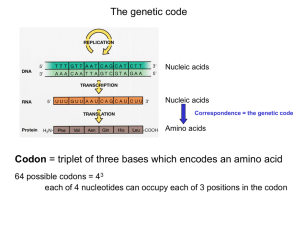
Study Questions for Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein
... RNA splicing takes out sections of mRNA that are not coding for a section of the protein; introns are spliced out and exons are then joined together to make a continuous coding sequence 12) Introns (non-coding regions) were once thought to be “junk DNA” but now it is thought that they do have biolog ...
... RNA splicing takes out sections of mRNA that are not coding for a section of the protein; introns are spliced out and exons are then joined together to make a continuous coding sequence 12) Introns (non-coding regions) were once thought to be “junk DNA” but now it is thought that they do have biolog ...
Chapter_17_answers
... tRNA (transfer RNA) translates the mRNA code by transferring amino acids within the cytoplasm to the ribosome o each type of tRNA links a specific codon wth its corresponding amino acid o anticodon: sequence of tRNA complementary to mRNA codon o made in the nucleus during transcription o strand of ...
... tRNA (transfer RNA) translates the mRNA code by transferring amino acids within the cytoplasm to the ribosome o each type of tRNA links a specific codon wth its corresponding amino acid o anticodon: sequence of tRNA complementary to mRNA codon o made in the nucleus during transcription o strand of ...
- thevignanam
... • If a protein is made up of more than one polypeptide chain it is said to have quaternary structure. • This refers to the spatial arrangement of the polypeptide subunits and the nature of the interactions between them. ...
... • If a protein is made up of more than one polypeptide chain it is said to have quaternary structure. • This refers to the spatial arrangement of the polypeptide subunits and the nature of the interactions between them. ...
DNA, RNA, and Protein
... mRNA docks on ribosome. Its 1st codon is AUG tRNA with met binds via its anticodon UAC. tRNA with its amino binds to 2nd codon. Ribosome detaches met from 1st tRNA. Peptide bond forms between met & 2nd amino acid. First tRNA exits the ribosome & 3rd tRNA enters. Elongation continues until reaches st ...
... mRNA docks on ribosome. Its 1st codon is AUG tRNA with met binds via its anticodon UAC. tRNA with its amino binds to 2nd codon. Ribosome detaches met from 1st tRNA. Peptide bond forms between met & 2nd amino acid. First tRNA exits the ribosome & 3rd tRNA enters. Elongation continues until reaches st ...
Biology Today is Monday Aug 31, 2015
... A scientist removed the cell membranes from bacteria cells in a culture. She analyzed the cell membranes for specific molecules. Which of these was probably the most common type of molecule present in the bacteria cell membranes? ...
... A scientist removed the cell membranes from bacteria cells in a culture. She analyzed the cell membranes for specific molecules. Which of these was probably the most common type of molecule present in the bacteria cell membranes? ...
Carbon-Based Molecules
... Carbon has unique bonding properties Carbon = building block of life because it makes ...
... Carbon has unique bonding properties Carbon = building block of life because it makes ...
The Body`s Fundamental Building Blocks
... What are amino acids and why are they important? Known as the “building blocks” of proteins, amino acids have many important functions in the body including the regulation of muscle and hormone activity and the formation and maintenance of every tissue in the body (i.e., bone, ligaments, tendons, mu ...
... What are amino acids and why are they important? Known as the “building blocks” of proteins, amino acids have many important functions in the body including the regulation of muscle and hormone activity and the formation and maintenance of every tissue in the body (i.e., bone, ligaments, tendons, mu ...
AP Biology
... There are only 20 different amino acids Most amino acids correspond to more than one codon ...
... There are only 20 different amino acids Most amino acids correspond to more than one codon ...
How does this relate to the number of amino acids?
... The Genetic Code • Groups of 3 DNA nucleotides are called triplets and each represents an amino acid or an instruction to “start” or “stop”. – There are 4 nucleotides, so how many possible combinations of 3 are there? – How does this relate to the number of amino acids? – The code is redundant. ...
... The Genetic Code • Groups of 3 DNA nucleotides are called triplets and each represents an amino acid or an instruction to “start” or “stop”. – There are 4 nucleotides, so how many possible combinations of 3 are there? – How does this relate to the number of amino acids? – The code is redundant. ...
Protein Synthesis
... The sequence (order) of bases in a strand of DNA makes the code for building proteins. EX: The three bases “CCA” form the code for the amino acid proline. A long string of amino acids forms a protein. Each gene is usually a set of instructions for making a protein. Proteins are responsible for most ...
... The sequence (order) of bases in a strand of DNA makes the code for building proteins. EX: The three bases “CCA” form the code for the amino acid proline. A long string of amino acids forms a protein. Each gene is usually a set of instructions for making a protein. Proteins are responsible for most ...
AUG
... 61 codons encode amino acids, 3 codons do not specify amino acids Specialized codons: - for start of translation - AUG - for STOP - UAA, UAG, UGA 61 codons encode 20 amino acids - most amino acids are specified by more than one codon - degeneracy of the genetic code ...
... 61 codons encode amino acids, 3 codons do not specify amino acids Specialized codons: - for start of translation - AUG - for STOP - UAA, UAG, UGA 61 codons encode 20 amino acids - most amino acids are specified by more than one codon - degeneracy of the genetic code ...
From DNA to Protein
... • If moved from an aqueous environment to a nonpolar organic solvent, the protein will turn inside out • Chemicals can disrupt disulfide and hydrogen bonds that stabilize secondary and tertiary structure ...
... • If moved from an aqueous environment to a nonpolar organic solvent, the protein will turn inside out • Chemicals can disrupt disulfide and hydrogen bonds that stabilize secondary and tertiary structure ...
RNA codons and correlant Amino Acids
... half of your code was in the head of a sperm which fused with your other half of your code in the centre of an egg to form a single cell a single code - the zygote. This single cell then multiplied table.jpg with along with its code - through the process of mitosis to form the trillions of cells and ...
... half of your code was in the head of a sperm which fused with your other half of your code in the centre of an egg to form a single cell a single code - the zygote. This single cell then multiplied table.jpg with along with its code - through the process of mitosis to form the trillions of cells and ...
Title of Assignment:
... 3. A multicellular organism develops from a single zygote, and its phenotype depends on its genotype, which is established at fertilization. 4. Genes are a set of instructions encoded in the DNA sequence of each organism that specify the sequence of amino acids in proteins characteristic of that org ...
... 3. A multicellular organism develops from a single zygote, and its phenotype depends on its genotype, which is established at fertilization. 4. Genes are a set of instructions encoded in the DNA sequence of each organism that specify the sequence of amino acids in proteins characteristic of that org ...
1) In a single molecule of water, the two hydrogen atoms are bonded
... Starting at the level of the gene, describe how a secretory protein called pepsinogen, a digestive enzyme, is made, modified and secreted into the stomach. Be sure to discuss how and where every macromolecule is made starting at the gene level including the ribosome and tRNA. Be sure to include the ...
... Starting at the level of the gene, describe how a secretory protein called pepsinogen, a digestive enzyme, is made, modified and secreted into the stomach. Be sure to discuss how and where every macromolecule is made starting at the gene level including the ribosome and tRNA. Be sure to include the ...
AminoSelect - Moss Nutrition
... The human body is not efficient at storing excess amino acids for later use; therefore, amino acids must be consumed daily. Ideally, the typical American diet would provide sufficient quantities of essential amino acids but numerous metabolic and environmental factors (high stress levels, illness or ...
... The human body is not efficient at storing excess amino acids for later use; therefore, amino acids must be consumed daily. Ideally, the typical American diet would provide sufficient quantities of essential amino acids but numerous metabolic and environmental factors (high stress levels, illness or ...
1 Protein Structure I I. Proteins are made up of amino acids. Amino
... I. Proteins are made up of amino acids. Amino acids share a general structure: COOH H 2N ...
... I. Proteins are made up of amino acids. Amino acids share a general structure: COOH H 2N ...
Proteins and Genes
... Proteins are used by cells to build structures and are used in chemical activities. Enzymes are proteins that aid in chemical reactions such as digestion and cellular respiration. Proteins are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. They also contain nitrogen and some sulphur. They help build cell ...
... Proteins are used by cells to build structures and are used in chemical activities. Enzymes are proteins that aid in chemical reactions such as digestion and cellular respiration. Proteins are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. They also contain nitrogen and some sulphur. They help build cell ...
Genes
... • The alphabet of RNA is A, U, G and C • Within a molecule of mRNA, groups of 3 sequential nucleotides form meaningful “words” called codons – complementary to triplets in the template strand of the gene that was transcribed by RNA polymerase • each codon is a code for an amino acid of the protein c ...
... • The alphabet of RNA is A, U, G and C • Within a molecule of mRNA, groups of 3 sequential nucleotides form meaningful “words” called codons – complementary to triplets in the template strand of the gene that was transcribed by RNA polymerase • each codon is a code for an amino acid of the protein c ...
protein synthesis - Science with Mrs Beggs
... information • tRNA has an anti-codon which matches a specific codon of mRNA • Each tRNA attaches to a specific amino acid that compliments its anti-codon • There are 20 different tRNA types (one for each type of amino acid) ...
... information • tRNA has an anti-codon which matches a specific codon of mRNA • Each tRNA attaches to a specific amino acid that compliments its anti-codon • There are 20 different tRNA types (one for each type of amino acid) ...
Translation/Genetic Code
... The genetic code is degenerate There are >20 but < 64 tRNAs How does the same tRNA bind to different codons? ...
... The genetic code is degenerate There are >20 but < 64 tRNAs How does the same tRNA bind to different codons? ...
Translation
... The genetic code is degenerate There are >20 but < 64 tRNAs How does the same tRNA bind to different codons? ...
... The genetic code is degenerate There are >20 but < 64 tRNAs How does the same tRNA bind to different codons? ...
Expanded genetic code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 encoded proteinogenic amino acids.The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: the non-standard amino acid to encode, an unused codon to adopt, a tRNA that recognises this codon, and a tRNA synthase that recognises only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid.Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science.