here
... one with an omega fixed at 1, a second where each site can be either have an omega between 0 and 1, or an omega of 1, and third a model that uses three omegas as described before for MrBayes. The output is written into a file called Hv1.sites.codeml_out (as directed by the control file). Point out l ...
... one with an omega fixed at 1, a second where each site can be either have an omega between 0 and 1, or an omega of 1, and third a model that uses three omegas as described before for MrBayes. The output is written into a file called Hv1.sites.codeml_out (as directed by the control file). Point out l ...
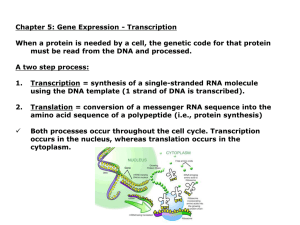
Chapter 10 Protein Synthesis
... translated into amino acid sequences – The flow of information from gene to protein is based on a triplet code: the genetic instructions for the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide chain are written in DNA and RNA as a series of nonoverlapping threebase “words” called codons. – Translation involves ...
... translated into amino acid sequences – The flow of information from gene to protein is based on a triplet code: the genetic instructions for the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide chain are written in DNA and RNA as a series of nonoverlapping threebase “words” called codons. – Translation involves ...
Enzymes - SAVE MY EXAMS!
... (ii) State the maximum number of amino acids coded for by this length of mRNA. ...
... (ii) State the maximum number of amino acids coded for by this length of mRNA. ...
Controlling complexity and water penetration in functional de novo
... challenge to delineating individual amino acid functions in natural enzymes and raises major barriers to their redesign while engineering new functions in artificial proteins. Two complementary principles (Figure 1) illustrate the roots of natural protein complexity. First, individual amino acids ar ...
... challenge to delineating individual amino acid functions in natural enzymes and raises major barriers to their redesign while engineering new functions in artificial proteins. Two complementary principles (Figure 1) illustrate the roots of natural protein complexity. First, individual amino acids ar ...
Hypothesis for the evolutionary origin of the chloroplast ribosomal
... data for S 12 (Table 1, c), an r-protein for which sequences from mitochondria and chloroplasts are known. The pattern of homology found in Table 1 (c) is clearly much more similar to the data for L21 than are the patterns found in Table 1 (a) and (b). Judging by comparison to the analyses for 16S r ...
... data for S 12 (Table 1, c), an r-protein for which sequences from mitochondria and chloroplasts are known. The pattern of homology found in Table 1 (c) is clearly much more similar to the data for L21 than are the patterns found in Table 1 (a) and (b). Judging by comparison to the analyses for 16S r ...
Table II presents the enzyme activity as well as the... bers of an ordered tetrad. The strains were grown...
... Among the mutant strains investigated, only one turned out to be defective in cross pathway control. This carried the mts (MN1) mutation selected by D.E.A. Catcheside (1978, Neurospora Newsl. 25:17-18) via its 5-methyltryptophan sensitivity. It did not only fail to derepress the OCT and LAT enzymes ...
... Among the mutant strains investigated, only one turned out to be defective in cross pathway control. This carried the mts (MN1) mutation selected by D.E.A. Catcheside (1978, Neurospora Newsl. 25:17-18) via its 5-methyltryptophan sensitivity. It did not only fail to derepress the OCT and LAT enzymes ...
Nucleic Acids: RNA and chemistry
... # base-pairs of DNA in the gene… because that’s how transcription works BUT the number of bases in the unmodified mRNA > # bases in the final mRNA that actually codes for a protein SO there needs to be a process for getting rid of the unwanted bases in the mRNA: that’s what splicing is! ...
... # base-pairs of DNA in the gene… because that’s how transcription works BUT the number of bases in the unmodified mRNA > # bases in the final mRNA that actually codes for a protein SO there needs to be a process for getting rid of the unwanted bases in the mRNA: that’s what splicing is! ...
The Methylation Cycle and Mental Health by Phyllis D. Light, MA
... present and closer to balance. Whether someone is already taking medication or are considering natural options, being equipped with current information can help make well informed decisions for improved mental health. Methylation Methylation is not one specific reaction that occurs in one location i ...
... present and closer to balance. Whether someone is already taking medication or are considering natural options, being equipped with current information can help make well informed decisions for improved mental health. Methylation Methylation is not one specific reaction that occurs in one location i ...
Chapters 5, 7, 11, 17 ppt
... Disruption of protein structure is denaturation (reverse is renaturation) Denaturation does not disrupt primary protein structure ...
... Disruption of protein structure is denaturation (reverse is renaturation) Denaturation does not disrupt primary protein structure ...
Characterization of the amino acid response element within the
... Among these genes are those that contain AAREs (AAR elements) that mediate the enhanced transcription (reviewed in [11]), and function as enhancer elements [12,13]. AARE-binding proteins have only been reported for two genes, ASNS (asparagine synthetase) and CHOP [C/EBP (CCAAT/enhancerbinding protei ...
... Among these genes are those that contain AAREs (AAR elements) that mediate the enhanced transcription (reviewed in [11]), and function as enhancer elements [12,13]. AARE-binding proteins have only been reported for two genes, ASNS (asparagine synthetase) and CHOP [C/EBP (CCAAT/enhancerbinding protei ...
chapter 16: the molecular basis of inheritance
... 10) Explain how RNA polymerase recognizes where transcription should begin. Describe the promoter, the terminator, and the transcription unit. 11) Explain the general process of transcription, including the three major steps of initiation, elongation, and termination. 12) Explain how RNA is modified ...
... 10) Explain how RNA polymerase recognizes where transcription should begin. Describe the promoter, the terminator, and the transcription unit. 11) Explain the general process of transcription, including the three major steps of initiation, elongation, and termination. 12) Explain how RNA is modified ...
Bolsum and PAM Matrix
... associated with possible substitutions. • However, similarity does not necessarily imply common ancestor or visa versa Zvelebil and Baum (2008 p. 74) suggest this can occur in convergent evolution/divergent evolution. • So the results need to be contextualised the findings of alignment tests. (bat a ...
... associated with possible substitutions. • However, similarity does not necessarily imply common ancestor or visa versa Zvelebil and Baum (2008 p. 74) suggest this can occur in convergent evolution/divergent evolution. • So the results need to be contextualised the findings of alignment tests. (bat a ...
IvDimitrov_slides
... 684 non-allergen from food origin 1157 non-allergens from inhalant origin 553 non-allergens from species with toxins, venom or salivary allergens ...
... 684 non-allergen from food origin 1157 non-allergens from inhalant origin 553 non-allergens from species with toxins, venom or salivary allergens ...
Full Text - Science and Education Publishing
... prefers to be in another secondary structure, therefore the local conformation will be slightly destabilized. The wildtype residue is not conserved at this position, while the mutant residue was not among the residue types observed at this position in other, homologous sequences which might indicate ...
... prefers to be in another secondary structure, therefore the local conformation will be slightly destabilized. The wildtype residue is not conserved at this position, while the mutant residue was not among the residue types observed at this position in other, homologous sequences which might indicate ...
Laboratory 9 Protein assay
... Proteins are also a functional component of enzymes, hormones, antibodies, etc. they are used for energy only when carbohydrates and fats are not available. An enzyme is any protein that acts as a catalyst in living organisms. A catalyst is a chemical that mediates or speeds up a specific chemical r ...
... Proteins are also a functional component of enzymes, hormones, antibodies, etc. they are used for energy only when carbohydrates and fats are not available. An enzyme is any protein that acts as a catalyst in living organisms. A catalyst is a chemical that mediates or speeds up a specific chemical r ...
OPTIMIZER: a web server for optimizing the codon usage of DNA
... type of sequence introduced (DNA or protein) and the reference set chosen, different optimization methods are available (see below for a description of the optimization methods). Calculation of the reference sets One of the main features of the OPTIMIZER server is that it contains a series of pre-com ...
... type of sequence introduced (DNA or protein) and the reference set chosen, different optimization methods are available (see below for a description of the optimization methods). Calculation of the reference sets One of the main features of the OPTIMIZER server is that it contains a series of pre-com ...
Gene expression: Transcription
... Different types and levels of sigma factors influence the level and dynamics of gene expression (how much and efficiency). ...
... Different types and levels of sigma factors influence the level and dynamics of gene expression (how much and efficiency). ...
Protein and proteome analytics
... infections up to systemic candidiasis. To identify the proteins which are important for the pathogen’s infection potential, differential proteome analyses with 2D-PAGE were performed at Fraunhofer IGB. In these investigations, the infection was simulated by C. albicans on human epithelial tissues in ...
... infections up to systemic candidiasis. To identify the proteins which are important for the pathogen’s infection potential, differential proteome analyses with 2D-PAGE were performed at Fraunhofer IGB. In these investigations, the infection was simulated by C. albicans on human epithelial tissues in ...
slides - NMRbox
... As shown, the Native, G0F, and Deglycosylated samples are well-clustered. Note also that the NUS reconstructions are systematically different from the conventional data. In practice, this kind of PCA analysis is very sensitive to processing details such as baseline correction and phasing. ...
... As shown, the Native, G0F, and Deglycosylated samples are well-clustered. Note also that the NUS reconstructions are systematically different from the conventional data. In practice, this kind of PCA analysis is very sensitive to processing details such as baseline correction and phasing. ...
Lactic Acid Bacteria
... to amplify one or more DNA fragments, located by specific sequences. The PCR technique uses two oligonucleotide primers, chosen for their complementary sequences: each one is complementary to a single strand of the DNA target. ...
... to amplify one or more DNA fragments, located by specific sequences. The PCR technique uses two oligonucleotide primers, chosen for their complementary sequences: each one is complementary to a single strand of the DNA target. ...
View as PDF document
... one sensitive, and the other resistant, to insecticides. They discover that there are 28 nucleotide differences between the two strains. Next, they align the protein sequences, and discover that there is only ONE difference between the two strains. This activity demonstrates silent mutations – chang ...
... one sensitive, and the other resistant, to insecticides. They discover that there are 28 nucleotide differences between the two strains. Next, they align the protein sequences, and discover that there is only ONE difference between the two strains. This activity demonstrates silent mutations – chang ...
A program for annotating and predicting the effects of single
... We describe a new computer program, SnpEff, for rapidly categorizing the effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and other variants such as multiple nucleotide polymorphism (MNPs) and insertion-deletions (InDels), in whole genome sequences. Once a genome is sequenced, the SnpEff program ca ...
... We describe a new computer program, SnpEff, for rapidly categorizing the effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and other variants such as multiple nucleotide polymorphism (MNPs) and insertion-deletions (InDels), in whole genome sequences. Once a genome is sequenced, the SnpEff program ca ...
Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation
... of the polypeptides of hemoglobin. The numbers under the RNA refer to the codons. β globin is 146 amino acids long. The β globin gene and its pre mRNA transcript have three exons corresponding to sequences that will leave the nucleus as RNA. (The 5’ UTR and 3’ UTR are parts of exons because they are ...
... of the polypeptides of hemoglobin. The numbers under the RNA refer to the codons. β globin is 146 amino acids long. The β globin gene and its pre mRNA transcript have three exons corresponding to sequences that will leave the nucleus as RNA. (The 5’ UTR and 3’ UTR are parts of exons because they are ...
Cheese Flavor and the Genomics of Lactic Acid Bacteria
... cheese is consumed. Second, some of the lowmolecular-weight peptides produced in these reactions directly affect flavor, but this consequence is generally negative since these peptides impart bitterness. Third, the free amino acids that are liberated can also directly affect flavor. For instance, gl ...
... cheese is consumed. Second, some of the lowmolecular-weight peptides produced in these reactions directly affect flavor, but this consequence is generally negative since these peptides impart bitterness. Third, the free amino acids that are liberated can also directly affect flavor. For instance, gl ...
Variation – Mutations
... chances of the mutated gene being reproduced will be less than that of the gene from an unaffected individual. In other words, essential genes and their expression are under stiff selection pressure to remain functional, hence they are conserved within a species and across species. 5. Explain why mo ...
... chances of the mutated gene being reproduced will be less than that of the gene from an unaffected individual. In other words, essential genes and their expression are under stiff selection pressure to remain functional, hence they are conserved within a species and across species. 5. Explain why mo ...
Expanded genetic code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 encoded proteinogenic amino acids.The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: the non-standard amino acid to encode, an unused codon to adopt, a tRNA that recognises this codon, and a tRNA synthase that recognises only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid.Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science.