Multiple Choice, continued
... • Binary stars are pairs of stars that revolve around each other and are held together by gravity. The center of mass, or barycenter, is somewhere between the two stars. • In star systems that have more than two stars, two stars may revolve rapidly around a common barycenter, while a third star revo ...
... • Binary stars are pairs of stars that revolve around each other and are held together by gravity. The center of mass, or barycenter, is somewhere between the two stars. • In star systems that have more than two stars, two stars may revolve rapidly around a common barycenter, while a third star revo ...
The Time of Day
... (Unit 13). Although the Sun’s position determines the day–night cycle, it is not a stable reference for measuring Earth’s spin. We can avoid most of the variation in the day’s length if, instead of using the Sun, we use a star as our reference. For example, if we pick a star that crosses our meridia ...
... (Unit 13). Although the Sun’s position determines the day–night cycle, it is not a stable reference for measuring Earth’s spin. We can avoid most of the variation in the day’s length if, instead of using the Sun, we use a star as our reference. For example, if we pick a star that crosses our meridia ...
Light of the Sun - Beck-Shop
... solar heating of different parts of the Earth produces the winds, which blow from hot to cold regions. The Earth glides through space at exactly the right distance from the Sun for life to thrive on our planet’s surface, whereas other planets in the solar system freeze or fry: We sit in the “comfort ...
... solar heating of different parts of the Earth produces the winds, which blow from hot to cold regions. The Earth glides through space at exactly the right distance from the Sun for life to thrive on our planet’s surface, whereas other planets in the solar system freeze or fry: We sit in the “comfort ...
earth science
... (1) 1.3 billion years (3) 7.9 billion years (2) 4.6 billion years (4) 13.8 billion years ...
... (1) 1.3 billion years (3) 7.9 billion years (2) 4.6 billion years (4) 13.8 billion years ...
1 Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum Lesson title
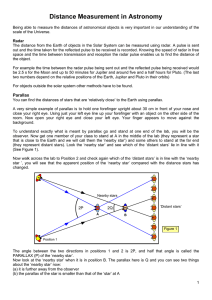
... apparent shift in position. Then they calculate the distance based on a trigonometric relationship between the parallax angle and the “baseline” (the radius of Earth's orbit). Considering that the more distant an object is, the smaller the angle it will make, why would parallax measurements be bette ...
... apparent shift in position. Then they calculate the distance based on a trigonometric relationship between the parallax angle and the “baseline” (the radius of Earth's orbit). Considering that the more distant an object is, the smaller the angle it will make, why would parallax measurements be bette ...
10.1 The Solar Neighborhood Barnard`s Star
... Giant stars have radii between 10 and 100 times the Sun’s. Dwarf stars have radii equal to, or less than, the Sun’s. Supergiant stars have radii more than 100 times the Sun’s. ...
... Giant stars have radii between 10 and 100 times the Sun’s. Dwarf stars have radii equal to, or less than, the Sun’s. Supergiant stars have radii more than 100 times the Sun’s. ...
April, 2004 Observer - Fort Bend Astronomy Club
... from physical evidence of long-period comets entering our planetary system. His interpretation of comet orbital distribution was made using only 19 well-measured orbits. Oort also determined the rotation of the Milky Way galaxy in the 1920’s. The Strange Case Of 3752 Cruithne Near Earth asteroids ar ...
... from physical evidence of long-period comets entering our planetary system. His interpretation of comet orbital distribution was made using only 19 well-measured orbits. Oort also determined the rotation of the Milky Way galaxy in the 1920’s. The Strange Case Of 3752 Cruithne Near Earth asteroids ar ...
PHYS103 Hour Exam No. 1 Page: 1 1 Which of the following
... 7 Einstein’s Theory of Gravity has passed every well-understood observational test for over 100 years. However there are some observations, which are not well-understood. For example, the Pioneer space probe is showing tiny deviations from its predicted course as it leaves the neighborhood of our so ...
... 7 Einstein’s Theory of Gravity has passed every well-understood observational test for over 100 years. However there are some observations, which are not well-understood. For example, the Pioneer space probe is showing tiny deviations from its predicted course as it leaves the neighborhood of our so ...
TLW design a model that describes the position and relationship of
... Our solar system is made up of planets, dwarf planets, moons, asteroids and comets. Planets, dwarf planets, plutoids, comets and asteroids orbit the Sun. Moons orbit the planets. There are currently eight planets and three or four (depending on the source) identified plutoids and dwarf planets in o ...
... Our solar system is made up of planets, dwarf planets, moons, asteroids and comets. Planets, dwarf planets, plutoids, comets and asteroids orbit the Sun. Moons orbit the planets. There are currently eight planets and three or four (depending on the source) identified plutoids and dwarf planets in o ...
Coordinate Systems for Astronomy or: How to get
... Our “year” is technically the Earth's “tropical period”. This is the time that elapses between two alignments of its axis of rotation with the Sun, or 365.242 days. The Earth's orbital (sidereal) period around the Sun is 365.256 days. The 0.014 day (= 20 minutes) difference is caused by precession, ...
... Our “year” is technically the Earth's “tropical period”. This is the time that elapses between two alignments of its axis of rotation with the Sun, or 365.242 days. The Earth's orbital (sidereal) period around the Sun is 365.256 days. The 0.014 day (= 20 minutes) difference is caused by precession, ...
Paper - Astrophysics - University of Oxford
... Next we calculate the time needed to complete the search and follow-up campaign. A 50-field survey is suitable to obtain a statistically significant number of SNe for each z-bin. The survey would consist of imaging 50 fields (200 sq arcmin) in the J(1h each), H(1h each) and K(1h each) bands at 4 di ...
... Next we calculate the time needed to complete the search and follow-up campaign. A 50-field survey is suitable to obtain a statistically significant number of SNe for each z-bin. The survey would consist of imaging 50 fields (200 sq arcmin) in the J(1h each), H(1h each) and K(1h each) bands at 4 di ...
Stars and Stellar Evolution
... = becomes 1 million times brighter (rare) Consumes most of its fuel -> gas pressure does not balance gravitational pull --> collapses --> huge implosion --> shock wave moves out and destroys the star (outer shell blasted into space) ...
... = becomes 1 million times brighter (rare) Consumes most of its fuel -> gas pressure does not balance gravitational pull --> collapses --> huge implosion --> shock wave moves out and destroys the star (outer shell blasted into space) ...
Chapter 5 Gravitational fields - crypt
... The gravitational field strength on the surface of the Earth is 9.81 N kg–1. A satellite in a geostationary orbit round the Earth experiences a gravitational field strength of 0.225 N kg–1. Determine the orbital radius r of the satellite from the centre of the Earth in terms of the radius of the Ear ...
... The gravitational field strength on the surface of the Earth is 9.81 N kg–1. A satellite in a geostationary orbit round the Earth experiences a gravitational field strength of 0.225 N kg–1. Determine the orbital radius r of the satellite from the centre of the Earth in terms of the radius of the Ear ...
meteor shower
... • The stream of debris is called the Perseid cloud and stretches along the orbit of the comet Swift-Tuttle. The cloud consists of particles ejected by the comet as it travels on its 130-year orbit. • Most of the dust in the cloud today is around a thousand years old. However, there is also a relativ ...
... • The stream of debris is called the Perseid cloud and stretches along the orbit of the comet Swift-Tuttle. The cloud consists of particles ejected by the comet as it travels on its 130-year orbit. • Most of the dust in the cloud today is around a thousand years old. However, there is also a relativ ...
Astronomy
... 31. ________ The brightness of a star as seen by human eyes on Earth. 32. ________ The tilt of the earth in relationship to the sun. 33. ________ A constellation so close to one of the celestial poles that it never sets or rises. 34. ________ The imaginary line around the sky directly above Earth’s ...
... 31. ________ The brightness of a star as seen by human eyes on Earth. 32. ________ The tilt of the earth in relationship to the sun. 33. ________ A constellation so close to one of the celestial poles that it never sets or rises. 34. ________ The imaginary line around the sky directly above Earth’s ...
Name: Date Assigned: 3/25/13 Period: This scavenger hunt will
... 11) a) Define “comet.” b) draw a picture of a comet with the parts labeled. (8-4.1) 12) a) Explain what an asteroid is. B) Include a picture of the asteroid belt. (8-4.1) 13) a) make a chart explaining the differences between a meteor, a meteoroid, and a meteorite. B) find and label a picture of a m ...
... 11) a) Define “comet.” b) draw a picture of a comet with the parts labeled. (8-4.1) 12) a) Explain what an asteroid is. B) Include a picture of the asteroid belt. (8-4.1) 13) a) make a chart explaining the differences between a meteor, a meteoroid, and a meteorite. B) find and label a picture of a m ...
S T A R S
... about 68 light years away. Aldebaran is one of the few first magnitude stars that may be occulted by the moon. The disappearance of the star is startlingly abrupt, particularly so at the moons dark edge. The V shaped central group is the Hyades star cluster group and represents the bull’s head – Ald ...
... about 68 light years away. Aldebaran is one of the few first magnitude stars that may be occulted by the moon. The disappearance of the star is startlingly abrupt, particularly so at the moons dark edge. The V shaped central group is the Hyades star cluster group and represents the bull’s head – Ald ...
Why Aren`t All Galaxies Barred?
... motion, implies that most stars would have highly eccentric orbits. We have no direct measurements of the velocity dispersion of stars in the disk of other galaxies, although we do know that close to the sun in the Milky Way, the disk stars have a dispersion of only 35 to 40 km/so Galaxies seen edge ...
... motion, implies that most stars would have highly eccentric orbits. We have no direct measurements of the velocity dispersion of stars in the disk of other galaxies, although we do know that close to the sun in the Milky Way, the disk stars have a dispersion of only 35 to 40 km/so Galaxies seen edge ...
Formation and Detectability of Terrestrial Planets around
... α Cen system was studied by Robrade, Schmitt, & Favata (2005) using X-ray data taken with XMM-Newton over a period of two years. They find that α Cen A’s X-ray luminosity declined by a factor of ten in this time period, an indication of a moderate coronal activity. In turn, α Cen B’s X-ray brightnes ...
... α Cen system was studied by Robrade, Schmitt, & Favata (2005) using X-ray data taken with XMM-Newton over a period of two years. They find that α Cen A’s X-ray luminosity declined by a factor of ten in this time period, an indication of a moderate coronal activity. In turn, α Cen B’s X-ray brightnes ...
Front Matter - Assets - Cambridge University Press
... The more effective illustrations from previous spacecraft have been retained, without an excessive increase in the length of the book, including those from the Apollo missions to the Earth’s Moon, the Viking 1 and 2 missions to Mars, the Mars Global Surveyor, the Voyager 1 and 2 missions to the four ...
... The more effective illustrations from previous spacecraft have been retained, without an excessive increase in the length of the book, including those from the Apollo missions to the Earth’s Moon, the Viking 1 and 2 missions to Mars, the Mars Global Surveyor, the Voyager 1 and 2 missions to the four ...
Chapter 9 “The Family of Stars “
... Mars' orbit is larger than Earth's, and stars would show a larger parallax when observed from Mars as compared to Earth. We would be able to determine the distance to nearby stars more accurately and determine the distance to stars that are currently too far to be measured using parallax from Earth. ...
... Mars' orbit is larger than Earth's, and stars would show a larger parallax when observed from Mars as compared to Earth. We would be able to determine the distance to nearby stars more accurately and determine the distance to stars that are currently too far to be measured using parallax from Earth. ...
Rare Earth hypothesis

In planetary astronomy and astrobiology, the Rare Earth Hypothesis argues that the origin of life and the evolution of biological complexity such as sexually reproducing, multicellular organisms on Earth (and, subsequently, human intelligence) required an improbable combination of astrophysical and geological events and circumstances. The hypothesis argues that complex extraterrestrial life is a very improbable phenomenon and likely to be extremely rare. The term ""Rare Earth"" originates from Rare Earth: Why Complex Life Is Uncommon in the Universe (2000), a book by Peter Ward, a geologist and paleontologist, and Donald E. Brownlee, an astronomer and astrobiologist, both faculty members at the University of Washington.An alternative view point was argued by Carl Sagan and Frank Drake, among others. It holds that Earth is a typical rocky planet in a typical planetary system, located in a non-exceptional region of a common barred-spiral galaxy. Given the principle of mediocrity (also called the Copernican principle), it is probable that the universe teems with complex life. Ward and Brownlee argue to the contrary: that planets, planetary systems, and galactic regions that are as friendly to complex life as are the Earth, the Solar System, and our region of the Milky Way are very rare.