FOSS Earth and Sun Module Glossary NGSS Edition © 2016 absorb
... planet a large, round object orbiting a star (SRB, IG) precipitation rain, snow, sleet, or hail that falls to the ground (SRB, IG) pressure the force or push caused by moving molecules (IG) radiant energy energy that travels through air and space (SRB, IG) radiation energy that travels through air ...
... planet a large, round object orbiting a star (SRB, IG) precipitation rain, snow, sleet, or hail that falls to the ground (SRB, IG) pressure the force or push caused by moving molecules (IG) radiant energy energy that travels through air and space (SRB, IG) radiation energy that travels through air ...
... • Galaxies and other objects may have motions that have nothing to do with the expansion of space • When galaxies orbit each other, sometimes their orbital speed is much larger than the redshift caused by expansion. • We cannot use Hubble’s law for nearby galaxies, and certainly not for any objects ...
Background Information on Galaxy Classification
... Elliptical galaxies contain mostly old stars, with very little gas and dust found between stars. Since new stars form from clouds of interstellar gas and dust, elliptical galaxies lack the raw ingredients to make new stars. Spiral galaxies, on the other hand, have a mix of young and old stars. Inter ...
... Elliptical galaxies contain mostly old stars, with very little gas and dust found between stars. Since new stars form from clouds of interstellar gas and dust, elliptical galaxies lack the raw ingredients to make new stars. Spiral galaxies, on the other hand, have a mix of young and old stars. Inter ...
1 The Hubble Story (10:56)
... Hubble has also measured the mass of a planet – only the second time such a calculation has been performed with any accuracy – by detecting the way in which the planet causes its star to wobble. Hubble also found the oldest planet so far discovered. The planet orbits a tiny stellar husk, which was o ...
... Hubble has also measured the mass of a planet – only the second time such a calculation has been performed with any accuracy – by detecting the way in which the planet causes its star to wobble. Hubble also found the oldest planet so far discovered. The planet orbits a tiny stellar husk, which was o ...
Test 4 Review Clicker Questions
... The Doppler shifts of 21-cm radiation from hydrogen in the spiral arms provides astronomers with a tool to map out the Galaxy’s structure. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... The Doppler shifts of 21-cm radiation from hydrogen in the spiral arms provides astronomers with a tool to map out the Galaxy’s structure. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Document
... spacetime, caused by the presence of any object Was experimentally verified in 1919 and explained observations which were at odds with Newton’s theories. Journey Through the Universe -- Cosmology ...
... spacetime, caused by the presence of any object Was experimentally verified in 1919 and explained observations which were at odds with Newton’s theories. Journey Through the Universe -- Cosmology ...
Neutrinos in an Expanding Universe Paper (IOP)
... source of gravitational fields. The effects of this extended over intergalactic distances, to regions far away from these sources. The velocity distribution of the relic neutrinos has thus gradually changed in the non-uniform gravitational fields that resulted from baryon clustering, i.e., galaxy form ...
... source of gravitational fields. The effects of this extended over intergalactic distances, to regions far away from these sources. The velocity distribution of the relic neutrinos has thus gradually changed in the non-uniform gravitational fields that resulted from baryon clustering, i.e., galaxy form ...
The Solar System and Beyond
... is probably a remnant of supernova explosions. No dense clouds populate this Bubble, and only a few diffuse and partially ionized cloudlets have survived in the hot and extremely tenuous gas that fills most of the “bubble” space (Fig. 1a). Because the cloudlets in the Sun’s vicinity are so tiny, the ...
... is probably a remnant of supernova explosions. No dense clouds populate this Bubble, and only a few diffuse and partially ionized cloudlets have survived in the hot and extremely tenuous gas that fills most of the “bubble” space (Fig. 1a). Because the cloudlets in the Sun’s vicinity are so tiny, the ...
Matter Cycle in the Interstellar Medium (ISM)
... ➙ obscuring matter rather than vacuum, blocking light from more distant stars.! ...
... ➙ obscuring matter rather than vacuum, blocking light from more distant stars.! ...
Chapter 12: Stars and Galaxies
... When light from a star is passed through a spectroscope, astronomers see dark absorption lines that are produced as light passes through the star’s cooler, less dense atmosphere. Each element contributes its own set of absorption lines to this absorption spectrum, such as those shown in Figure 5. Wh ...
... When light from a star is passed through a spectroscope, astronomers see dark absorption lines that are produced as light passes through the star’s cooler, less dense atmosphere. Each element contributes its own set of absorption lines to this absorption spectrum, such as those shown in Figure 5. Wh ...
Properties of dust - McDonald Observatory
... Collect dust samples using the cleaning pad or clear tape. Carefully remove particles from the pad (scrape with the tweezers and gently shake the pad) onto the graph paper. Then sort the contents by features (size, color, shape) on the graph paper. Clear tape can be used to hold down the samples whi ...
... Collect dust samples using the cleaning pad or clear tape. Carefully remove particles from the pad (scrape with the tweezers and gently shake the pad) onto the graph paper. Then sort the contents by features (size, color, shape) on the graph paper. Clear tape can be used to hold down the samples whi ...
1 A CLOSED NON-COLLAPSING 3-D UNIVERSE PREDICTING A
... produced. This process began in a symmetry-breaking event in an embedding mdimensional Euclidean epi-space. This event led to the compaction of a small 4-D ball and our 3-D universe on its surface. Immediately the contrast is evident with the big-bang model for a closed universe in which all of the ...
... produced. This process began in a symmetry-breaking event in an embedding mdimensional Euclidean epi-space. This event led to the compaction of a small 4-D ball and our 3-D universe on its surface. Immediately the contrast is evident with the big-bang model for a closed universe in which all of the ...
r202 the new astronomy
... This book containing information about 2800 stars and 88 constellations is the result of an enormous work, begun by Prof. Helmut Werner shortly after the Second World War. This project of H. Werner, who was astronomer and member of the staff of the Carl Zeiss firm was continued after his death in 19 ...
... This book containing information about 2800 stars and 88 constellations is the result of an enormous work, begun by Prof. Helmut Werner shortly after the Second World War. This project of H. Werner, who was astronomer and member of the staff of the Carl Zeiss firm was continued after his death in 19 ...
our planet the earth byalko - ArvindGuptaToys Books Gallery
... Our wish has been to explain the structure of the world and t o demonstrate what makes it so "convenient" to live in. We begin with pinpointing the exact location of our great home in space and time, namely, describe the part of the universe immediately around us, and the motion of the Earth around ...
... Our wish has been to explain the structure of the world and t o demonstrate what makes it so "convenient" to live in. We begin with pinpointing the exact location of our great home in space and time, namely, describe the part of the universe immediately around us, and the motion of the Earth around ...
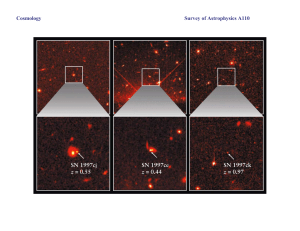
Survey of Astrophysics A110 Cosmology
... conservation of energy law (remember energy and mass are equivalent), is not a real problem. After all, when the issue is the origin of the Universe, at some point matter must be created. [Only one atom would have to be created in a cubic cm of space every million billion years (1015 years)]. • In i ...
... conservation of energy law (remember energy and mass are equivalent), is not a real problem. After all, when the issue is the origin of the Universe, at some point matter must be created. [Only one atom would have to be created in a cubic cm of space every million billion years (1015 years)]. • In i ...
CHAPTER 8 Survey of Solar Systems
... When several planets appear near each other in the evening sky, we can see that they lie along a linear band extending away from the Sun (fig. 8.4). The planets appear to lie along a line because their orbits, as well as the Earth’s, all lie in nearly the same plane, as shown in the side view of the ...
... When several planets appear near each other in the evening sky, we can see that they lie along a linear band extending away from the Sun (fig. 8.4). The planets appear to lie along a line because their orbits, as well as the Earth’s, all lie in nearly the same plane, as shown in the side view of the ...
Stellar Metamorphosis
... It is suggested to the reader to realize that gravity theory is a failed theory [13] as it is not a force [14] and cannot accrete material what so ever. [15][16] These stars simply formed in different areas of the galaxy and took up orbit around each other further along their life spans. 8. Gas cont ...
... It is suggested to the reader to realize that gravity theory is a failed theory [13] as it is not a force [14] and cannot accrete material what so ever. [15][16] These stars simply formed in different areas of the galaxy and took up orbit around each other further along their life spans. 8. Gas cont ...
Seeding the Universe with Life
... Nature creates objects and patterns but does not call them names. Only humans use definitions. Therefore, “what is Life” cannot be answered by Nature. It must be answered by human beings using human faculties: our instincts, emotions and rational arguments. Whomever we accept as living beings – they ...
... Nature creates objects and patterns but does not call them names. Only humans use definitions. Therefore, “what is Life” cannot be answered by Nature. It must be answered by human beings using human faculties: our instincts, emotions and rational arguments. Whomever we accept as living beings – they ...
Galaxies
... • Origin, early history, and fate of the Universe • Does the Universe have a beginning? An end? What physics processes “caused” the Universe to be what it is? Are other universes possible? Would they look like ours (have the same physics)? • Cosmological Principle - the Universe appears the same ...
... • Origin, early history, and fate of the Universe • Does the Universe have a beginning? An end? What physics processes “caused” the Universe to be what it is? Are other universes possible? Would they look like ours (have the same physics)? • Cosmological Principle - the Universe appears the same ...
Galaxies at High Redshift Encyclopedia of Astronomy & Astrophysics eaa.iop.org Mauro Giavalisco
... sudden dimming of the light at wavelengths shorter than the ‘Lyman limit’, as we shall discuss later. ...
... sudden dimming of the light at wavelengths shorter than the ‘Lyman limit’, as we shall discuss later. ...
The Case of the Galactic Vacation
... Starship 2040, where Mr. Wang of NASA Marshall Space Flight Center explains what tourism in space will be like in about 50 years. Now the detectives realize that no matter where they go in the solar system or galaxy, the current rocket system will not get them there and back quickly enough. They hea ...
... Starship 2040, where Mr. Wang of NASA Marshall Space Flight Center explains what tourism in space will be like in about 50 years. Now the detectives realize that no matter where they go in the solar system or galaxy, the current rocket system will not get them there and back quickly enough. They hea ...
the solar system and your community
... the distance between the Earth and moon) in October 2028. A day later, NASA scientists revised the estimate to 800,000 kilometers. News reports described how an iron asteroid had once blasted a hole more than 1 kilometer wide and 200 meters deep, and probably killed every living thing within 50 kilo ...
... the distance between the Earth and moon) in October 2028. A day later, NASA scientists revised the estimate to 800,000 kilometers. News reports described how an iron asteroid had once blasted a hole more than 1 kilometer wide and 200 meters deep, and probably killed every living thing within 50 kilo ...
APS Slide Presentation
... substantial increase in the matter and energy in the new universe over the amount in the singularity. The Singularity Acceleration hypothesis suggests that the larger the singularity, the more efficient the CP violation process or equivalent process is at making mass and annihilating antimatter, the ...
... substantial increase in the matter and energy in the new universe over the amount in the singularity. The Singularity Acceleration hypothesis suggests that the larger the singularity, the more efficient the CP violation process or equivalent process is at making mass and annihilating antimatter, the ...
Ch17_lecture
... Measuring the Mass of Galaxies • The mass of a galaxy is determined from the modified form of Kepler’s third law • To use this method, one concentrates on some stars or gas on the outer fringes of the galaxy • The semimajor axis distance used in Kepler’s third law is simply half the galaxy’s pre-de ...
... Measuring the Mass of Galaxies • The mass of a galaxy is determined from the modified form of Kepler’s third law • To use this method, one concentrates on some stars or gas on the outer fringes of the galaxy • The semimajor axis distance used in Kepler’s third law is simply half the galaxy’s pre-de ...
Chapter 16
... given volume – Distant galaxies show more signs of disturbance by neighboring galaxies (odd shapes, bent arms, twisted disks), what astronomers call “harassment” ...
... given volume – Distant galaxies show more signs of disturbance by neighboring galaxies (odd shapes, bent arms, twisted disks), what astronomers call “harassment” ...
Outer space
Outer space, or just space, is the void that exists between celestial bodies, including the Earth. It is not completely empty, but consists of a hard vacuum containing a low density of particles, predominantly a plasma of hydrogen and helium as well as electromagnetic radiation, magnetic fields, neutrinos, dust and cosmic rays. The baseline temperature, as set by the background radiation from the Big Bang, is 2.7 kelvin (K). Plasma with a number density of less than one hydrogen atom per cubic metre and a temperature of millions of kelvin in the space between galaxies accounts for most of the baryonic (ordinary) matter in outer space; local concentrations have condensed into stars and galaxies. In most galaxies, observations provide evidence that 90% of the mass is in an unknown form, called dark matter, which interacts with other matter through gravitational but not electromagnetic forces. Data indicates that the majority of the mass-energy in the observable Universe is a poorly understood vacuum energy of space which astronomers label dark energy. Intergalactic space takes up most of the volume of the Universe, but even galaxies and star systems consist almost entirely of empty space.There is no firm boundary where space begins. However the Kármán line, at an altitude of 100 km (62 mi) above sea level, is conventionally used as the start of outer space in space treaties and for aerospace records keeping. The framework for international space law was established by the Outer Space Treaty, which was passed by the United Nations in 1967. This treaty precludes any claims of national sovereignty and permits all states to freely explore outer space. Despite the drafting of UN resolutions for the peaceful uses of outer space, anti-satellite weapons have been tested in Earth orbit.Humans began the physical exploration of space during the 20th century with the advent of high-altitude balloon flights, followed by manned rocket launches. Earth orbit was first achieved by Yuri Gagarin of the Soviet Union in 1961 and unmanned spacecraft have since reached all of the known planets in the Solar System. Due to the high cost of getting into space, manned spaceflight has been limited to low Earth orbit and the Moon.Outer space represents a challenging environment for human exploration because of the dual hazards of vacuum and radiation. Microgravity also has a negative effect on human physiology that causes both muscle atrophy and bone loss. In addition to these health and environmental issues, the economic cost of putting objects, including humans, into space is high.