Science 9 Unit 5: Space Name:
... A galaxy is a grouping of millions or billions of stars, gas and dust. It is held together by gravity. The Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy our solar system is a part of. It is a spiral galaxy, shaped like a flattened pinwheel, with arms spiraling out from the center. ...
... A galaxy is a grouping of millions or billions of stars, gas and dust. It is held together by gravity. The Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy our solar system is a part of. It is a spiral galaxy, shaped like a flattened pinwheel, with arms spiraling out from the center. ...
Unit 3 *The Solar System* 6th Grade Space Science
... System by characteristics, such as: shape, and appearance, what they orbit, how large they are, and how far away their orbits are from the Sun. ...
... System by characteristics, such as: shape, and appearance, what they orbit, how large they are, and how far away their orbits are from the Sun. ...
Name: ________________________ Date: Chapter 13: Earth
... solar system p. 492 constellation p. 493 moon p. 482 universe p. 498 crater p. 482 galaxy p. 498 1. The path that Earth takes as it moves around the sun is its _____________________________. 2. The sun is the center of our _________________________. 3. Everything that exists, including planets, star ...
... solar system p. 492 constellation p. 493 moon p. 482 universe p. 498 crater p. 482 galaxy p. 498 1. The path that Earth takes as it moves around the sun is its _____________________________. 2. The sun is the center of our _________________________. 3. Everything that exists, including planets, star ...
Geology Outline (and other key issues)
... Windows to the Universe, a project of the National Earth Science Teachers Association, is sponsored in part is sponsored in part through grants from federal agencies (NASA and NOAA), and partnerships with affiliated organizations, including the American Geophysical Union, the Howard Hughes Medical I ...
... Windows to the Universe, a project of the National Earth Science Teachers Association, is sponsored in part is sponsored in part through grants from federal agencies (NASA and NOAA), and partnerships with affiliated organizations, including the American Geophysical Union, the Howard Hughes Medical I ...
3OriginoftheUniverseandSS
... Inflationary Theory - predicts that there was a sudden expansion when the universe was very young, more extreme than predicted by the big bang theory! • Considered to be a “revised” Big Bang theory • The universe expanded and cooled until about 10-35 second after the big bang when it became so cool ...
... Inflationary Theory - predicts that there was a sudden expansion when the universe was very young, more extreme than predicted by the big bang theory! • Considered to be a “revised” Big Bang theory • The universe expanded and cooled until about 10-35 second after the big bang when it became so cool ...
space - jennseymour
... When the Universe formed, the chaos divided itself into a set order that had large masses break into smaller masses. Universe was broken into galaxies which they were then broken into solar systems, which had their own star at the center of those systems, which were then surrounded by a few sma ...
... When the Universe formed, the chaos divided itself into a set order that had large masses break into smaller masses. Universe was broken into galaxies which they were then broken into solar systems, which had their own star at the center of those systems, which were then surrounded by a few sma ...
Space - WG Murdoch School
... unconscious within 15 seconds because there is no oxygen. your blood and body fluids would "boil" and then freeze because there is little or no air pressure. your tissues (skin, heart, other internal organs) would expand because of the boiling fluids. ...
... unconscious within 15 seconds because there is no oxygen. your blood and body fluids would "boil" and then freeze because there is little or no air pressure. your tissues (skin, heart, other internal organs) would expand because of the boiling fluids. ...
Ch. 1 Guided Notes P2
... • Regions get unity from __________________ Combination of _____________/cultural features and _____________ elements Modern term = ______________ Studies • Each region = a ___________________ landscape • _______________ = the most important agents of change to Earth’s surface • Social, economic, a ...
... • Regions get unity from __________________ Combination of _____________/cultural features and _____________ elements Modern term = ______________ Studies • Each region = a ___________________ landscape • _______________ = the most important agents of change to Earth’s surface • Social, economic, a ...
370KB - NZQA
... Check that the National Student Number (NSN) on your admission slip is the same as the number at the top of this page. You should attempt ALL the questions in this booklet. If you need more room for any answer, use the extra space provided at the back of this booklet and clearly number the question. ...
... Check that the National Student Number (NSN) on your admission slip is the same as the number at the top of this page. You should attempt ALL the questions in this booklet. If you need more room for any answer, use the extra space provided at the back of this booklet and clearly number the question. ...
AGN-Hubble
... The Hubble Constant and the Age of the Universe If you plot the scale of the Universe vs time, the Hubble constant is the slope of the line now. If it’s really constant, then the age of the Universe is just 1/H [since H=v/D=(d/t)/d]. That’s because if you know how fast we are expanding, you can run ...
... The Hubble Constant and the Age of the Universe If you plot the scale of the Universe vs time, the Hubble constant is the slope of the line now. If it’s really constant, then the age of the Universe is just 1/H [since H=v/D=(d/t)/d]. That’s because if you know how fast we are expanding, you can run ...
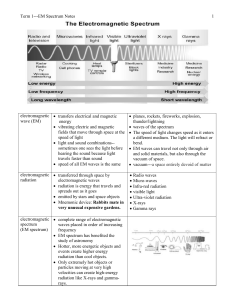
EM Spectrum notes - Biloxi Public Schools
... Some have been used to monitor radio signals given off by earthquakes To map sources and analyze their composition Stars and other "hot" objects in space emit UV radiation (determines the hottest stars in our galaxy) To study planets around other stars in space, IR light maps the dust between star ...
... Some have been used to monitor radio signals given off by earthquakes To map sources and analyze their composition Stars and other "hot" objects in space emit UV radiation (determines the hottest stars in our galaxy) To study planets around other stars in space, IR light maps the dust between star ...
Chapter 19 The Solar System
... Science 9—Will it ever end? 4th quarter—EARTH SCIENCE Outer space—our solar system and all of its contents (stars, planets, and their satellites) Where did the universe come from? Layers of the Earth (Plate Tectonics) The Earth as a System (atmosphere, biosphere, lithosphere, & hydrosphere) Innovat ...
... Science 9—Will it ever end? 4th quarter—EARTH SCIENCE Outer space—our solar system and all of its contents (stars, planets, and their satellites) Where did the universe come from? Layers of the Earth (Plate Tectonics) The Earth as a System (atmosphere, biosphere, lithosphere, & hydrosphere) Innovat ...
microwaves - TeacherWeb
... with them because they exist at low temperatures in space • very little enters our atmosphere so use telescopes at high altitudes or in space to monitor this type of radiation • might be useful for high altitude communications • future use to transfer data 1000 faster than with microwaves! ...
... with them because they exist at low temperatures in space • very little enters our atmosphere so use telescopes at high altitudes or in space to monitor this type of radiation • might be useful for high altitude communications • future use to transfer data 1000 faster than with microwaves! ...
File
... momentum, the Sun would pull Earth into itself. If an object does not have enough orbital speed or momentum to resist the pull of gravity, then it will be pulled into the surface of the larger object. That is why meteorites crash into the surface of moons and planets. That is also why the Moon does ...
... momentum, the Sun would pull Earth into itself. If an object does not have enough orbital speed or momentum to resist the pull of gravity, then it will be pulled into the surface of the larger object. That is why meteorites crash into the surface of moons and planets. That is also why the Moon does ...
Stars and Galaxies
... collection of stars, gas, and dust Earth’s galaxy is Milky Way which is part of a galaxy cluster named the Local Group Spiral galaxies—spiral arms wind out from inner section; some have barred spirals with stars and gas in a central bar Elliptical galaxies—large, three-dimensional ellipses; most ...
... collection of stars, gas, and dust Earth’s galaxy is Milky Way which is part of a galaxy cluster named the Local Group Spiral galaxies—spiral arms wind out from inner section; some have barred spirals with stars and gas in a central bar Elliptical galaxies—large, three-dimensional ellipses; most ...
The Sun: close-up of a spectral class G main sequence star
... • A wind past the Earth at 400 km/sec • The Sun is “melting away” • Density 19 orders of magnitude less than atmosphere • A medium for solar events • May have “sandblasted” the early atmosphere of Mars ...
... • A wind past the Earth at 400 km/sec • The Sun is “melting away” • Density 19 orders of magnitude less than atmosphere • A medium for solar events • May have “sandblasted” the early atmosphere of Mars ...
technics
... The solar wind, the supersonic stream of charged particles that flows out from the Sun, moves out into space in every direction at speeds of about a million mph. The Earth’s strong magnetic field shields our planet from the solar wind. The Moon, with its relatively weak magnetic field, has no such p ...
... The solar wind, the supersonic stream of charged particles that flows out from the Sun, moves out into space in every direction at speeds of about a million mph. The Earth’s strong magnetic field shields our planet from the solar wind. The Moon, with its relatively weak magnetic field, has no such p ...
File
... (93 million miles, 150 million kilometers). It’s a useful unit when describing distances in a solar system. The Earth is 1 AU (one Astronomical Unit) from the Sun. Jupiter is 5.2 AU from the Sun. Pluto is 40 AU from the Sun. Distance to the next closest star (after the Sun) ...
... (93 million miles, 150 million kilometers). It’s a useful unit when describing distances in a solar system. The Earth is 1 AU (one Astronomical Unit) from the Sun. Jupiter is 5.2 AU from the Sun. Pluto is 40 AU from the Sun. Distance to the next closest star (after the Sun) ...
Topic 3 Earth in the Universe
... • Galileo saw Venus experience phases like the Moon and saw satellites orbiting Jupiter ...
... • Galileo saw Venus experience phases like the Moon and saw satellites orbiting Jupiter ...
Astronomy Unit Test – Chapter 21
... 7. Create a flow-map that shows the organization of the universe, from smallest to largest unit? star, star cluster, galaxy, galactic cluster, universe 8. The H-R diagram is based upon which 2 criteria? temperature and brightness 9. The tilt of Earth on its axis affects Climate, Seasons, length of d ...
... 7. Create a flow-map that shows the organization of the universe, from smallest to largest unit? star, star cluster, galaxy, galactic cluster, universe 8. The H-R diagram is based upon which 2 criteria? temperature and brightness 9. The tilt of Earth on its axis affects Climate, Seasons, length of d ...
Lecture 39. Does Life Elsewhere Seem Likely? The
... dark spots at their intersections were oases changed with the seasons canals constructed to channel Mars’ scanty water supply ...
... dark spots at their intersections were oases changed with the seasons canals constructed to channel Mars’ scanty water supply ...
here
... 12. Which of the following statements about Inflation is FALSE? (a) The Universe expands faster than the speed of light during Inflation. (b) The rapid expansion during Inflation naturally explains why spacetime appears to be “flat” in terms of its geometric properties. (c) Inflation solves the CMB ...
... 12. Which of the following statements about Inflation is FALSE? (a) The Universe expands faster than the speed of light during Inflation. (b) The rapid expansion during Inflation naturally explains why spacetime appears to be “flat” in terms of its geometric properties. (c) Inflation solves the CMB ...
The eleventh annual AST poster session - Home
... One thought that has been on humans minds since we first started looking to sky was if we are alone in the universe. Instead of just sitting and waiting for a visitor to come to our planet to answer the question, U.C. Berkeley started recording radio transmissions from space on November 20, 1998 fro ...
... One thought that has been on humans minds since we first started looking to sky was if we are alone in the universe. Instead of just sitting and waiting for a visitor to come to our planet to answer the question, U.C. Berkeley started recording radio transmissions from space on November 20, 1998 fro ...
Outer space
Outer space, or just space, is the void that exists between celestial bodies, including the Earth. It is not completely empty, but consists of a hard vacuum containing a low density of particles, predominantly a plasma of hydrogen and helium as well as electromagnetic radiation, magnetic fields, neutrinos, dust and cosmic rays. The baseline temperature, as set by the background radiation from the Big Bang, is 2.7 kelvin (K). Plasma with a number density of less than one hydrogen atom per cubic metre and a temperature of millions of kelvin in the space between galaxies accounts for most of the baryonic (ordinary) matter in outer space; local concentrations have condensed into stars and galaxies. In most galaxies, observations provide evidence that 90% of the mass is in an unknown form, called dark matter, which interacts with other matter through gravitational but not electromagnetic forces. Data indicates that the majority of the mass-energy in the observable Universe is a poorly understood vacuum energy of space which astronomers label dark energy. Intergalactic space takes up most of the volume of the Universe, but even galaxies and star systems consist almost entirely of empty space.There is no firm boundary where space begins. However the Kármán line, at an altitude of 100 km (62 mi) above sea level, is conventionally used as the start of outer space in space treaties and for aerospace records keeping. The framework for international space law was established by the Outer Space Treaty, which was passed by the United Nations in 1967. This treaty precludes any claims of national sovereignty and permits all states to freely explore outer space. Despite the drafting of UN resolutions for the peaceful uses of outer space, anti-satellite weapons have been tested in Earth orbit.Humans began the physical exploration of space during the 20th century with the advent of high-altitude balloon flights, followed by manned rocket launches. Earth orbit was first achieved by Yuri Gagarin of the Soviet Union in 1961 and unmanned spacecraft have since reached all of the known planets in the Solar System. Due to the high cost of getting into space, manned spaceflight has been limited to low Earth orbit and the Moon.Outer space represents a challenging environment for human exploration because of the dual hazards of vacuum and radiation. Microgravity also has a negative effect on human physiology that causes both muscle atrophy and bone loss. In addition to these health and environmental issues, the economic cost of putting objects, including humans, into space is high.