* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download meteor shower
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Directed panspermia wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Sample-return mission wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Impact event wikipedia , lookup
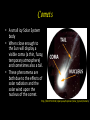
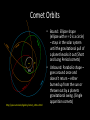
When Opportunity Knocks You must answer The Perseid Meteor Shower is going on NOW Perseid meteor from the ISS (2011) A few topics to cover first • Comets Comet Swift Tuttle • Meteoroids • Meteors • Meteor Showers Dec 15, 1992 http://cometography.com/pcomets/109p.html • Meteorites Comets • A small icy Solar System body • When close enough to the Sun will display a visible coma (a thin, fuzzy, temporary atmosphere) and sometimes also a tail. • These phenomena are both due to the effects of solar radiation and the solar wind upon the nucleus of the comet. http://64.107.216.64/cyberspace/Explorers/Solar_System/Comets/ Comet Orbits http://epoxi.umd.edu/3gallery/comet_orbits.shtml • Bound: Ellipse shape (ellipse with e = 0 is a circle) – stays in the solar system until the gravitational pull of a planet knocks it out (Short and Long Period comets) • Unbound: Parabolic shape – goes around once and doesn’t return – either burned up from the sun or thrown out by a planets gravitational swing. (Single apparition comets) Comets • http://spaceplace.nasa.gov/tails-of-wonder/# Comets • Comet nuclei range from Comet Temple 1 a few hundred meters to tens of kilometers across and are composed of loose collections of ice, dust, and small rocky particles. • Comets have been observed since ancient Visited in 2005 by Deep Impact Space Probe times and have traditionally been considered bad omens. http://epoxi.umd.edu/3gallery/comet_orbits.shtml Comet Temple 1 • http://spaceplace.nasa.gov/review/cometnucleus/ Deep Impact http://spaceplace.nasa.gov/comet-impact/ Meteoroids • As of 2011 the International Astronomical Union officially defines a meteoroid as "a solid object moving in interplanetary space, of a size considerably smaller than an asteroid and considerably larger than an atom". • However, very small meteoroids are called micrometeoroids. Meteor – or a falling star (but no star) • A meteor is the visible path of a meteoroid that has entered the Earth's atmosphere. • Meteors typically occur in the mesosphere, and most range in altitude from 75 km to 100 km. • Millions of meteors occur in the Earth's atmosphere every day. • Most meteoroids that cause meteors are about the size of a pebble. • They become visible between about 40 and 75 miles (65 and 120 kilometers) above the Earth. • They disintegrate at altitudes of 30 to 60 miles (50 to 95 kilometers). Leonid Meteor Shower 2010 Meteor Showers • A meteor shower is the result of an interaction between a planet, such as Earth, and streams of debris from a comet. • Meteor showers are known to occur when the Earth passes near the orbit of a comet and so are then associated with that comet. • We know that as a comet gets closer to the Sun, it heats up and sheds some dust and debris. • Any of the dust or debris that enters the Earth's atmosphere, burns up and we see this as a meteor. Meteor Showers • A meteor shower is a celestial event in which a number of meteors are observed to radiate from one point in the night sky. 2012 Perseids • The Perseids: is the name of the meteor shower associated with the comet Swift-Tuttle. • The Perseids are so-called because the point they appear to come from, called the radiant, lies in the constellation Perseus, • The stream of debris is called the Perseid cloud and stretches along the orbit of the comet Swift-Tuttle. The cloud consists of particles ejected by the comet as it travels on its 130-year orbit. • Most of the dust in the cloud today is around a thousand years old. However, there is also a relatively young filament of dust in the stream that was pulled off the comet in 1862. The rate of meteors originating from this filament is much higher than for the older part of the stream. Perseid Meteor Shower Where to look in the sky http://shadowandsubstance.com/ • When is the best time to view the Perseids? • How many shooting stars should I be able to see? Lets check the FLUXTIMATOR http://leonid.arc.nasa.gov/estimator.html • Be aware: The moon will be near full. The light from the moon will make it difficult for you to see meteors. • Good news: The full moon doesn’t rise until midnight – so you should have a nice dark sky from 9:00 pm – 12:00 am. You should still see about 5 meteors per hour Find Tips for meteor watching here: • http://stardate.org/nightsky/meteors Meteor Counting We can use our computers to count meteors! This is a seriously cool set up. Practice it first. • http://meteor-counting.heroku.com/ NEO’s Meteorite • If a meteor doesn’t completely burn up in the Earth’s atmosphere and lands on the Earth it is called a meteorite. • Impact Craters • Believe it or not… http://titaniumringco.com/meteorite-inlaytitanium-rings15/?gclid=CLqhsK22xqoCFY125QodWwRoyg More on Meteor Showers • http://spaceplace.nasa.gov/meteor-shower/