2 MB - Gravity Probe B
... Gravity Pulls Harder on Some Things? What exactly is happening here? How can two objects with dramatically different masses fall to the ground at the same rate? The answer to this paradox lies in the remarkable balance between the amount that gravity pulls on an object (the object’s weight) and the ...
... Gravity Pulls Harder on Some Things? What exactly is happening here? How can two objects with dramatically different masses fall to the ground at the same rate? The answer to this paradox lies in the remarkable balance between the amount that gravity pulls on an object (the object’s weight) and the ...
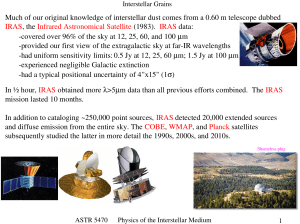
Much of our original knowledge of interstellar dust comes from a
... Suppose we have very big particles, e.g., planets or asteroids. Now in general, the l.h.s. of the radiative balance is dominated by optical/UV photons and the r.h.s. by the emission of infrared photons. Let us take the average visual albedo to be A, implying Qabs=1A, and the average emissivity ...
... Suppose we have very big particles, e.g., planets or asteroids. Now in general, the l.h.s. of the radiative balance is dominated by optical/UV photons and the r.h.s. by the emission of infrared photons. Let us take the average visual albedo to be A, implying Qabs=1A, and the average emissivity ...
- Mastering Physics Answers
... Alpha Centauri A has a much higher surface temperature than the Sun. Alpha Centauri A must have a vastly different interior structure than the Sun. Alpha Centauri A is much farther from Earth than the Sun. Alpha Centauri A fuses hydrogen into helium in its core at a higher rate than our Sun. ...
... Alpha Centauri A has a much higher surface temperature than the Sun. Alpha Centauri A must have a vastly different interior structure than the Sun. Alpha Centauri A is much farther from Earth than the Sun. Alpha Centauri A fuses hydrogen into helium in its core at a higher rate than our Sun. ...
Compartive Planetology I: Our Solar. System
... across—about i/. of the width of a human hair and far too small to be seen without a microscope. The planets themselves are very small compared to the distances between them. Indeed, while an airliner traveling at 1000 km/h (620 mi/h) can fly around Earth in less than two days, at this speed it woul ...
... across—about i/. of the width of a human hair and far too small to be seen without a microscope. The planets themselves are very small compared to the distances between them. Indeed, while an airliner traveling at 1000 km/h (620 mi/h) can fly around Earth in less than two days, at this speed it woul ...
ASTRONOMIA SPAIN inglés.qxd
... These are some of the results we present in ‘Astronomy made in Spain’, a project of the Spanish Astronomical Society (Sociedad Española de Astronomía, SEA) to commemorate the International Year of Astronomy 2009. This book is a collection of conversations with the Spanish astronomers who have publis ...
... These are some of the results we present in ‘Astronomy made in Spain’, a project of the Spanish Astronomical Society (Sociedad Española de Astronomía, SEA) to commemorate the International Year of Astronomy 2009. This book is a collection of conversations with the Spanish astronomers who have publis ...
space charge formation under dc conditions and its influence on
... electric field would be fully reflected in the space charge behaviour. They would also make it possible to investigate the effect of a temperature gradient in radial insulation on the space charge accumulation, and hence replicate the conditions experienced when the cable is loaded in service. In a ...
... electric field would be fully reflected in the space charge behaviour. They would also make it possible to investigate the effect of a temperature gradient in radial insulation on the space charge accumulation, and hence replicate the conditions experienced when the cable is loaded in service. In a ...
09- 04- 00004.000 - Standards Development and Review
... coherent—document. These standards are intended to be used as guidance and recommended practices for astrodynamics applications in Earth orbit where interoperability and consistency of results is a priority. For those users who are purely engaged in research activities, these standards can provide a ...
... coherent—document. These standards are intended to be used as guidance and recommended practices for astrodynamics applications in Earth orbit where interoperability and consistency of results is a priority. For those users who are purely engaged in research activities, these standards can provide a ...
Quiz 2 Lecture 12
... a. Ring galaxies can be produced by head-on collisions between galaxies. b. The ratio of the number of elliptical to spiral galaxies remains constant over time. c. The Magellanic Clouds may eventually be "cannibalized" by our Galaxy. d. The shape of a galaxy can be influenced by collision with anoth ...
... a. Ring galaxies can be produced by head-on collisions between galaxies. b. The ratio of the number of elliptical to spiral galaxies remains constant over time. c. The Magellanic Clouds may eventually be "cannibalized" by our Galaxy. d. The shape of a galaxy can be influenced by collision with anoth ...
Cosmic Topology: A Brief Overview
... ancient Greek finite-world response, widely accepted in medieval Europe, is at a first sight open to a devastating objection: in being finite the world must have a limiting boundary. But this is impossible, because a boundary can only separate one part of the space from another: why not redefine the ...
... ancient Greek finite-world response, widely accepted in medieval Europe, is at a first sight open to a devastating objection: in being finite the world must have a limiting boundary. But this is impossible, because a boundary can only separate one part of the space from another: why not redefine the ...
Sun, Stars and Planets Part 1: The Sun: its structure and energy
... and so the plasma has a higher density than you might intuitively expect is possible for an ideal gas. Plasma also differs from an ordinary gas because the forces between electrons and ions have a much longer range than the forces between neutral atoms. In contrast to many space plasmas that are low ...
... and so the plasma has a higher density than you might intuitively expect is possible for an ideal gas. Plasma also differs from an ordinary gas because the forces between electrons and ions have a much longer range than the forces between neutral atoms. In contrast to many space plasmas that are low ...
Elliptical galaxies
... The effective radius Re is strongly correlated with the absolute magnitude MB ...
... The effective radius Re is strongly correlated with the absolute magnitude MB ...
Chapter 17
... (iv) Cold dark matter; an exotic form of matter, moving at relatively slow speed, which can be detected only by its gravitational interactions; it appears to be quite abundant throughout the universe. 8. It seems that the universe is only about 4% normal matter and 20% dark matter, the remaining 76% ...
... (iv) Cold dark matter; an exotic form of matter, moving at relatively slow speed, which can be detected only by its gravitational interactions; it appears to be quite abundant throughout the universe. 8. It seems that the universe is only about 4% normal matter and 20% dark matter, the remaining 76% ...
matter and dark energy Gravitational lensing: a unique probe of dark
... gravitational lensing? Zwicky was correct that galaxies and galaxy clusters serve as more probable lenses than individual stars, but even so three factors seriously limit the visibility of lensed images. Firstly, it is useful to introduce the concept of optical depth τ in considering the probability ...
... gravitational lensing? Zwicky was correct that galaxies and galaxy clusters serve as more probable lenses than individual stars, but even so three factors seriously limit the visibility of lensed images. Firstly, it is useful to introduce the concept of optical depth τ in considering the probability ...
here - Ira-Inaf
... the Solar Circle, defined as the circular orbit whose radius is that of the distance of the Sun from the Galactic Center, commonly denoted as Ro. In 1985, the International Astronomical Union recommended that a value of 8.5 kpc be adopted for Ro (Kerr and Lynden-Bell, 1986), though more recent work ...
... the Solar Circle, defined as the circular orbit whose radius is that of the distance of the Sun from the Galactic Center, commonly denoted as Ro. In 1985, the International Astronomical Union recommended that a value of 8.5 kpc be adopted for Ro (Kerr and Lynden-Bell, 1986), though more recent work ...
Galactic Evolution - Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics
... they must have been very much more massive than any stars existing today, hence very much shorter lived than any stars now known. Such pure gas, lacking in C and O that normally help clouds to cool and condense, would have needed more mass to contract than stars typically now, >10 Gy after the bang ...
... they must have been very much more massive than any stars existing today, hence very much shorter lived than any stars now known. Such pure gas, lacking in C and O that normally help clouds to cool and condense, would have needed more mass to contract than stars typically now, >10 Gy after the bang ...
The hot, early universe - Cosmology Block
... 11 B formation through the late-time 11 C decay. (A color version of this figure is available in the online journal.) ...
... 11 B formation through the late-time 11 C decay. (A color version of this figure is available in the online journal.) ...
Virtual Science Fair - Dark Matter Alexander Mashaal
... Dark Matter: In cosmology, dark matter has matter particles that cannot be spotted by their releases of radiation but when they are there, they can be taken from gravitational effects on visible matter such as stars and galaxies. Black Holes: A black hole is a part of space that has so much mass con ...
... Dark Matter: In cosmology, dark matter has matter particles that cannot be spotted by their releases of radiation but when they are there, they can be taken from gravitational effects on visible matter such as stars and galaxies. Black Holes: A black hole is a part of space that has so much mass con ...
PowerPoint
... • They do not involve colliding stars– but rather gravitational fields • Might form hot intergalactic gas • Could initiate rapid star formation - called Starburst Galaxies • Collision causes stars to be scattered into “tails” • Causes galaxy mergers called “galactic cannibalism” ...
... • They do not involve colliding stars– but rather gravitational fields • Might form hot intergalactic gas • Could initiate rapid star formation - called Starburst Galaxies • Collision causes stars to be scattered into “tails” • Causes galaxy mergers called “galactic cannibalism” ...
Starburst Galaxies - Beck-Shop
... region, which is a gaseous nebula with an emission-line spectrum (Box 2.2). H II regions are some of the most spectacular sights in the sky – rivalling galaxies – and the well-known Orion Nebula (M 42, Fig. 2.1) is exactly just such a region that has developed on the nearest side to us of the Orion ...
... region, which is a gaseous nebula with an emission-line spectrum (Box 2.2). H II regions are some of the most spectacular sights in the sky – rivalling galaxies – and the well-known Orion Nebula (M 42, Fig. 2.1) is exactly just such a region that has developed on the nearest side to us of the Orion ...
Astronomy 140 Lecture Notes, Spring 2008 c
... By measuring the spectrum of a star, one can determine its temperature by comparing the line strengths of lines with highly excited lower levels to the strengths of lines with low excitation lower levels. Since the populations in states with energy E is proportional to exp(−E/kT ) (Boltzmann), this ...
... By measuring the spectrum of a star, one can determine its temperature by comparing the line strengths of lines with highly excited lower levels to the strengths of lines with low excitation lower levels. Since the populations in states with energy E is proportional to exp(−E/kT ) (Boltzmann), this ...
Thermal history of the universe with dark energy
... ter, to explain the orbital velocities of stars in galaxies, which could not be reached only accounting the visible, or baryonic, matter. The particles that may comprise it are being sought after, believed to interact weakly with normal matter. Among the many candidates proposed [1–4], one of the mo ...
... ter, to explain the orbital velocities of stars in galaxies, which could not be reached only accounting the visible, or baryonic, matter. The particles that may comprise it are being sought after, believed to interact weakly with normal matter. Among the many candidates proposed [1–4], one of the mo ...
Chapter 1
... • The pattern of weather of a place over many years is climate. • The sun provides the earth with heat and light thus shaping climate. • As the earth moves through space, it rotates, or spins like a top. • Geographers say that it spins on its axis, an imaginary line that runs through the earth ...
... • The pattern of weather of a place over many years is climate. • The sun provides the earth with heat and light thus shaping climate. • As the earth moves through space, it rotates, or spins like a top. • Geographers say that it spins on its axis, an imaginary line that runs through the earth ...
Effects of Thomson-Scattering Geometry on White-Light
... Howard and Tappin (2009), the interpretation of observations of the leading edge of a CME can be fraught with difficulties, especially at large elongations. Scattered sunlight in the inner heliosphere is not only determined by the local electron density, but also by Thomsonscattering theory. The Tho ...
... Howard and Tappin (2009), the interpretation of observations of the leading edge of a CME can be fraught with difficulties, especially at large elongations. Scattered sunlight in the inner heliosphere is not only determined by the local electron density, but also by Thomsonscattering theory. The Tho ...
The density of very massive evolved galaxies to z≃ 1.7
... of the seven galaxies are shown. The spectra drops very rapidly at ∼0.9–1 µm concurrent with the 4000 Å break placing the galaxies at z > 1.3 and suggesting an early-type spectral nature. We searched for the best-fitting template by comparing the observed spectral energy distribution (SED) of each g ...
... of the seven galaxies are shown. The spectra drops very rapidly at ∼0.9–1 µm concurrent with the 4000 Å break placing the galaxies at z > 1.3 and suggesting an early-type spectral nature. We searched for the best-fitting template by comparing the observed spectral energy distribution (SED) of each g ...
Outer space
Outer space, or just space, is the void that exists between celestial bodies, including the Earth. It is not completely empty, but consists of a hard vacuum containing a low density of particles, predominantly a plasma of hydrogen and helium as well as electromagnetic radiation, magnetic fields, neutrinos, dust and cosmic rays. The baseline temperature, as set by the background radiation from the Big Bang, is 2.7 kelvin (K). Plasma with a number density of less than one hydrogen atom per cubic metre and a temperature of millions of kelvin in the space between galaxies accounts for most of the baryonic (ordinary) matter in outer space; local concentrations have condensed into stars and galaxies. In most galaxies, observations provide evidence that 90% of the mass is in an unknown form, called dark matter, which interacts with other matter through gravitational but not electromagnetic forces. Data indicates that the majority of the mass-energy in the observable Universe is a poorly understood vacuum energy of space which astronomers label dark energy. Intergalactic space takes up most of the volume of the Universe, but even galaxies and star systems consist almost entirely of empty space.There is no firm boundary where space begins. However the Kármán line, at an altitude of 100 km (62 mi) above sea level, is conventionally used as the start of outer space in space treaties and for aerospace records keeping. The framework for international space law was established by the Outer Space Treaty, which was passed by the United Nations in 1967. This treaty precludes any claims of national sovereignty and permits all states to freely explore outer space. Despite the drafting of UN resolutions for the peaceful uses of outer space, anti-satellite weapons have been tested in Earth orbit.Humans began the physical exploration of space during the 20th century with the advent of high-altitude balloon flights, followed by manned rocket launches. Earth orbit was first achieved by Yuri Gagarin of the Soviet Union in 1961 and unmanned spacecraft have since reached all of the known planets in the Solar System. Due to the high cost of getting into space, manned spaceflight has been limited to low Earth orbit and the Moon.Outer space represents a challenging environment for human exploration because of the dual hazards of vacuum and radiation. Microgravity also has a negative effect on human physiology that causes both muscle atrophy and bone loss. In addition to these health and environmental issues, the economic cost of putting objects, including humans, into space is high.