Spectra of Cosmic Ray Protons and Helium Produced in Supernova
... cosmic ray halo boundaries into intergalactic space, where cosmic ray density is negligible. We employ the plain diffusion model with a flat cosmic ray halo (Ginzburg & Ptuskin 1976; Strong et al. 2007) for calculations of cosmic ray propagation in the Galaxy. The leaky-box approximation to the diff ...
... cosmic ray halo boundaries into intergalactic space, where cosmic ray density is negligible. We employ the plain diffusion model with a flat cosmic ray halo (Ginzburg & Ptuskin 1976; Strong et al. 2007) for calculations of cosmic ray propagation in the Galaxy. The leaky-box approximation to the diff ...
Galaxies - Stockton University
... – Black-holes are also efficient although less so than neutron stars • This is because black-holes have no surface so much of the energy is never released but is swallowed up by the black-hole directly and also orbits are unstable within three times the Schwarschild radius and little energy is retur ...
... – Black-holes are also efficient although less so than neutron stars • This is because black-holes have no surface so much of the energy is never released but is swallowed up by the black-hole directly and also orbits are unstable within three times the Schwarschild radius and little energy is retur ...
Lesson Plan - ScienceA2Z.com
... The bulge of the Milky Way is more spherical than the disk and is composed of stars which are more reddish than those in the disk. The bulge its self is around 20,000 x 13,000 light years in size and holds up to 1,600 stars per cubic light year (ly x ly). The Galactic Center is the rotational center ...
... The bulge of the Milky Way is more spherical than the disk and is composed of stars which are more reddish than those in the disk. The bulge its self is around 20,000 x 13,000 light years in size and holds up to 1,600 stars per cubic light year (ly x ly). The Galactic Center is the rotational center ...
POISE AND EVOLUTION OF THE GALAXY : STRUCTURE ,
... specialists themselves, even the high galactic field values considered, ~ 10-10 Tesla, would still be insufficient to stabilise such a long lasting confinement, at least for the highest energies of cosmic rays (above ~ 1019 eV) [3] ! Moreover, such an order of ~ 10-10 Tesla for the magnetic field sh ...
... specialists themselves, even the high galactic field values considered, ~ 10-10 Tesla, would still be insufficient to stabilise such a long lasting confinement, at least for the highest energies of cosmic rays (above ~ 1019 eV) [3] ! Moreover, such an order of ~ 10-10 Tesla for the magnetic field sh ...
The Digital Carousel
... "Astrobiology is the science of the consideration of life in the universe, with the goal of trying to understand where else there might be life or how widely distributed life might be...Our data is the history of life on Earth and the requirements of life on Earth and what we know about the environm ...
... "Astrobiology is the science of the consideration of life in the universe, with the goal of trying to understand where else there might be life or how widely distributed life might be...Our data is the history of life on Earth and the requirements of life on Earth and what we know about the environm ...
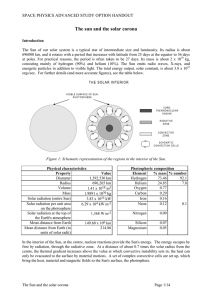
The sun and the solar corona
... key parameters: density, temperature and pressure with radius can be deduced. But unless we find a way to “see” inside the Sun, to verify the calculations, we cannot be certain that the model deduced with its many assumptions is anywhere near correct. Fortunately, a very powerful way has been found. ...
... key parameters: density, temperature and pressure with radius can be deduced. But unless we find a way to “see” inside the Sun, to verify the calculations, we cannot be certain that the model deduced with its many assumptions is anywhere near correct. Fortunately, a very powerful way has been found. ...
Facilitator`s Guide PDF
... 1. Describe and explain how astronomers use luminosity and redshift to measure the distance and speed of celestial objects. 2. Describe, using pictures, graphs and/or words, what astronomers mean by an expanding universe. Describe several different ways that the expansion could change over time (e.g ...
... 1. Describe and explain how astronomers use luminosity and redshift to measure the distance and speed of celestial objects. 2. Describe, using pictures, graphs and/or words, what astronomers mean by an expanding universe. Describe several different ways that the expansion could change over time (e.g ...
The kinematics of Galaxies in Compact Groups
... agreement does not tell us much about the DM (outer halo). ...
... agreement does not tell us much about the DM (outer halo). ...
Standard Four: Earth in Space
... 2. As a force, gravity causes tides, pulls matter together to make spherical stars and planets, maintains the orbits of planets, and gathers cosmic gas and dust to form stars and star systems. 3. Stars are separated by vast distances. Light which reaches Earth from distant galaxies is millions of ye ...
... 2. As a force, gravity causes tides, pulls matter together to make spherical stars and planets, maintains the orbits of planets, and gathers cosmic gas and dust to form stars and star systems. 3. Stars are separated by vast distances. Light which reaches Earth from distant galaxies is millions of ye ...
Scientific Evidence for A
... the seventh day God completed His work which He had done; and He rested on the seventh day from all His work which He had done. Then God blessed the seventh day and sanctified it, because in it He rested from all His work which God had created and made. This is the account of the heavens and the ear ...
... the seventh day God completed His work which He had done; and He rested on the seventh day from all His work which He had done. Then God blessed the seventh day and sanctified it, because in it He rested from all His work which God had created and made. This is the account of the heavens and the ear ...
NASA-TV Highlights
... What is the oldest thing you've ever seen? The Earth, Sun, Moon, and planets are 4.6 billion years old. The age record for people who occasionally glance at the sky might be Arcturus, about 7 billion years old. But with a pair of binoculars, you can pick up the 7.2-magnitude star HD 140283 in Libra, ...
... What is the oldest thing you've ever seen? The Earth, Sun, Moon, and planets are 4.6 billion years old. The age record for people who occasionally glance at the sky might be Arcturus, about 7 billion years old. But with a pair of binoculars, you can pick up the 7.2-magnitude star HD 140283 in Libra, ...
TF_final3 - Arecibo Observatory
... approximately 100 new stars per year. LIRGs are effect, the frequency scale of the spectrum was converted into velocity scale. The velocity width of the result of mix or collisions of galaxies. the line is related to the rotational speed of the HI Line : Neutral hydrogen in galaxies emit a line gala ...
... approximately 100 new stars per year. LIRGs are effect, the frequency scale of the spectrum was converted into velocity scale. The velocity width of the result of mix or collisions of galaxies. the line is related to the rotational speed of the HI Line : Neutral hydrogen in galaxies emit a line gala ...
The Galactic Environment of the Sun
... a fascinating area of research. Here we describe what space scientists and astrophysicists have learned about the sun’s galactic environment and its interaction with the solar system. The Solar Neighborhood We tend to think of our neighborhood in the Milky Way galaxy as motionless: Various nebulae a ...
... a fascinating area of research. Here we describe what space scientists and astrophysicists have learned about the sun’s galactic environment and its interaction with the solar system. The Solar Neighborhood We tend to think of our neighborhood in the Milky Way galaxy as motionless: Various nebulae a ...
Earth in Space Conceptest
... of several distant objects that were similar size or larger than Pluto • International Astronomical Union (IAU) could either 1. Consider the new objects as new planets OR 2. Classify the new objects – and Pluto – as a new group of objects ...
... of several distant objects that were similar size or larger than Pluto • International Astronomical Union (IAU) could either 1. Consider the new objects as new planets OR 2. Classify the new objects – and Pluto – as a new group of objects ...
OUTLINE
... Alpha Monitor (EPAM): particle intensity at five different energy levels. This data is used to detect the onset of an event, several days in advance, and to predict the ESP event / IP shock arrival. ...
... Alpha Monitor (EPAM): particle intensity at five different energy levels. This data is used to detect the onset of an event, several days in advance, and to predict the ESP event / IP shock arrival. ...
Lecture 12: Galaxies View of the Galaxy from within Comparison to
... dust and gas strongly concentrated in the disk plane. • The Sun orbits around the Galactic centre at a speed of about 220 km s-1. • It takes about 220 million years to complete one orbit ...
... dust and gas strongly concentrated in the disk plane. • The Sun orbits around the Galactic centre at a speed of about 220 km s-1. • It takes about 220 million years to complete one orbit ...
Interstellar Space Not as Empty as you Might Think
... • The more interstellar gas along the sight line, the more reddening occurs • Distant stars appear redder than nearby ones • Astronomers have to correct (de-redden) a stellar spectrum to account for this and to derive the star’s true color. ...
... • The more interstellar gas along the sight line, the more reddening occurs • Distant stars appear redder than nearby ones • Astronomers have to correct (de-redden) a stellar spectrum to account for this and to derive the star’s true color. ...
The Odin satellite`s sharp eyes in space
... chain of events that brings about life has to start with the formation of a sun – a star. This is one of many good reasons why Odin’s astronomers want to find out how stars are formed. Odin is an important tool for astronomers who study how stars come into being. The satellite’s sensitive instrument ...
... chain of events that brings about life has to start with the formation of a sun – a star. This is one of many good reasons why Odin’s astronomers want to find out how stars are formed. Odin is an important tool for astronomers who study how stars come into being. The satellite’s sensitive instrument ...
**** 1 - Asiaa
... constant with time, we can adopt the Local bulgeblack hole mass relation to high-z Universe. 2. At z > 10, quasar density is expected to decrease significantly, and GRBs are good candidate radio ...
... constant with time, we can adopt the Local bulgeblack hole mass relation to high-z Universe. 2. At z > 10, quasar density is expected to decrease significantly, and GRBs are good candidate radio ...
Our Place in Space
... This activity consists of a series of 15 cards that include images of astronomical objects on the front and information about these objects on the reverse. The card backs include information on the location of the object, its size, and its distance from Earth. Teachers should print out the card ...
... This activity consists of a series of 15 cards that include images of astronomical objects on the front and information about these objects on the reverse. The card backs include information on the location of the object, its size, and its distance from Earth. Teachers should print out the card ...
Science and a Christian World View A Christian View
... and these are all moving away from us are we at the center of the universe (a very special place)? A fundamental assumption in the study of cosmology is that we are not located in a unique region within the universe – this is the “Copernican Principle”. In addition, we assume that the universe at th ...
... and these are all moving away from us are we at the center of the universe (a very special place)? A fundamental assumption in the study of cosmology is that we are not located in a unique region within the universe – this is the “Copernican Principle”. In addition, we assume that the universe at th ...
The Big Bang Theory
... Weak and Strong forces) were indistinguishable (unified field theory). As the universe began to expand and cool, the symmetry is broken and triggered a sudden inflation in the size of universe! Inflation of the universe solves the flatness problem. Take a balloon as example. If the balloon expands i ...
... Weak and Strong forces) were indistinguishable (unified field theory). As the universe began to expand and cool, the symmetry is broken and triggered a sudden inflation in the size of universe! Inflation of the universe solves the flatness problem. Take a balloon as example. If the balloon expands i ...
Outer space
Outer space, or just space, is the void that exists between celestial bodies, including the Earth. It is not completely empty, but consists of a hard vacuum containing a low density of particles, predominantly a plasma of hydrogen and helium as well as electromagnetic radiation, magnetic fields, neutrinos, dust and cosmic rays. The baseline temperature, as set by the background radiation from the Big Bang, is 2.7 kelvin (K). Plasma with a number density of less than one hydrogen atom per cubic metre and a temperature of millions of kelvin in the space between galaxies accounts for most of the baryonic (ordinary) matter in outer space; local concentrations have condensed into stars and galaxies. In most galaxies, observations provide evidence that 90% of the mass is in an unknown form, called dark matter, which interacts with other matter through gravitational but not electromagnetic forces. Data indicates that the majority of the mass-energy in the observable Universe is a poorly understood vacuum energy of space which astronomers label dark energy. Intergalactic space takes up most of the volume of the Universe, but even galaxies and star systems consist almost entirely of empty space.There is no firm boundary where space begins. However the Kármán line, at an altitude of 100 km (62 mi) above sea level, is conventionally used as the start of outer space in space treaties and for aerospace records keeping. The framework for international space law was established by the Outer Space Treaty, which was passed by the United Nations in 1967. This treaty precludes any claims of national sovereignty and permits all states to freely explore outer space. Despite the drafting of UN resolutions for the peaceful uses of outer space, anti-satellite weapons have been tested in Earth orbit.Humans began the physical exploration of space during the 20th century with the advent of high-altitude balloon flights, followed by manned rocket launches. Earth orbit was first achieved by Yuri Gagarin of the Soviet Union in 1961 and unmanned spacecraft have since reached all of the known planets in the Solar System. Due to the high cost of getting into space, manned spaceflight has been limited to low Earth orbit and the Moon.Outer space represents a challenging environment for human exploration because of the dual hazards of vacuum and radiation. Microgravity also has a negative effect on human physiology that causes both muscle atrophy and bone loss. In addition to these health and environmental issues, the economic cost of putting objects, including humans, into space is high.