 to 40 micrometers, and spectrophotometry from 5 to 100 micrometers.