Astronomy - Learn Earth Science
... focus, Foucault Pendulum, galaxy, geocentric model, heliocentric model, local time, luminosity, meteor, revolution, rotation, solar system, tides, universe THE UNIVERSE: ...
... focus, Foucault Pendulum, galaxy, geocentric model, heliocentric model, local time, luminosity, meteor, revolution, rotation, solar system, tides, universe THE UNIVERSE: ...
Stars and Galaxies
... It may take several years for a spacecraft to reach other planets in our solar system. It may take several centuries to reach other stars in our galaxy. ...
... It may take several years for a spacecraft to reach other planets in our solar system. It may take several centuries to reach other stars in our galaxy. ...
Sorting the Solar System - California Academy of Sciences
... way up to the massive star at its center. Yet it is common for us to think of the Solar System as consisting of the Sun and the planets – a misconception reinforced by the typical depiction of the Solar System as planetary orbits circling the Sun. Other common misconceptions are that there is more t ...
... way up to the massive star at its center. Yet it is common for us to think of the Solar System as consisting of the Sun and the planets – a misconception reinforced by the typical depiction of the Solar System as planetary orbits circling the Sun. Other common misconceptions are that there is more t ...
A Red Giant - Cloudfront.net
... Stars like our Sun Stars with masses similar to our Sun fuse at a rate that allows them to “live” as mainsequence stars for about 10 billion years. Then they run out of Hydrogen in their core Hydrostatic Equilibrium is lost… They Shrink a bit And begin to fuse Hydrogen into Helium in a shell outsid ...
... Stars like our Sun Stars with masses similar to our Sun fuse at a rate that allows them to “live” as mainsequence stars for about 10 billion years. Then they run out of Hydrogen in their core Hydrostatic Equilibrium is lost… They Shrink a bit And begin to fuse Hydrogen into Helium in a shell outsid ...
Astronomy Library wk 4 .cwk (WP)
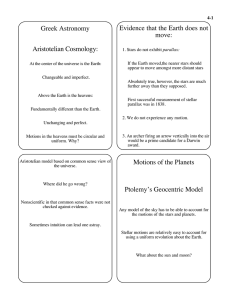
... Thus, belief in the Geocentric model persisted. Same as order by distance from the sun! ...
... Thus, belief in the Geocentric model persisted. Same as order by distance from the sun! ...
04 Lines in the Sky
... the sky. We will look at two methods of measuring locations in the sky. • Both methods require measuring angles. • These methods have long been used not only for timekeeping but for navigation as well. ...
... the sky. We will look at two methods of measuring locations in the sky. • Both methods require measuring angles. • These methods have long been used not only for timekeeping but for navigation as well. ...
Time - Academic Computer Center
... • Scientific method – Astronomy is a mostly observational science – Can do only a few controlled experiments in astronomy • Stellar evolution nuclear reactors • Cosmology particle accelerators • Solar System – Send satellites & rovers to planets – Crash probe into comet: Deep Impact Mission ...
... • Scientific method – Astronomy is a mostly observational science – Can do only a few controlled experiments in astronomy • Stellar evolution nuclear reactors • Cosmology particle accelerators • Solar System – Send satellites & rovers to planets – Crash probe into comet: Deep Impact Mission ...
Waves
... that lived in a particular geologic age, used to identify or date the rock or rock layer in which it is found ...
... that lived in a particular geologic age, used to identify or date the rock or rock layer in which it is found ...
Physics 20 Concept 22 Orbits and Satellites
... ⇒ The equation above is not on your formula sheet. You should be able to derive the equation when you need it. ⇒ The orbit does not depend on the mass of the satellite as long as the mass of the planet or star around which the satellite is orbiting is much, much larger than the mass of the satellite ...
... ⇒ The equation above is not on your formula sheet. You should be able to derive the equation when you need it. ⇒ The orbit does not depend on the mass of the satellite as long as the mass of the planet or star around which the satellite is orbiting is much, much larger than the mass of the satellite ...
File - Mr. Fifield`s Corner
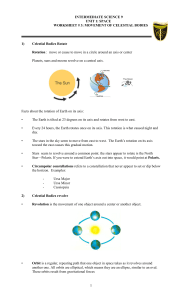
... Because Earth moves around the Sun every year, we see a different part of the sky every season . Some constellations are visible all year long but change positions, and some constellations are visible in certain seasons only, ...
... Because Earth moves around the Sun every year, we see a different part of the sky every season . Some constellations are visible all year long but change positions, and some constellations are visible in certain seasons only, ...
Neptune and Beyond, Asteroids, Comets
... Chunks of rock and debris in space that are in a collision course with Earth are called meteoroids. When meteoroids enter the Earth's atmosphere they heat up by friction and burn, and are called meteors (shooting stars). Most meteors burn up in the atmosphere, but if they survive the burn and strike ...
... Chunks of rock and debris in space that are in a collision course with Earth are called meteoroids. When meteoroids enter the Earth's atmosphere they heat up by friction and burn, and are called meteors (shooting stars). Most meteors burn up in the atmosphere, but if they survive the burn and strike ...
lecture3
... Besides a being more ‘sensible’ picture, are there observational advantages of the new ideas? Copernicus did give a more plausible explanation for the maximum angle between Venus (or Mercury) and Sun: Since Venus is closer to Sun on a smaller circle, it never deviates from the Sun by more than angl ...
... Besides a being more ‘sensible’ picture, are there observational advantages of the new ideas? Copernicus did give a more plausible explanation for the maximum angle between Venus (or Mercury) and Sun: Since Venus is closer to Sun on a smaller circle, it never deviates from the Sun by more than angl ...
Document
... b. the star’s continuous spectrum. c. the star’s absorption spectrum. d. the star’s color. _____ 8. The majority of stars in our galaxy are a. blue stars. b. white dwarfs. c.main-sequence stars. d. red giants. Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the o ...
... b. the star’s continuous spectrum. c. the star’s absorption spectrum. d. the star’s color. _____ 8. The majority of stars in our galaxy are a. blue stars. b. white dwarfs. c.main-sequence stars. d. red giants. Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the o ...
Astronomy_Stars_n_Galaxies_PowerPoint
... Look at the spectra for stars A, B, and C. Compare each star’s spectrum to the spectra of the known elements above. Write the chemical composition of stars A, B, and C. ...
... Look at the spectra for stars A, B, and C. Compare each star’s spectrum to the spectra of the known elements above. Write the chemical composition of stars A, B, and C. ...
Parallax and Its role In the helIocentrIc/GeocentrIc debate
... Your finger is like a nearby star, and the far wall is like the distant stars in the background. Your two eyes are like a telescope on Earth that is in two different positions as the Earth moves around the Sun. For example, in April a nearby star appears in one location (like looking through one eye ...
... Your finger is like a nearby star, and the far wall is like the distant stars in the background. Your two eyes are like a telescope on Earth that is in two different positions as the Earth moves around the Sun. For example, in April a nearby star appears in one location (like looking through one eye ...
Name: Period: ______ Date: 1/16/07
... kilometers from Earth. Such a large number is difficult to understand and use in calculations. For this reason, astronomers use a different unit of measurement when they talk about distances between stars. ...
... kilometers from Earth. Such a large number is difficult to understand and use in calculations. For this reason, astronomers use a different unit of measurement when they talk about distances between stars. ...
Solutions 1
... For the sun to appear on the zenith an observer must live between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn or between +23½ o and -23½ o of the Earth's equator (celestial equator). This is the result of the 23½ o tilt of the Earth's celestial equator with respect to the ecliptic (the path of ...
... For the sun to appear on the zenith an observer must live between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn or between +23½ o and -23½ o of the Earth's equator (celestial equator). This is the result of the 23½ o tilt of the Earth's celestial equator with respect to the ecliptic (the path of ...
Our Solar System - Mrs. Carter
... The Sun is a huge ball of burning gas that sends energy far out into the Solar System. The Sun plays a very important part in our daily lives, providing energy that supports all life on Earth. The Sun causes seasons, climate, ocean currents, air circulation, and weather. Without the Sun’s energy, pl ...
... The Sun is a huge ball of burning gas that sends energy far out into the Solar System. The Sun plays a very important part in our daily lives, providing energy that supports all life on Earth. The Sun causes seasons, climate, ocean currents, air circulation, and weather. Without the Sun’s energy, pl ...
Notes on Precession in Astronomy
... Precession is the slow gyration of the Earth’s spin axis, due to the gravitational pull of the Moon, Sun and planets on the unevenly distributed mass of the Earth. The Earth slowly wobbles, much as a top, or gyroscope, does when spun. This wobble is called the Earth's Precession. ...
... Precession is the slow gyration of the Earth’s spin axis, due to the gravitational pull of the Moon, Sun and planets on the unevenly distributed mass of the Earth. The Earth slowly wobbles, much as a top, or gyroscope, does when spun. This wobble is called the Earth's Precession. ...
Final Exam Review
... The remnant of the protostellar disk around a newborn star out of which planets may form. The remnant of the explosion of a sun-like star at the end of its life. The remnant of the explosion of a very massive star (more than 8 solar masses) at the end of its life. The combined image of many planets ...
... The remnant of the protostellar disk around a newborn star out of which planets may form. The remnant of the explosion of a sun-like star at the end of its life. The remnant of the explosion of a very massive star (more than 8 solar masses) at the end of its life. The combined image of many planets ...
Chapter 04
... 9. Why did the model of the universe proposed by Copernicus gain support soon after its publication? a. It more accurately predicted the position of planets. b. It gave a better explanation for the phases of the Moon. c. It was a more elegant explanation of retrograde motion. d. The old system of Pt ...
... 9. Why did the model of the universe proposed by Copernicus gain support soon after its publication? a. It more accurately predicted the position of planets. b. It gave a better explanation for the phases of the Moon. c. It was a more elegant explanation of retrograde motion. d. The old system of Pt ...
The Origin of Modern Astronomy(Seeds)
... 9. Why did the model of the universe proposed by Copernicus gain support soon after its publication? a. It more accurately predicted the position of planets. b. It gave a better explanation for the phases of the Moon. c. It was a more elegant explanation of retrograde motion. d. The old system of Pt ...
... 9. Why did the model of the universe proposed by Copernicus gain support soon after its publication? a. It more accurately predicted the position of planets. b. It gave a better explanation for the phases of the Moon. c. It was a more elegant explanation of retrograde motion. d. The old system of Pt ...
STUDY QUESTIONS #10 The MILKY WAY GALAXY diameter face
... 3. Label the following where appropriate: spiral arms, disk, halo, bulge, globular clusters, galactic center 4. What is the evidence for a massive black hole in the center of the Galaxy? 5. According to Kepler's laws, the velocity of one object orbiting a second object depends on the mass of the sec ...
... 3. Label the following where appropriate: spiral arms, disk, halo, bulge, globular clusters, galactic center 4. What is the evidence for a massive black hole in the center of the Galaxy? 5. According to Kepler's laws, the velocity of one object orbiting a second object depends on the mass of the sec ...
Rare Earth hypothesis

In planetary astronomy and astrobiology, the Rare Earth Hypothesis argues that the origin of life and the evolution of biological complexity such as sexually reproducing, multicellular organisms on Earth (and, subsequently, human intelligence) required an improbable combination of astrophysical and geological events and circumstances. The hypothesis argues that complex extraterrestrial life is a very improbable phenomenon and likely to be extremely rare. The term ""Rare Earth"" originates from Rare Earth: Why Complex Life Is Uncommon in the Universe (2000), a book by Peter Ward, a geologist and paleontologist, and Donald E. Brownlee, an astronomer and astrobiologist, both faculty members at the University of Washington.An alternative view point was argued by Carl Sagan and Frank Drake, among others. It holds that Earth is a typical rocky planet in a typical planetary system, located in a non-exceptional region of a common barred-spiral galaxy. Given the principle of mediocrity (also called the Copernican principle), it is probable that the universe teems with complex life. Ward and Brownlee argue to the contrary: that planets, planetary systems, and galactic regions that are as friendly to complex life as are the Earth, the Solar System, and our region of the Milky Way are very rare.