Outline 8: History of the Universe and Solar System
... Total time is 5 hours. Total distance is 380 miles. If you were observed traveling at 60 mph and had covered 380 miles, the assumption would be made that you had traveled for 6 hours and 20 minutes (380miles/60mph) rather than 5 hours. ...
... Total time is 5 hours. Total distance is 380 miles. If you were observed traveling at 60 mph and had covered 380 miles, the assumption would be made that you had traveled for 6 hours and 20 minutes (380miles/60mph) rather than 5 hours. ...
Lesson 4: Object`s Motion in the Sky
... * Orbits are slightly egg-shaped, which is called an ellipse, or elliptical orbit. ...
... * Orbits are slightly egg-shaped, which is called an ellipse, or elliptical orbit. ...
By plugging their latest findings into Earth`s climate patterns
... When analyzing a star’s light, scientists look for spectral “fingerprints,” a pattern of colors different for every individual element, to determine that star’s composition. This process, called spectroscopy, is also useful for determining the chemical makeup of exoplanets and their atmospheres when ...
... When analyzing a star’s light, scientists look for spectral “fingerprints,” a pattern of colors different for every individual element, to determine that star’s composition. This process, called spectroscopy, is also useful for determining the chemical makeup of exoplanets and their atmospheres when ...
Stellar Parallax
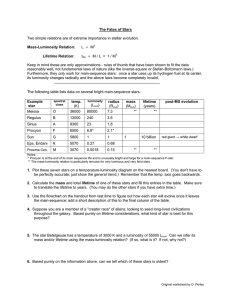
... Stellar Brightness • Stellar separations and intensities vary over many orders-of magnitude. As a result it is convenient to use logarithmic scales. • Astronomers use relative measures of Intensity. The system is based on the assumption that iVEGA = 1.0 and the apparent intensities of all other sta ...
... Stellar Brightness • Stellar separations and intensities vary over many orders-of magnitude. As a result it is convenient to use logarithmic scales. • Astronomers use relative measures of Intensity. The system is based on the assumption that iVEGA = 1.0 and the apparent intensities of all other sta ...
Lesson Overviews and Content Standards
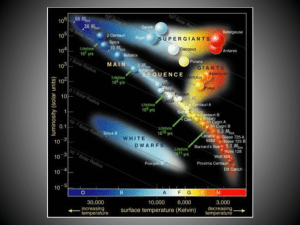
... • Low mass stars have less hydrogen to convert to helium than do high mass stars, but live much longer. • Our sun has lived about half of its life as a main sequence star. • For most of the history of the Earth (and the sun), bacteria and other microorganisms were the only form of life on our planet ...
... • Low mass stars have less hydrogen to convert to helium than do high mass stars, but live much longer. • Our sun has lived about half of its life as a main sequence star. • For most of the history of the Earth (and the sun), bacteria and other microorganisms were the only form of life on our planet ...
astro 001.101 summer 2002 exam 2
... This effect is not observed (using only the naked eye); consequently the Greeks concluded that Earth does not orbit the Sun. However, the Greeks failed to realize that stars lie at very great distances. For the nearest star to the Sun, the angle is only ~ 1/1800o. The smallest angular separation t ...
... This effect is not observed (using only the naked eye); consequently the Greeks concluded that Earth does not orbit the Sun. However, the Greeks failed to realize that stars lie at very great distances. For the nearest star to the Sun, the angle is only ~ 1/1800o. The smallest angular separation t ...
Third problem set
... Now let’s move on to (B). We can use the inverse square law to find the flux we receive from the planet, and we can see if this flux is big enough for our telescopes to detect. Practically speaking, our best telescopes can detect anything whose flux is bigger than Minimum detectable flux = fminimum ...
... Now let’s move on to (B). We can use the inverse square law to find the flux we receive from the planet, and we can see if this flux is big enough for our telescopes to detect. Practically speaking, our best telescopes can detect anything whose flux is bigger than Minimum detectable flux = fminimum ...
25 Study Guide
... 3. Neutron stars are thought to be the remnants of supernova explosions. 4. A massive star ends as a supernova. The two possible products of this event are a neutron star and a black hole. 5. In sequence, the stages in the evolution of a medium-mass star are: dust and gases, protostar, mainsequence ...
... 3. Neutron stars are thought to be the remnants of supernova explosions. 4. A massive star ends as a supernova. The two possible products of this event are a neutron star and a black hole. 5. In sequence, the stages in the evolution of a medium-mass star are: dust and gases, protostar, mainsequence ...
Rotation and Revolution - Where Science Meets Life
... What causes night and day? The rotation of the Earth • The side of the Earth that is facing the sun has daylight, the side of the Earth away from the sun has night. • It takes 24 hours for the Earth to complete one rotation. • The Earth is tilted on it’s axis at a 23.5 degree angle. • The Earth’s ti ...
... What causes night and day? The rotation of the Earth • The side of the Earth that is facing the sun has daylight, the side of the Earth away from the sun has night. • It takes 24 hours for the Earth to complete one rotation. • The Earth is tilted on it’s axis at a 23.5 degree angle. • The Earth’s ti ...
PHSC1053-Review02
... Taking into account the motions, interactions and geometry between the Earth, Moon, and Sun, be able to explain and/or illustrate the following: Phases of the Moon The Earth’s seasons The Earth’s tides Conditions for eclipses ...
... Taking into account the motions, interactions and geometry between the Earth, Moon, and Sun, be able to explain and/or illustrate the following: Phases of the Moon The Earth’s seasons The Earth’s tides Conditions for eclipses ...
PTYS/ASTR 206 – Section 2 - Lunar and Planetary Laboratory
... Galilean satellites. You may also be able to see two large bands of gas clouds on the planet, but do not have enough magnification to make out the giant red spot. At 30 arcminutes, you can easily see Saturn as a ringed planet. However, you would have trouble making out the Cassini division in its ri ...
... Galilean satellites. You may also be able to see two large bands of gas clouds on the planet, but do not have enough magnification to make out the giant red spot. At 30 arcminutes, you can easily see Saturn as a ringed planet. However, you would have trouble making out the Cassini division in its ri ...
NORTH SOUTH EAST WEST
... opposite the sun in the sky as seen from Earth. Planets at opposition are visible all night. Saturn is in opposition on June 15. In contrast, conjunction means that two objects appear in the same place in the sky as seen from Earth. Mercury is in conjunction with the Sun on June 21. Planets in conju ...
... opposite the sun in the sky as seen from Earth. Planets at opposition are visible all night. Saturn is in opposition on June 15. In contrast, conjunction means that two objects appear in the same place in the sky as seen from Earth. Mercury is in conjunction with the Sun on June 21. Planets in conju ...
Schedule for Spring 2013 SCI 103 Introductory Astronomy
... Rate of mass conversion into energy Maximum lifetime of the Sun Relationship between the radius, temperature and luminosity of the Sun ...
... Rate of mass conversion into energy Maximum lifetime of the Sun Relationship between the radius, temperature and luminosity of the Sun ...
Galaxies
... particularly in arms, circular orbits, high concentration (3%) heavy elements Population II – red, old, found in bulge and halo, elliptical orbits, low concentration of heavy elements Probably smooth transition between end members (i.e. the sun). ? Population III ? – pure H and He ...
... particularly in arms, circular orbits, high concentration (3%) heavy elements Population II – red, old, found in bulge and halo, elliptical orbits, low concentration of heavy elements Probably smooth transition between end members (i.e. the sun). ? Population III ? – pure H and He ...
05Sky1.ppt - NMSU Astronomy
... Reflex motion from Earth’s rotation • Earth spins around an imaginary axis, once per day • As a result, the celestial sphere appears to spin around the Earth – Stars that happen to be located in the direction of the Earth’s rotation axis appear to stand still • There is such a star above the North ...
... Reflex motion from Earth’s rotation • Earth spins around an imaginary axis, once per day • As a result, the celestial sphere appears to spin around the Earth – Stars that happen to be located in the direction of the Earth’s rotation axis appear to stand still • There is such a star above the North ...
Rare Earth hypothesis

In planetary astronomy and astrobiology, the Rare Earth Hypothesis argues that the origin of life and the evolution of biological complexity such as sexually reproducing, multicellular organisms on Earth (and, subsequently, human intelligence) required an improbable combination of astrophysical and geological events and circumstances. The hypothesis argues that complex extraterrestrial life is a very improbable phenomenon and likely to be extremely rare. The term ""Rare Earth"" originates from Rare Earth: Why Complex Life Is Uncommon in the Universe (2000), a book by Peter Ward, a geologist and paleontologist, and Donald E. Brownlee, an astronomer and astrobiologist, both faculty members at the University of Washington.An alternative view point was argued by Carl Sagan and Frank Drake, among others. It holds that Earth is a typical rocky planet in a typical planetary system, located in a non-exceptional region of a common barred-spiral galaxy. Given the principle of mediocrity (also called the Copernican principle), it is probable that the universe teems with complex life. Ward and Brownlee argue to the contrary: that planets, planetary systems, and galactic regions that are as friendly to complex life as are the Earth, the Solar System, and our region of the Milky Way are very rare.