Evidence for a signature of the galactic bar in the solar neighbourhood
... 1 kpc-diameter at a distance R = R0 = 8 kpc from the center of the Galaxy. We follow the mean radial motion u of particles as a function of time across this region. In the considered models, built with particules which essentially represent the old disc, the global deviation with respect to axisymme ...
... 1 kpc-diameter at a distance R = R0 = 8 kpc from the center of the Galaxy. We follow the mean radial motion u of particles as a function of time across this region. In the considered models, built with particules which essentially represent the old disc, the global deviation with respect to axisymme ...
Pathways to Astronomy/Space
... Many visible changes to the old science curriculum are evident, but the most obvious difference is the layout of ordering of the expectations. Previously, the Relating Science to Technology, Society and the Environment (STSE) expectations were listed at the end of the strand’s expectations, but are ...
... Many visible changes to the old science curriculum are evident, but the most obvious difference is the layout of ordering of the expectations. Previously, the Relating Science to Technology, Society and the Environment (STSE) expectations were listed at the end of the strand’s expectations, but are ...
ASBA Yearlongplan Science 8
... Describe the largest moons of each of the outer planets. Describe how comets change when they approach the Sun. Distinguish among comets, meteoroids, and asteroids. Explain that objects from space sometimes impact Earth. Chapter 13: Stars and Galaxies Content: For many years, people have b ...
... Describe the largest moons of each of the outer planets. Describe how comets change when they approach the Sun. Distinguish among comets, meteoroids, and asteroids. Explain that objects from space sometimes impact Earth. Chapter 13: Stars and Galaxies Content: For many years, people have b ...
19. Our Galaxy 19.1 The Milky Way Revealed Our goals for learning
... • What is the significance of a rotation curve that is flat at large distances from the galactic center? • The Milky Way’s flat rotation curve implies that the matter associated with our galaxy extends to large distances from the center. A rotation curve is a plot of the orbital speed of stars or ga ...
... • What is the significance of a rotation curve that is flat at large distances from the galactic center? • The Milky Way’s flat rotation curve implies that the matter associated with our galaxy extends to large distances from the center. A rotation curve is a plot of the orbital speed of stars or ga ...
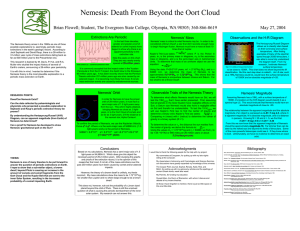
Nemesis - The Evergreen State College
... 65-million years ago. It has been recently shown that the PermianTriassic extinction 251-million years ago was also caused by an asteroid impact. It is becoming more likely that most, if not all, mass extinction events are caused by extraterrestrial sources. ...
... 65-million years ago. It has been recently shown that the PermianTriassic extinction 251-million years ago was also caused by an asteroid impact. It is becoming more likely that most, if not all, mass extinction events are caused by extraterrestrial sources. ...
Astronomical Circumstances
... based on their brightness (magnitude), temperature, receive each moment, so the warmer the planet will get radius, luminosity, mix of colors (spectral class), and (all other things being equal). This being the case, mass. For our purposes, we are going to use mass as around all stars there is a dist ...
... based on their brightness (magnitude), temperature, receive each moment, so the warmer the planet will get radius, luminosity, mix of colors (spectral class), and (all other things being equal). This being the case, mass. For our purposes, we are going to use mass as around all stars there is a dist ...
Galaxies (and stars) in the far infrared: results from the AKARI All
... Supply of metals to the interstellar space II: final life stages of stars The death of light stars : planetary nebulae (PNe) Stars with masses similar to the Sun run out the hydrogen in the core, change their equilibrium structure and expand, and become cool huge stars (red giant branch stars: RGBs ...
... Supply of metals to the interstellar space II: final life stages of stars The death of light stars : planetary nebulae (PNe) Stars with masses similar to the Sun run out the hydrogen in the core, change their equilibrium structure and expand, and become cool huge stars (red giant branch stars: RGBs ...
EvoluGon of high mass stars Solar-‐type stars end their lives by
... Depending on the mass of the progenitor star, the inner core leh behind either forms a neutron star or a black hole. ...
... Depending on the mass of the progenitor star, the inner core leh behind either forms a neutron star or a black hole. ...
Abiotic formation of O $\ mathsf {_2} $ and O $\ mathsf {_3} $ in high
... Both of the “false positives” mentioned above apply to planets that lie outside of the liquid water habitable zone around their parent star. The boundaries of this zone can be estimated to first order from climate models (Kasting et al. 1993), and it should be possible to determine observationally w ...
... Both of the “false positives” mentioned above apply to planets that lie outside of the liquid water habitable zone around their parent star. The boundaries of this zone can be estimated to first order from climate models (Kasting et al. 1993), and it should be possible to determine observationally w ...
Notes for Class 7, March 2
... • We are finding other stars with planets o Present techniques best for planets close to star o So far, too close to star, too hot o If planets around other stars are common, maybe there will be some planets with the right conditions, and maybe some of them will have life ...
... • We are finding other stars with planets o Present techniques best for planets close to star o So far, too close to star, too hot o If planets around other stars are common, maybe there will be some planets with the right conditions, and maybe some of them will have life ...
Publisher: Emily Barrosse Acquisitions Editor: Kelley Tyner
... Though the details can differ, all stars containing less than about ten times the Sun’s mass will have the same fate. As fusion exhausts the hydrogen in their centers, their internal pressure will diminish. Gravity will pull the core in, and the core will heat up again. Hydrogen will begin “burning” ...
... Though the details can differ, all stars containing less than about ten times the Sun’s mass will have the same fate. As fusion exhausts the hydrogen in their centers, their internal pressure will diminish. Gravity will pull the core in, and the core will heat up again. Hydrogen will begin “burning” ...
TISHTRIYA - Earth`s second Sun
... The heliacal rising of Tishtriya in the pre-dawn sky Once in a year the heliacal rising of Tishtriya occurs when it first becomes visible above the eastern horizon for a brief moment just before sunrise, after a period of time when it had not been visible. Each day after the first heliacal rising, t ...
... The heliacal rising of Tishtriya in the pre-dawn sky Once in a year the heliacal rising of Tishtriya occurs when it first becomes visible above the eastern horizon for a brief moment just before sunrise, after a period of time when it had not been visible. Each day after the first heliacal rising, t ...
An Eclectic View of our Milky Way Galaxy
... for simple Galactic rotation. The Sun’s local standard of rest (LSR) velocity is ∼ 14 km s−1 rather than 20 km s−1 , the local circular velocity is 251±9 km s−1 rather than 220 km s−1 , and young groups of stars exhibit a 10–20 km s−1 “kick” relative to what is expected from Galactic rotation. By im ...
... for simple Galactic rotation. The Sun’s local standard of rest (LSR) velocity is ∼ 14 km s−1 rather than 20 km s−1 , the local circular velocity is 251±9 km s−1 rather than 220 km s−1 , and young groups of stars exhibit a 10–20 km s−1 “kick” relative to what is expected from Galactic rotation. By im ...
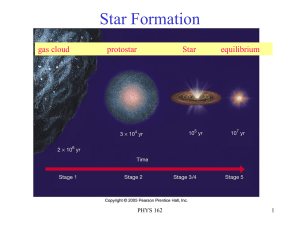
Lecture 15 Star Formation and Evolution 3/7
... about 100,000,000 degrees K for He burning Stars like our Sun remain main sequence longer due to this PHYS 162 ...
... about 100,000,000 degrees K for He burning Stars like our Sun remain main sequence longer due to this PHYS 162 ...
Preview Sample 3
... 6) A million years from now, Alpha Centauri will no longer be the nearest star system to our own. Answer: D 7) If Earth's axis had no tilt, would we still have seasons? Why or why not? Answer: We would no longer have seasons, because the Sun's light would hit at the same angle all throughout the yea ...
... 6) A million years from now, Alpha Centauri will no longer be the nearest star system to our own. Answer: D 7) If Earth's axis had no tilt, would we still have seasons? Why or why not? Answer: We would no longer have seasons, because the Sun's light would hit at the same angle all throughout the yea ...
Rare Earth hypothesis

In planetary astronomy and astrobiology, the Rare Earth Hypothesis argues that the origin of life and the evolution of biological complexity such as sexually reproducing, multicellular organisms on Earth (and, subsequently, human intelligence) required an improbable combination of astrophysical and geological events and circumstances. The hypothesis argues that complex extraterrestrial life is a very improbable phenomenon and likely to be extremely rare. The term ""Rare Earth"" originates from Rare Earth: Why Complex Life Is Uncommon in the Universe (2000), a book by Peter Ward, a geologist and paleontologist, and Donald E. Brownlee, an astronomer and astrobiologist, both faculty members at the University of Washington.An alternative view point was argued by Carl Sagan and Frank Drake, among others. It holds that Earth is a typical rocky planet in a typical planetary system, located in a non-exceptional region of a common barred-spiral galaxy. Given the principle of mediocrity (also called the Copernican principle), it is probable that the universe teems with complex life. Ward and Brownlee argue to the contrary: that planets, planetary systems, and galactic regions that are as friendly to complex life as are the Earth, the Solar System, and our region of the Milky Way are very rare.