powerpoint file
... Cosmology: The History of the Universe The Universe originated in an explosion called the “Big Bang”. Everything started out 13.7 billion years ago with “zero” size and “infinite” temperature. Since then, it has been expanding and cooling. Now its temperature is 2.735 K. While the temperature was s ...
... Cosmology: The History of the Universe The Universe originated in an explosion called the “Big Bang”. Everything started out 13.7 billion years ago with “zero” size and “infinite” temperature. Since then, it has been expanding and cooling. Now its temperature is 2.735 K. While the temperature was s ...
Cosmological solutions of the Einstein
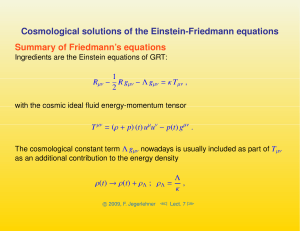
... That a non-vanishing Λ spoils the geometry ⇔ matter duality, because the Einstein equation remains true no matter on which side of the equation we write the cosmological term. Many believe it has some thing to do with quantum vacuum fluctuations, but no answer can be given why it is so small. In any ...
... That a non-vanishing Λ spoils the geometry ⇔ matter duality, because the Einstein equation remains true no matter on which side of the equation we write the cosmological term. Many believe it has some thing to do with quantum vacuum fluctuations, but no answer can be given why it is so small. In any ...
Cosmic Rays near Proxima Centauri b
... Sadovski 2017). Stellar cosmic rays (SCR) were considered in many papers (Tabataba-Vakili et al. 2016; Atri 2017; Struminsky & Sadovski 2017) as an important factor of space weather in a habitable zone of star. Since the details of SCR spectrum is unknown to model the effect of SCR one may use spect ...
... Sadovski 2017). Stellar cosmic rays (SCR) were considered in many papers (Tabataba-Vakili et al. 2016; Atri 2017; Struminsky & Sadovski 2017) as an important factor of space weather in a habitable zone of star. Since the details of SCR spectrum is unknown to model the effect of SCR one may use spect ...
Astrophysics Questions (DRAFT)
... type II supernovae. What are the observational di erences among these? 55. How much energy is typically released in a type II supernova? What fractions of that energy are in the form of neutrinos, visible light, gas kinetic energy, and gravitational radiation? ...
... type II supernovae. What are the observational di erences among these? 55. How much energy is typically released in a type II supernova? What fractions of that energy are in the form of neutrinos, visible light, gas kinetic energy, and gravitational radiation? ...
File
... containing a dense nucleus of many stars. Extended spherical halo of faint, old stars. Spiral Arms Spiral arms contain a large amount of gas and dust (15% of disk mass), with many hot, young stars (looking blue). New star formation in on-going. The spiral arms spin, as stars orbit around the galacti ...
... containing a dense nucleus of many stars. Extended spherical halo of faint, old stars. Spiral Arms Spiral arms contain a large amount of gas and dust (15% of disk mass), with many hot, young stars (looking blue). New star formation in on-going. The spiral arms spin, as stars orbit around the galacti ...
M. Sc. Atmospheric Space
... The final assessment for theory courses will be in the form of written examination for the whole course. As the courses are for smaller credits and if a particular course is completed well before the term ends then teacher concerned need not wait for the end of term examination to conduct the final ...
... The final assessment for theory courses will be in the form of written examination for the whole course. As the courses are for smaller credits and if a particular course is completed well before the term ends then teacher concerned need not wait for the end of term examination to conduct the final ...
Collisions that make waves in Space (MaxPlanckResearch 2002/1)
... galaxy such as the Milky Way, about two or three “heavy” stars explode every century. However, if as scientists hope, such events can be observed at distances as great as tens of millions of light years, then it should be possible to register several events of this sort every year. Merging neutron s ...
... galaxy such as the Milky Way, about two or three “heavy” stars explode every century. However, if as scientists hope, such events can be observed at distances as great as tens of millions of light years, then it should be possible to register several events of this sort every year. Merging neutron s ...
2.3 Peculiar galaxies
... a bright starlike nucleus, with strange properties which we will discuss below. This “activity” shows itself fairly obviously in about 1% of local galaxies, known as Seyfert galaxies after Karl Seyfert who first studied them in the 1940s. However, we now know that at a much lower level, something si ...
... a bright starlike nucleus, with strange properties which we will discuss below. This “activity” shows itself fairly obviously in about 1% of local galaxies, known as Seyfert galaxies after Karl Seyfert who first studied them in the 1940s. However, we now know that at a much lower level, something si ...
teach with space
... How can we find the barycentre of a system? For any system in space where two or more objects are orbiting each other, the system will have a centre of mass, or barycentre, about which all bodies orbit. The simple case: a two-body system For the simple case of a two-body system, the centre of mass o ...
... How can we find the barycentre of a system? For any system in space where two or more objects are orbiting each other, the system will have a centre of mass, or barycentre, about which all bodies orbit. The simple case: a two-body system For the simple case of a two-body system, the centre of mass o ...
CIS Curriculum Maps - Central School District 51
... Explore how shadows on Earth change with the Sun’s position. Describe the position of the Sun during summer and winter. Describe Earth’s rotation and what it causes. Describe Earth’s revolution and the cause of the seasons. Explain how the Sun is Earth’s energy source. Explore and explain the phases ...
... Explore how shadows on Earth change with the Sun’s position. Describe the position of the Sun during summer and winter. Describe Earth’s rotation and what it causes. Describe Earth’s revolution and the cause of the seasons. Explain how the Sun is Earth’s energy source. Explore and explain the phases ...
Galaxies
... • They often look like a star, due to their great distance (the rest of their galaxy structure can’t be seen). • Many quasars reveal more structure when viewed in radio wavelengths. ...
... • They often look like a star, due to their great distance (the rest of their galaxy structure can’t be seen). • Many quasars reveal more structure when viewed in radio wavelengths. ...
The Milky Way By
... exact figure depending on the number of very low-mass, or dwarf stars, which are hard to detect. Padurariu Cristian & Danciu Serban ...
... exact figure depending on the number of very low-mass, or dwarf stars, which are hard to detect. Padurariu Cristian & Danciu Serban ...
The escape of planetary atmospheres
... really close to their parent stars. For orbits less than about 3 million kilometers around a Sun-like star, hydrodynamic escape could remove the atmosphere of a Jupiter-like planet within a few billion years, leaving behind only a scorched remnant of its dense core. The direct observation of a plane ...
... really close to their parent stars. For orbits less than about 3 million kilometers around a Sun-like star, hydrodynamic escape could remove the atmosphere of a Jupiter-like planet within a few billion years, leaving behind only a scorched remnant of its dense core. The direct observation of a plane ...
The Milky Way and Its Neighbors
... 2)Mapping HII regions via Hα emission lines - HII regions trace active star formation Old data showed that there were 4 arms New data from Spitzer indicates that there are only 2 major spiral arms: -Scutum and Perseus Arms ...
... 2)Mapping HII regions via Hα emission lines - HII regions trace active star formation Old data showed that there were 4 arms New data from Spitzer indicates that there are only 2 major spiral arms: -Scutum and Perseus Arms ...
Earth in Space - Learning Outcomes
... The development of what we know about the Earth, Solar System and Universe is a fascinating study in its own right. From earliest times Man has wondered at and speculated over the ‘Nature of the Heavens’. It is hardly surprising that most people (until around 1500 A.D.) thought that the Sun revolved ...
... The development of what we know about the Earth, Solar System and Universe is a fascinating study in its own right. From earliest times Man has wondered at and speculated over the ‘Nature of the Heavens’. It is hardly surprising that most people (until around 1500 A.D.) thought that the Sun revolved ...
Cosmology with GMRT
... – Apply to a single object (optical results are averages over large redshift range) – Not subject to the same systematics – Currently probe a complementary redshift range ...
... – Apply to a single object (optical results are averages over large redshift range) – Not subject to the same systematics – Currently probe a complementary redshift range ...
Design and the Anthropic Principle
... claimed that 0.001 percent of all stars could have a planet upon which advanced life resides. 13 While their analysis was a step in the right direction, it overestimated the range of permissible star types and the range of permissible planetary distances. It also ignored many other significant facto ...
... claimed that 0.001 percent of all stars could have a planet upon which advanced life resides. 13 While their analysis was a step in the right direction, it overestimated the range of permissible star types and the range of permissible planetary distances. It also ignored many other significant facto ...
Characteristics of Our Galaxy
... lumps of matter, radiation, and gravitational forces. While 98% of matter is believed to be Dark in nature, 90% of which is believed to be composed of non-baryonic particles, the 2% of all matter in the Universe which we can directly detect, known as Baryonic Luminous Matter, exists almost entirely ...
... lumps of matter, radiation, and gravitational forces. While 98% of matter is believed to be Dark in nature, 90% of which is believed to be composed of non-baryonic particles, the 2% of all matter in the Universe which we can directly detect, known as Baryonic Luminous Matter, exists almost entirely ...
Gravity, General Relativity, and Dark Matter
... While many people learn about Newton and his theory of gravity, most do not realize that our best understanding of gravity actually comes from Einstein. During the first decade of the 1900s, Einstein began to compose his theory of general relativity and it completely changed the way we view gravity. ...
... While many people learn about Newton and his theory of gravity, most do not realize that our best understanding of gravity actually comes from Einstein. During the first decade of the 1900s, Einstein began to compose his theory of general relativity and it completely changed the way we view gravity. ...
CENTRAL TEXAS COLLEGE
... Stars and Galaxies is one of the two introductory Astronomy classes we teach here at Central Texas College. The other class is what we call Solar System. Astronomy was the first of the sciences, and when colleges and universities were established in the middle Ages, it was one of the seven subjects ...
... Stars and Galaxies is one of the two introductory Astronomy classes we teach here at Central Texas College. The other class is what we call Solar System. Astronomy was the first of the sciences, and when colleges and universities were established in the middle Ages, it was one of the seven subjects ...
Solar System Astronomy Notes
... Time Systems • The earth rotates around an axis through its north and south poles. This means that celestial objects seem to move across the sky with time. In fact, many of our basic time divisions (days, months, and years for example) are based on this apparent motion of celestial objects as seen f ...
... Time Systems • The earth rotates around an axis through its north and south poles. This means that celestial objects seem to move across the sky with time. In fact, many of our basic time divisions (days, months, and years for example) are based on this apparent motion of celestial objects as seen f ...
Understanding Precession of the Equinox
... would slowly change the seasons within the calendar. For example, in the Northern Hemisphere it would eventually become winter in July and August, and summer in January and February. This is because the seasons are indirectly caused by axial tilt (summer when that hemisphere leans closer to Earth, a ...
... would slowly change the seasons within the calendar. For example, in the Northern Hemisphere it would eventually become winter in July and August, and summer in January and February. This is because the seasons are indirectly caused by axial tilt (summer when that hemisphere leans closer to Earth, a ...
CHAPTER 4 THE SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION OF GALAXIES 4.13
... Having looked at the properties of individual galaxies – both normal and active – in some detail, it is now appropriate to consider how these galaxies are distributed in space. Surveys of the region outside our own Milky Way show that there are galaxies all around us. Deep field images such as those ...
... Having looked at the properties of individual galaxies – both normal and active – in some detail, it is now appropriate to consider how these galaxies are distributed in space. Surveys of the region outside our own Milky Way show that there are galaxies all around us. Deep field images such as those ...
Magnificent Cosmos - Academic Program Pages at Evergreen
... star’s blazing coronal gases—remains unclear. These effect of the starlight. As a star sways to and fro relative to findings are mysterious, given that the radius of Jupiter’s Earth, its light waves become cyclically stretched, then com- orbit is five times larger than that of Earth. These pressed—s ...
... star’s blazing coronal gases—remains unclear. These effect of the starlight. As a star sways to and fro relative to findings are mysterious, given that the radius of Jupiter’s Earth, its light waves become cyclically stretched, then com- orbit is five times larger than that of Earth. These pressed—s ...
Outer space
Outer space, or just space, is the void that exists between celestial bodies, including the Earth. It is not completely empty, but consists of a hard vacuum containing a low density of particles, predominantly a plasma of hydrogen and helium as well as electromagnetic radiation, magnetic fields, neutrinos, dust and cosmic rays. The baseline temperature, as set by the background radiation from the Big Bang, is 2.7 kelvin (K). Plasma with a number density of less than one hydrogen atom per cubic metre and a temperature of millions of kelvin in the space between galaxies accounts for most of the baryonic (ordinary) matter in outer space; local concentrations have condensed into stars and galaxies. In most galaxies, observations provide evidence that 90% of the mass is in an unknown form, called dark matter, which interacts with other matter through gravitational but not electromagnetic forces. Data indicates that the majority of the mass-energy in the observable Universe is a poorly understood vacuum energy of space which astronomers label dark energy. Intergalactic space takes up most of the volume of the Universe, but even galaxies and star systems consist almost entirely of empty space.There is no firm boundary where space begins. However the Kármán line, at an altitude of 100 km (62 mi) above sea level, is conventionally used as the start of outer space in space treaties and for aerospace records keeping. The framework for international space law was established by the Outer Space Treaty, which was passed by the United Nations in 1967. This treaty precludes any claims of national sovereignty and permits all states to freely explore outer space. Despite the drafting of UN resolutions for the peaceful uses of outer space, anti-satellite weapons have been tested in Earth orbit.Humans began the physical exploration of space during the 20th century with the advent of high-altitude balloon flights, followed by manned rocket launches. Earth orbit was first achieved by Yuri Gagarin of the Soviet Union in 1961 and unmanned spacecraft have since reached all of the known planets in the Solar System. Due to the high cost of getting into space, manned spaceflight has been limited to low Earth orbit and the Moon.Outer space represents a challenging environment for human exploration because of the dual hazards of vacuum and radiation. Microgravity also has a negative effect on human physiology that causes both muscle atrophy and bone loss. In addition to these health and environmental issues, the economic cost of putting objects, including humans, into space is high.