DNA Structure Copy Cats Protein Nucleic Acids RANDOM!
... What is the purpose of the start codon? What is the purpose of a stop codon? ...
... What is the purpose of the start codon? What is the purpose of a stop codon? ...
DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis
... Imagine that you are a mechanic. The repair manual that you use is the DNA ladder. If you wanted to copy the instructions to install a radio in your car, would you copy the entire repair manual? NO!!! You would only copy the portion pertaining to installing the radio. That is what transcription ...
... Imagine that you are a mechanic. The repair manual that you use is the DNA ladder. If you wanted to copy the instructions to install a radio in your car, would you copy the entire repair manual? NO!!! You would only copy the portion pertaining to installing the radio. That is what transcription ...
Overview: The Flow of Genetic Information • The information content
... – First: a correct match between a tRNA and an amino acid, done by the enzyme aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase – Second: a correct match between the tRNA anticodon and an mRNA codon • Flexible pairing at the third base of a codon is called wobble and allows some tRNAs to bind to more than one codon Riboso ...
... – First: a correct match between a tRNA and an amino acid, done by the enzyme aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase – Second: a correct match between the tRNA anticodon and an mRNA codon • Flexible pairing at the third base of a codon is called wobble and allows some tRNAs to bind to more than one codon Riboso ...
Non-Living Inclusions
... They are soluble nitrogenous substances secreted by the protoplasm. They are digestive in function and convert the insoluble substances into soluble and complex compounds into simple ones, e.g. diastase converts starch into sugar, so that because of the action of this enzyme an insoluble substan ...
... They are soluble nitrogenous substances secreted by the protoplasm. They are digestive in function and convert the insoluble substances into soluble and complex compounds into simple ones, e.g. diastase converts starch into sugar, so that because of the action of this enzyme an insoluble substan ...
SAM Teachers Guide - RI
... The Proteins and Nucleic Acids activity focuses on the basic structure of protein, DNA and RNA—the monomers, the distribution of charges and polarity, and how charged surfaces contribute to their shape and function. Atomic Structure introduces students to the positive and negative parts of atoms. ...
... The Proteins and Nucleic Acids activity focuses on the basic structure of protein, DNA and RNA—the monomers, the distribution of charges and polarity, and how charged surfaces contribute to their shape and function. Atomic Structure introduces students to the positive and negative parts of atoms. ...
Chapter 3 Everyday Chemistry of Life Chemistry is crucial Biology
... o Atoms in this type of bond share electrons o This results in stable outer valence shells for all atoms involved o Covalent bonds are very important for biology o Most covalent bonds in humans involve C, H, O, N o In most of these bonds, the atoms share the electrons evenly ... except when hydrogen ...
... o Atoms in this type of bond share electrons o This results in stable outer valence shells for all atoms involved o Covalent bonds are very important for biology o Most covalent bonds in humans involve C, H, O, N o In most of these bonds, the atoms share the electrons evenly ... except when hydrogen ...
C11- DNA and Genes
... Translating the m-RNA Code • T-RNA leaves amino acid in position to form peptide bond with previous amino acid • The ribosome continues to assemble amino acids until stop codon is reached. • Translation is complete • Amino acid chain is released & twists into complex folded shape of protein • Becom ...
... Translating the m-RNA Code • T-RNA leaves amino acid in position to form peptide bond with previous amino acid • The ribosome continues to assemble amino acids until stop codon is reached. • Translation is complete • Amino acid chain is released & twists into complex folded shape of protein • Becom ...
C2005/F2401 `09
... but it is nonsense, not missense – it creates a premature stop codon. B-3. See the code table. The two correct choices are synonymous, although CGA to AGA doesn’t look it at first. (Note that the ability to use the same tRNA or a different one is not important here. That’s an issue of wobble, and th ...
... but it is nonsense, not missense – it creates a premature stop codon. B-3. See the code table. The two correct choices are synonymous, although CGA to AGA doesn’t look it at first. (Note that the ability to use the same tRNA or a different one is not important here. That’s an issue of wobble, and th ...
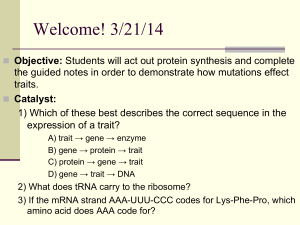
Welcome! 3/21/14
... does not always result in a visible change. n Mutations may change the DNA but not the amino acid n That mutations MAY result in a change in the PHENOTYPE of an organism, but not always. n Think-Pair-Share n WHY ...
... does not always result in a visible change. n Mutations may change the DNA but not the amino acid n That mutations MAY result in a change in the PHENOTYPE of an organism, but not always. n Think-Pair-Share n WHY ...
Planet Earth and Its Environment A 5000
... of the tRNA is able to bind with an amino acid temporarily. Each tRNA molecule will only attach to one particular amino acid. The specific sequence of three bases at the anticodon end determines which amino acid will be carried by that tRNA. ...
... of the tRNA is able to bind with an amino acid temporarily. Each tRNA molecule will only attach to one particular amino acid. The specific sequence of three bases at the anticodon end determines which amino acid will be carried by that tRNA. ...
Mutations and Genetic Disorders
... nucleotides in a gene – alters the expression of the gene’s protein and can affect the cell 2. Chromosomal mutations – changes due to errors in cell division, usually meiosis that alters the structure or number of chromosome in a cell ...
... nucleotides in a gene – alters the expression of the gene’s protein and can affect the cell 2. Chromosomal mutations – changes due to errors in cell division, usually meiosis that alters the structure or number of chromosome in a cell ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... What are hetero polysaccharides? Give an example. ...
... What are hetero polysaccharides? Give an example. ...
Transcription lesson
... Ribonucleic acid Is single-stranded, but can fold back on itself Ribose sugar (not deoxyribose like DNA) Uracil is in place of thymine ...
... Ribonucleic acid Is single-stranded, but can fold back on itself Ribose sugar (not deoxyribose like DNA) Uracil is in place of thymine ...
Rapid communication: Nucleotide sequence of the river buffalo beta
... (5′ GGAAAAAAGGAATTGAGAGCC 3′) designed on the basis of conserved regions, through a multiple alignment of bovine, ovine, caprine, and porcine cDNA sequences. A single and specific PCR product was obtained that was cloned into pMOSblue T-vector (Amersham, U.K.) after purification. Two individual posi ...
... (5′ GGAAAAAAGGAATTGAGAGCC 3′) designed on the basis of conserved regions, through a multiple alignment of bovine, ovine, caprine, and porcine cDNA sequences. A single and specific PCR product was obtained that was cloned into pMOSblue T-vector (Amersham, U.K.) after purification. Two individual posi ...
Slide 1 - Oceanside Moodle
... DNA and RNA molecules Nucleic acids are made up of nucleotides Nucleotides are made up of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a base ...
... DNA and RNA molecules Nucleic acids are made up of nucleotides Nucleotides are made up of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a base ...
Document
... 4. What are the building blocks of DNA? 5. This building block consists of three components. What are they? 6. Name (not just letter) the four nitrogen bases and how the pair. 7. The process that produces two new double helixes that are identical to the original is called? 8. Why does this process t ...
... 4. What are the building blocks of DNA? 5. This building block consists of three components. What are they? 6. Name (not just letter) the four nitrogen bases and how the pair. 7. The process that produces two new double helixes that are identical to the original is called? 8. Why does this process t ...
The Genetic Code and Transcription Chapter 12 Honors Genetics
... • Each “word” in the mRNA strand is composed of a 3-letter sequence called a CODON. • Each CODON specifies a SINGLE Amino Acid. • There is 1 start codon for initiation of protein synthesis and 3 stop codons for ending protein synthesis for a specific protein. • A given amino acid can have more than ...
... • Each “word” in the mRNA strand is composed of a 3-letter sequence called a CODON. • Each CODON specifies a SINGLE Amino Acid. • There is 1 start codon for initiation of protein synthesis and 3 stop codons for ending protein synthesis for a specific protein. • A given amino acid can have more than ...
The Major Transitions in Evolution
... Ribozyme doing peptidyl transfer during protein synthesis in ribosomes • Amino acyl-tRNA synthetases are NOT the most ancient proteins • 20 residues are better than 4 in catalysis ...
... Ribozyme doing peptidyl transfer during protein synthesis in ribosomes • Amino acyl-tRNA synthetases are NOT the most ancient proteins • 20 residues are better than 4 in catalysis ...
Towards and Extended Evolutionary Synthesis
... Ribozyme doing peptidyl transfer during protein synthesis in ribosomes • Amino acyl-tRNA synthetases are NOT the most ancient proteins • 20 residues are better than 4 in catalysis ...
... Ribozyme doing peptidyl transfer during protein synthesis in ribosomes • Amino acyl-tRNA synthetases are NOT the most ancient proteins • 20 residues are better than 4 in catalysis ...
From Gene to Protein
... The subunits exit the nucleus via nuclear pores. The large and small subunits join to form a functional ribosome only when they attach to an mRNA molecule. While very similar in structure and function, prokaryotic and eukaryotic ribosomes have enough differences that certain antibiotic drugs (like t ...
... The subunits exit the nucleus via nuclear pores. The large and small subunits join to form a functional ribosome only when they attach to an mRNA molecule. While very similar in structure and function, prokaryotic and eukaryotic ribosomes have enough differences that certain antibiotic drugs (like t ...
Carbon-Based Molecules
... A polymer is a large molecule, or macromolecule, made of many monomers bonded together. All of the monomers in a polymer may be the same, as they are in starches (like potatoes), or they may be different, as they are in ...
... A polymer is a large molecule, or macromolecule, made of many monomers bonded together. All of the monomers in a polymer may be the same, as they are in starches (like potatoes), or they may be different, as they are in ...
Expanded genetic code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 encoded proteinogenic amino acids.The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: the non-standard amino acid to encode, an unused codon to adopt, a tRNA that recognises this codon, and a tRNA synthase that recognises only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid.Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science.