ExamView - Untitled.tst
... a. their size and density. b. their rates of rotation. c. their atmospheres. d. their direction of rotation. 14. Which is the smallest terrestrial planet? a. Mars b. Mercury c. Venus d. Earth 15. The atmospheres of the gas giant planets cannot escape into space because a. the gases are too heavy. b. ...
... a. their size and density. b. their rates of rotation. c. their atmospheres. d. their direction of rotation. 14. Which is the smallest terrestrial planet? a. Mars b. Mercury c. Venus d. Earth 15. The atmospheres of the gas giant planets cannot escape into space because a. the gases are too heavy. b. ...
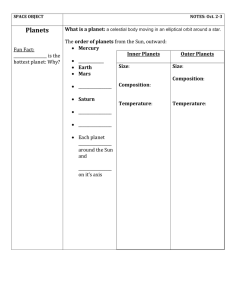
What is a planet
... **Moons revolve around ______________________ and rotate on their axis. Earth only has _______________ moon. How long does it takes our Moon to revolve: ______________ How long does it takes our Moon to rotate: _____________________ Planet with the MOST moons: ________________________(63) Plan ...
... **Moons revolve around ______________________ and rotate on their axis. Earth only has _______________ moon. How long does it takes our Moon to revolve: ______________ How long does it takes our Moon to rotate: _____________________ Planet with the MOST moons: ________________________(63) Plan ...
Earth Science SOL Review Sheet #1
... classic planets, dwarf planets, comets, and asteroids. The sun is made of mostly hydrogen gas and its energy comes from nuclear fusion reactions. Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars are terrestrial planets. Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune are gas giants. The asteroid belt is located between Mars ...
... classic planets, dwarf planets, comets, and asteroids. The sun is made of mostly hydrogen gas and its energy comes from nuclear fusion reactions. Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars are terrestrial planets. Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune are gas giants. The asteroid belt is located between Mars ...
Is the Earth special
... civilizations. Although there are many conceivable explanations for why other civilizations may not have interfered with us, almost all require implausible assumptions about the consistency of alien psychology (e.g. that advanced civilizations always wipe themselves out, or that they all subscribe t ...
... civilizations. Although there are many conceivable explanations for why other civilizations may not have interfered with us, almost all require implausible assumptions about the consistency of alien psychology (e.g. that advanced civilizations always wipe themselves out, or that they all subscribe t ...
Astronomy Final Exam Review
... • Light year- the distance light travels in a year • AU-(astronomical unit)- 1AU= distance from Earth to the sun ...
... • Light year- the distance light travels in a year • AU-(astronomical unit)- 1AU= distance from Earth to the sun ...
AST 105 HW #14 Solution
... The rare Earth hypothesis is the idea that Earth's hospitality is the result of rare planetary luck. The arguments in favor of this hypothesis are that there may be a fairly narrow ring at about our solar system's distance from the center of the galaxy where habitable planets might have enough hea ...
... The rare Earth hypothesis is the idea that Earth's hospitality is the result of rare planetary luck. The arguments in favor of this hypothesis are that there may be a fairly narrow ring at about our solar system's distance from the center of the galaxy where habitable planets might have enough hea ...
Science 9 Test Review-Space Answers 1. pg 434 2a
... Axis – an imaginary straight line between the North and South Pole Orbital period – the period of time required for an orbiting object to complete one revolution Constellations – a group of stars that forms shapes or patterns Probe – an unmanned space craft sent into space to obtain data and complet ...
... Axis – an imaginary straight line between the North and South Pole Orbital period – the period of time required for an orbiting object to complete one revolution Constellations – a group of stars that forms shapes or patterns Probe – an unmanned space craft sent into space to obtain data and complet ...
Astronomers use astronomical units(AU) to measure distances
... others are bluish, white or bluish-white • Density: some stars have such low density that they could float on water; others are so dense that 1g would crush the CN Tower ...
... others are bluish, white or bluish-white • Density: some stars have such low density that they could float on water; others are so dense that 1g would crush the CN Tower ...
The Children of Earth
... the ocean of matter; plunge into it where it is deepest and most violent; struggle in its currents and drink of its waters. ...
... the ocean of matter; plunge into it where it is deepest and most violent; struggle in its currents and drink of its waters. ...
Astronomy Test Review
... 8. Why can we see some stars all year round, but others only during certain seasons? 9. Draw what the moon looks like in each of the following phases: a. Waxing crescent b. Waning gibbous c. First quarter 10. Why is it that we can see Jupiter, Mars and Saturn very well during some nights, but Venus ...
... 8. Why can we see some stars all year round, but others only during certain seasons? 9. Draw what the moon looks like in each of the following phases: a. Waxing crescent b. Waning gibbous c. First quarter 10. Why is it that we can see Jupiter, Mars and Saturn very well during some nights, but Venus ...
Can you write numbers in scientific notation
... Are you familiar with the following planetary properties? Perihelion, aphelion, surface gravity, escape velocity, oblateness, and eccentricity. Explain the process that is believed to have formed the Moon. Life on Earth ...
... Are you familiar with the following planetary properties? Perihelion, aphelion, surface gravity, escape velocity, oblateness, and eccentricity. Explain the process that is believed to have formed the Moon. Life on Earth ...
File
... notation. This is 4.22 light years (4.22 ly). A light year is the distance that light travels in one year. (equaling 9.46 x 1012 km). Book analogy: If the Sun is a pinhead, the next star is another pinhead 35 miles away. This shows that the universe is made mostly of empty space. ...
... notation. This is 4.22 light years (4.22 ly). A light year is the distance that light travels in one year. (equaling 9.46 x 1012 km). Book analogy: If the Sun is a pinhead, the next star is another pinhead 35 miles away. This shows that the universe is made mostly of empty space. ...
OH Science Standards for STARS
... The solar system includes the sun and all celestial bodies that orbit the sun. Each planet in the solar system has unique characteristics. o The distance from the sun, size, composition and movement of each planet are unique. Planets revolve around the sun in elliptical orbits. Some of the planets ...
... The solar system includes the sun and all celestial bodies that orbit the sun. Each planet in the solar system has unique characteristics. o The distance from the sun, size, composition and movement of each planet are unique. Planets revolve around the sun in elliptical orbits. Some of the planets ...
Notes
... E. _________________________ holds the solar system together 1. We usually think of gravity as the ____________________ that pulls us to the Earth. 2. True definition of gravity is the attractive force between ____________. 3. The more _________ an object has the ________ its gravitational pull. a. ...
... E. _________________________ holds the solar system together 1. We usually think of gravity as the ____________________ that pulls us to the Earth. 2. True definition of gravity is the attractive force between ____________. 3. The more _________ an object has the ________ its gravitational pull. a. ...
Study Guide_galaxies, Tools, and Stars Test
... 3. What is the name of the galaxy our solar system is located in? 4. What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 5. The ________ is the largest star in our solar system. 6. Name and describe the 3 types of galaxies. 7. Where is our solar system located in the Milky Way galaxy? 8. What is a light ye ...
... 3. What is the name of the galaxy our solar system is located in? 4. What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 5. The ________ is the largest star in our solar system. 6. Name and describe the 3 types of galaxies. 7. Where is our solar system located in the Milky Way galaxy? 8. What is a light ye ...
CRCT Review 1
... B. London receives more sunshine in the winter than other places farther south. C. London's climate is affected by warm ocean currents that flow from the south. D. The Sun's rays shine at a higher angle in London than in Chicago. ...
... B. London receives more sunshine in the winter than other places farther south. C. London's climate is affected by warm ocean currents that flow from the south. D. The Sun's rays shine at a higher angle in London than in Chicago. ...
Rare Earth hypothesis

In planetary astronomy and astrobiology, the Rare Earth Hypothesis argues that the origin of life and the evolution of biological complexity such as sexually reproducing, multicellular organisms on Earth (and, subsequently, human intelligence) required an improbable combination of astrophysical and geological events and circumstances. The hypothesis argues that complex extraterrestrial life is a very improbable phenomenon and likely to be extremely rare. The term ""Rare Earth"" originates from Rare Earth: Why Complex Life Is Uncommon in the Universe (2000), a book by Peter Ward, a geologist and paleontologist, and Donald E. Brownlee, an astronomer and astrobiologist, both faculty members at the University of Washington.An alternative view point was argued by Carl Sagan and Frank Drake, among others. It holds that Earth is a typical rocky planet in a typical planetary system, located in a non-exceptional region of a common barred-spiral galaxy. Given the principle of mediocrity (also called the Copernican principle), it is probable that the universe teems with complex life. Ward and Brownlee argue to the contrary: that planets, planetary systems, and galactic regions that are as friendly to complex life as are the Earth, the Solar System, and our region of the Milky Way are very rare.