Ch. 10 Presentation
... 10.10 Eukaryotic RNA is processed before leaving the nucleus as mRNA Messenger RNA (mRNA) – encodes amino acid sequences and – conveys genetic messages from DNA to the translation machinery of the cell, which in – prokaryotes, occurs in the same place that mRNA is made, but in – eukaryotes, mRNA ...
... 10.10 Eukaryotic RNA is processed before leaving the nucleus as mRNA Messenger RNA (mRNA) – encodes amino acid sequences and – conveys genetic messages from DNA to the translation machinery of the cell, which in – prokaryotes, occurs in the same place that mRNA is made, but in – eukaryotes, mRNA ...
Factors Affecting synonymous codon Usage Bias in chloroplast
... of compositional constraints. We did further correspondence analysis (Table 1). The first axis can explain 24.12% of the total variation, and the next three axes explained 12.49%, 7.37%, 5.65%. The ordination of genes on the first four COA axes was examined for correlations with indices of codon usa ...
... of compositional constraints. We did further correspondence analysis (Table 1). The first axis can explain 24.12% of the total variation, and the next three axes explained 12.49%, 7.37%, 5.65%. The ordination of genes on the first four COA axes was examined for correlations with indices of codon usa ...
10 Day Lesson Plan - Joseph L. Anderson
... critical role in protein production. Before we examine the process further, we must know the fundamental difference between DNA and RNA. RNA does not have two sides as DNA. There is a slight difference in the sugar phosphate structure. RNA has one base that is different than DNA. This base replaces ...
... critical role in protein production. Before we examine the process further, we must know the fundamental difference between DNA and RNA. RNA does not have two sides as DNA. There is a slight difference in the sugar phosphate structure. RNA has one base that is different than DNA. This base replaces ...
Test 1
... a. Central Dogma: DNA RNA Protein. Transcription makes RNA by reading DNA and translation makes protein by reading RNA. i. RNA 1. Uses AUGC 2. mRNA, rRNA, tRNA ii. Genetic Code (Tab 4.2) 1. Each triplet codes for one amino acid (or stop codon) 2. 64 possibilites with 20 a.a., therefore redundanc ...
... a. Central Dogma: DNA RNA Protein. Transcription makes RNA by reading DNA and translation makes protein by reading RNA. i. RNA 1. Uses AUGC 2. mRNA, rRNA, tRNA ii. Genetic Code (Tab 4.2) 1. Each triplet codes for one amino acid (or stop codon) 2. 64 possibilites with 20 a.a., therefore redundanc ...
Text S6
... identified for the production of nematophin, which might be an NRPS-derived dipeptide, and putative clusters involved in its biosynthesis are currently being analyzed in detail. A biosynthesis gene cluster involved in the production of the isonitril compound rhabduscin [14] is highly conserved among ...
... identified for the production of nematophin, which might be an NRPS-derived dipeptide, and putative clusters involved in its biosynthesis are currently being analyzed in detail. A biosynthesis gene cluster involved in the production of the isonitril compound rhabduscin [14] is highly conserved among ...
Biology Slide 1 of 39 End Show
... Translation is the decoding of an mRNA message into a polypeptide chain (protein). Translation takes place on ribosomes. During translation, the cell uses information from messenger RNA to produce proteins. Nucleus ...
... Translation is the decoding of an mRNA message into a polypeptide chain (protein). Translation takes place on ribosomes. During translation, the cell uses information from messenger RNA to produce proteins. Nucleus ...
Chapter 3 – The Molecules of Cells
... (nucleotides), and proteins are made with only twenty monomers (amino acids), but both macromolecules are incredible diverse. The proteins in you and a fungus are made with the same twenty amino acids! ...
... (nucleotides), and proteins are made with only twenty monomers (amino acids), but both macromolecules are incredible diverse. The proteins in you and a fungus are made with the same twenty amino acids! ...
ELSI Learning Objective
... Biology Learning Objective • Describe the three major types of RNA and their functions. ELSI Learning Objective • Discriminate between jargon and literal uses of terms that can lead to misunderstandings about science. ...
... Biology Learning Objective • Describe the three major types of RNA and their functions. ELSI Learning Objective • Discriminate between jargon and literal uses of terms that can lead to misunderstandings about science. ...
Genes and RNA
... domains of the sigma subunit bind to the core enzyme in a position to recognize the promoter elements. The DNA is numbered relative to the transcription start site at +1. The σ2 domain recognizes the 10 region (red), while the σ3 domain binds to the flanking base pairs of the extended -10 region. Th ...
... domains of the sigma subunit bind to the core enzyme in a position to recognize the promoter elements. The DNA is numbered relative to the transcription start site at +1. The σ2 domain recognizes the 10 region (red), while the σ3 domain binds to the flanking base pairs of the extended -10 region. Th ...
Pharmacogenomics Module Presentation
... nucleotides that encode for many genes. Gene RNA: A single-stranded copy of one gene. RNA Protein: Proteins are composed of amino acids. Amino acids are made from triplets of nucleotides called codons. ...
... nucleotides that encode for many genes. Gene RNA: A single-stranded copy of one gene. RNA Protein: Proteins are composed of amino acids. Amino acids are made from triplets of nucleotides called codons. ...
A General Model of Codon Bias Due to GC Mutational Bias
... patterns of codons used without recourse to the added complexity of including non-synonymous mutations. Consider the codons relating to any particular amino acid. For any two codons X and Y that differ by a single nucleotide, we assume that the rates of mutation from X to Y and from Y to X are the s ...
... patterns of codons used without recourse to the added complexity of including non-synonymous mutations. Consider the codons relating to any particular amino acid. For any two codons X and Y that differ by a single nucleotide, we assume that the rates of mutation from X to Y and from Y to X are the s ...
Thesis-Codon Bias in Escherichia coli Cells
... entire cell. In E. coli cells, two of the six leucine codons have the largest and second smallest relative synonymous codon usage of all E. coli codons. Thus, these codons were targeted for experimental mutation, and an ampicillin resistance gene was engineered, replacing the eight preferred leucine ...
... entire cell. In E. coli cells, two of the six leucine codons have the largest and second smallest relative synonymous codon usage of all E. coli codons. Thus, these codons were targeted for experimental mutation, and an ampicillin resistance gene was engineered, replacing the eight preferred leucine ...
Transcription and Translation
... metabolism; determining physical characteristics and producing genetic disorders by their absence or presence in an altered form. ...
... metabolism; determining physical characteristics and producing genetic disorders by their absence or presence in an altered form. ...
Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, Electron Transport Chain
... 2. Where in the cell does the glycolysis part of cellular respiration occur?Cytoplasm 3. Where in the cell does the Krebs (Citric Acid) cycle part of cellular respiration occur? Mitochondrion 4. Where in the cell does the electron transport part of cellular respiration occur? Mitochondrion 5. How ma ...
... 2. Where in the cell does the glycolysis part of cellular respiration occur?Cytoplasm 3. Where in the cell does the Krebs (Citric Acid) cycle part of cellular respiration occur? Mitochondrion 4. Where in the cell does the electron transport part of cellular respiration occur? Mitochondrion 5. How ma ...
Exam 2 (pdf - 449.81kb)
... White is dominant to both sable and copper colour. Sable colour is dominant to copper colour. Question 2 If two dogs with the genotypes AW ac and aS ac are mated, the resulting offspring could have A. 4 genotypes and 4 phenotypes. B. 4 genotypes and 3 phenotypes. C. 3 genotypes and 4 phenotypes. D. ...
... White is dominant to both sable and copper colour. Sable colour is dominant to copper colour. Question 2 If two dogs with the genotypes AW ac and aS ac are mated, the resulting offspring could have A. 4 genotypes and 4 phenotypes. B. 4 genotypes and 3 phenotypes. C. 3 genotypes and 4 phenotypes. D. ...
Document
... p8: "It is plausible that with the evolution, the deletion of the PUA domain led to merging of two different functional domains into one bifunctional enzymatic protein. p8: "P5CS genes of prokaryotes and unicellular eukaryotes are intron less. However, multicelluar eukaryotic P5CS genes are split wi ...
... p8: "It is plausible that with the evolution, the deletion of the PUA domain led to merging of two different functional domains into one bifunctional enzymatic protein. p8: "P5CS genes of prokaryotes and unicellular eukaryotes are intron less. However, multicelluar eukaryotic P5CS genes are split wi ...
chromatography
... • Sometimes chromatography with a single solvent is not enough to separate all the constituents of a mixture. • In this case the separation can be improved by two-dimensional chromatography, where the chromatography paper is turned through 90° and run a second time in a second solvent. • Solutes th ...
... • Sometimes chromatography with a single solvent is not enough to separate all the constituents of a mixture. • In this case the separation can be improved by two-dimensional chromatography, where the chromatography paper is turned through 90° and run a second time in a second solvent. • Solutes th ...
Structure-Function Relationship in DNA sequence Recognition by
... energies (EPD = Sab,s DEab(s)) for a given DNA sequence in a complexed form was defined as the energy for the sequences. The energy for a particular sequence, in a crystal structure for example, was normalized to measure specificity by the Z-score against random sequences. The Z-score was defined as ...
... energies (EPD = Sab,s DEab(s)) for a given DNA sequence in a complexed form was defined as the energy for the sequences. The energy for a particular sequence, in a crystal structure for example, was normalized to measure specificity by the Z-score against random sequences. The Z-score was defined as ...
Rate variation during molecular evolution: creationism and the
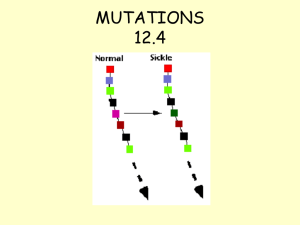
... Amino acid sequence comparisons for a specific protein can only be used as a molecular clock due to mutations in the gene coding for that protein. These mutations take place in the three-lettered DNA codons that code for the amino acids that make up the protein. The phrase “mutation rate” typically ...
... Amino acid sequence comparisons for a specific protein can only be used as a molecular clock due to mutations in the gene coding for that protein. These mutations take place in the three-lettered DNA codons that code for the amino acids that make up the protein. The phrase “mutation rate” typically ...
Biology - Meester Martinez
... A unit of heredity that is transferred from a parent to offspring and is held to determine some characteristic of the...: "proteins coded directly by genes." ...
... A unit of heredity that is transferred from a parent to offspring and is held to determine some characteristic of the...: "proteins coded directly by genes." ...
Chapter 14 Lecture Notes: Nucleic Acids
... 19. Given the primary structure of DNA or mRNA, use the genetic code table to predict the sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide that would be produced in translation. 20. Describe the three types of RNA and understand the role of each in translation. 21. Define the term “gene expression.” 22. D ...
... 19. Given the primary structure of DNA or mRNA, use the genetic code table to predict the sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide that would be produced in translation. 20. Describe the three types of RNA and understand the role of each in translation. 21. Define the term “gene expression.” 22. D ...
Expanded genetic code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 encoded proteinogenic amino acids.The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: the non-standard amino acid to encode, an unused codon to adopt, a tRNA that recognises this codon, and a tRNA synthase that recognises only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid.Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science.