Nova Scotia Grade One Earth and Space Science: Daily and
... Provide changes in the location, shape and relative size of a shadow when an object is placed in different positions and orientations relative to the light source. Grade Five Earth and Space Science: Weather Relate the transfer of energy from the sun to weather conditions. Grade 6 Space Exploration ...
... Provide changes in the location, shape and relative size of a shadow when an object is placed in different positions and orientations relative to the light source. Grade Five Earth and Space Science: Weather Relate the transfer of energy from the sun to weather conditions. Grade 6 Space Exploration ...
Intro to Earth science
... • Earth is the 3rd planet from the Sun in our SOLAR SYSTEM • Approximately 100 billion stars in our galaxy ...
... • Earth is the 3rd planet from the Sun in our SOLAR SYSTEM • Approximately 100 billion stars in our galaxy ...
From Rubber Bands to Big Bangs
... 1) Make one cut in you rubber band so that it makes a flat piece. 2) Draw a wave pattern from one end to the other end. 3) Place 4 stars randomly on the rubber band. Number each star starting with number one. 4) Now stretch the rubber band and describe: a) what happens to the distance between the st ...
... 1) Make one cut in you rubber band so that it makes a flat piece. 2) Draw a wave pattern from one end to the other end. 3) Place 4 stars randomly on the rubber band. Number each star starting with number one. 4) Now stretch the rubber band and describe: a) what happens to the distance between the st ...
From Rubber Bands to Big Bangs The Universe has been
... 1) Make one cut in you rubber band so that it makes a flat piece. 2) Draw a wave pattern from one end to the other end. 3) Place 4 stars randomly on the rubber band. Number each star starting with number one. 4) Now stretch the rubber band and describe: a) what happens to the distance between the st ...
... 1) Make one cut in you rubber band so that it makes a flat piece. 2) Draw a wave pattern from one end to the other end. 3) Place 4 stars randomly on the rubber band. Number each star starting with number one. 4) Now stretch the rubber band and describe: a) what happens to the distance between the st ...
Class 28, 27 July
... Helium in the universe was formed in the first 3 minutes after the Big Bang) – Nuclei, electrons, and photons in big “soup” • Nuclei try to collapse (gravity), photons push back (pressure) • This leads to OSCILLATIONS! • Size of oscillations measures geometry of universe (know physical size, angle, ...
... Helium in the universe was formed in the first 3 minutes after the Big Bang) – Nuclei, electrons, and photons in big “soup” • Nuclei try to collapse (gravity), photons push back (pressure) • This leads to OSCILLATIONS! • Size of oscillations measures geometry of universe (know physical size, angle, ...
Unit 1
... • a. The balance of gravity inward and gas pressure outward. • b. The balance of gas pressure inward and heat outward. • c. the balance of gas pressure outward and magnetic forces inward. • d. the creation of one helium nucleus for the "destruction" of every four helium nuclei. ...
... • a. The balance of gravity inward and gas pressure outward. • b. The balance of gas pressure inward and heat outward. • c. the balance of gas pressure outward and magnetic forces inward. • d. the creation of one helium nucleus for the "destruction" of every four helium nuclei. ...
CoRoT: a space project to listen to the songs of the stars
... launched from a Soyuz 2-1B, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. This European space mission is expected to be at work for 3 years. ...
... launched from a Soyuz 2-1B, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. This European space mission is expected to be at work for 3 years. ...
Semester #1 – GeoScience Review Guide – Final Exam Scale
... 1. What is a light-year? How big is it in kilometers? 2. In your scale model of the Solar System, the scale was 1 cm = 10,000,000,000 km. Jupiter is 778,000,000 km from the sun. On your scale model, how many cm was Jupiter from the sun? 3. Is this a true or false statement? 104 = 10 x 10 x 10 x 10 4 ...
... 1. What is a light-year? How big is it in kilometers? 2. In your scale model of the Solar System, the scale was 1 cm = 10,000,000,000 km. Jupiter is 778,000,000 km from the sun. On your scale model, how many cm was Jupiter from the sun? 3. Is this a true or false statement? 104 = 10 x 10 x 10 x 10 4 ...
Then another Big Bang will occur and the
... As objects move away from the Earth they emit a Red Light called the Red Shift. This was seen using the Hubble Telescope. ...
... As objects move away from the Earth they emit a Red Light called the Red Shift. This was seen using the Hubble Telescope. ...
Chapter 2: The Solar System
... geocentric system? • A geocentric system is one in which Earth is at the center of a system of revolving planets. ...
... geocentric system? • A geocentric system is one in which Earth is at the center of a system of revolving planets. ...
File
... offset from the center. The idea that the Sun was the center of the solar system was not new (similar theories had been proposed by Aristarchus and Nicholas of Cusa), but Copernicus also worked out his system in full mathematical detail. Even though the mathematics in his description was not any sim ...
... offset from the center. The idea that the Sun was the center of the solar system was not new (similar theories had been proposed by Aristarchus and Nicholas of Cusa), but Copernicus also worked out his system in full mathematical detail. Even though the mathematics in his description was not any sim ...
Canadian Contributions
... 3.Exploring space is expensive as Canada spends $300,000,000 per year on space exploration. ...
... 3.Exploring space is expensive as Canada spends $300,000,000 per year on space exploration. ...
Astronomy MCAS Questions Multiple Choice 1.) The diagram below
... a. Name two types of eclipses that involve the Sun, the Moon, and Earth. b. Identify the phase of the Moon during each type of eclipse you named in part (a). c. Choose one of the types of eclipses that you named in part (a) and describe (or draw a diagram that shows) the relative positions of the Su ...
... a. Name two types of eclipses that involve the Sun, the Moon, and Earth. b. Identify the phase of the Moon during each type of eclipse you named in part (a). c. Choose one of the types of eclipses that you named in part (a) and describe (or draw a diagram that shows) the relative positions of the Su ...
Section 26.1 - CPO Science
... The solar system is roughly divided into the inner planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars) and the outer planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune) The dwarf planet Pluto is the oldest known member of a smaller group of frozen worlds ...
... The solar system is roughly divided into the inner planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars) and the outer planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune) The dwarf planet Pluto is the oldest known member of a smaller group of frozen worlds ...
The Evolution of the Solar System
... that were formed. Inside the Milky Way, we have many stars, solar systems, and other types of space matter being created. ...
... that were formed. Inside the Milky Way, we have many stars, solar systems, and other types of space matter being created. ...
Standard
... Solar System bodies, tracking moon and planets Use of internet resources and star charts to identify man-made satellites and their orbits “Hubble Space Telescope” video and/or PowerPoint presentations of Hubble findings ...
... Solar System bodies, tracking moon and planets Use of internet resources and star charts to identify man-made satellites and their orbits “Hubble Space Telescope” video and/or PowerPoint presentations of Hubble findings ...
Astronomy review - Petal School District
... (no man has ever been farther than the moon) One way: space telescopes! the Hubble Space Telescope (looks at distant galaxies & at planets in our solar system) ...
... (no man has ever been farther than the moon) One way: space telescopes! the Hubble Space Telescope (looks at distant galaxies & at planets in our solar system) ...
Solar system
... because of its large size. It was estimated to be 25 miles long in diameter. People think that it was the most viewed comet in history because of its huge size and brightness. ...
... because of its large size. It was estimated to be 25 miles long in diameter. People think that it was the most viewed comet in history because of its huge size and brightness. ...
Bill Nye – Outer Space Worksheet
... c. 540 million kilometers 14. It will take light at least forty years to reach the nearest star. b. False ...
... c. 540 million kilometers 14. It will take light at least forty years to reach the nearest star. b. False ...
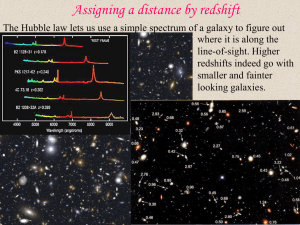
Redshift takes us from 2-D to 3-D
... 2) The Universe is observed to be expanding (so in the past it was smaller). The Steady State Universe tried to get around this by supposing that new galaxies appear out of nowhere to fill the increasing volume (no more unreasonable than supposing that the Universe appeared). But then the past shoul ...
... 2) The Universe is observed to be expanding (so in the past it was smaller). The Steady State Universe tried to get around this by supposing that new galaxies appear out of nowhere to fill the increasing volume (no more unreasonable than supposing that the Universe appeared). But then the past shoul ...
Outer space
Outer space, or just space, is the void that exists between celestial bodies, including the Earth. It is not completely empty, but consists of a hard vacuum containing a low density of particles, predominantly a plasma of hydrogen and helium as well as electromagnetic radiation, magnetic fields, neutrinos, dust and cosmic rays. The baseline temperature, as set by the background radiation from the Big Bang, is 2.7 kelvin (K). Plasma with a number density of less than one hydrogen atom per cubic metre and a temperature of millions of kelvin in the space between galaxies accounts for most of the baryonic (ordinary) matter in outer space; local concentrations have condensed into stars and galaxies. In most galaxies, observations provide evidence that 90% of the mass is in an unknown form, called dark matter, which interacts with other matter through gravitational but not electromagnetic forces. Data indicates that the majority of the mass-energy in the observable Universe is a poorly understood vacuum energy of space which astronomers label dark energy. Intergalactic space takes up most of the volume of the Universe, but even galaxies and star systems consist almost entirely of empty space.There is no firm boundary where space begins. However the Kármán line, at an altitude of 100 km (62 mi) above sea level, is conventionally used as the start of outer space in space treaties and for aerospace records keeping. The framework for international space law was established by the Outer Space Treaty, which was passed by the United Nations in 1967. This treaty precludes any claims of national sovereignty and permits all states to freely explore outer space. Despite the drafting of UN resolutions for the peaceful uses of outer space, anti-satellite weapons have been tested in Earth orbit.Humans began the physical exploration of space during the 20th century with the advent of high-altitude balloon flights, followed by manned rocket launches. Earth orbit was first achieved by Yuri Gagarin of the Soviet Union in 1961 and unmanned spacecraft have since reached all of the known planets in the Solar System. Due to the high cost of getting into space, manned spaceflight has been limited to low Earth orbit and the Moon.Outer space represents a challenging environment for human exploration because of the dual hazards of vacuum and radiation. Microgravity also has a negative effect on human physiology that causes both muscle atrophy and bone loss. In addition to these health and environmental issues, the economic cost of putting objects, including humans, into space is high.