American Scientist
... appear to lie roughly in the same orbital plane. The Kepler-16 system consists of a pair of stars orbited by a Saturnlike exoplanet, a harsh environment for any exoplanet to survive in because of the enhanced gravitational tugs of the stars. A diminutive red dwarf sits at the center of the Kepler-3 ...
... appear to lie roughly in the same orbital plane. The Kepler-16 system consists of a pair of stars orbited by a Saturnlike exoplanet, a harsh environment for any exoplanet to survive in because of the enhanced gravitational tugs of the stars. A diminutive red dwarf sits at the center of the Kepler-3 ...
a MS Word version.
... "weird" about the transition from the liquid hydrogen mantle of Jupiter to its gaseous hydrogen atmosphere? What is metallic liquid hydrogen and how is it related to Jupiter's and Saturn's strong magnetic fields? Both Jupiter and Saturn give off more energy than they receive from the Sun. What are t ...
... "weird" about the transition from the liquid hydrogen mantle of Jupiter to its gaseous hydrogen atmosphere? What is metallic liquid hydrogen and how is it related to Jupiter's and Saturn's strong magnetic fields? Both Jupiter and Saturn give off more energy than they receive from the Sun. What are t ...
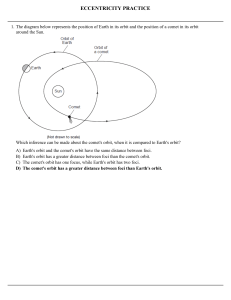
ECCENTRICITY PRACTICE
... Scientists studying a Sun-like star named Ogle-Tr-3 discovered a planet that is, on the average, 3.5 million kilometers away from the star’s surface. The planet was discovered as a result of observing a cyclic decrease in the brightness of Ogle-Tr-3 every 28.5 hours. The changing brightness is the r ...
... Scientists studying a Sun-like star named Ogle-Tr-3 discovered a planet that is, on the average, 3.5 million kilometers away from the star’s surface. The planet was discovered as a result of observing a cyclic decrease in the brightness of Ogle-Tr-3 every 28.5 hours. The changing brightness is the r ...
Ch#13 - KFUPM Faculty List
... meters. Find the magnitude of the gravitational force exerted on the particle located at the origin by the other two particles. A1 3.4* 10**(-11) N Q13: A moon is moving in a circular orbit around a planet with a period of 2.75* 10**4 s. Find the MASS of the planet if the radius of the orbit is 9.4* ...
... meters. Find the magnitude of the gravitational force exerted on the particle located at the origin by the other two particles. A1 3.4* 10**(-11) N Q13: A moon is moving in a circular orbit around a planet with a period of 2.75* 10**4 s. Find the MASS of the planet if the radius of the orbit is 9.4* ...
Chapter 13 - KFUPM Faculty List
... meters. Find the magnitude of the gravitational force exerted on the particle located at the origin by the other two particles. A1 3.4* 10**(-11) N Q13: A moon is moving in a circular orbit around a planet with a period of 2.75* 10**4 s. Find the MASS of the planet if the radius of the orbit is 9.4* ...
... meters. Find the magnitude of the gravitational force exerted on the particle located at the origin by the other two particles. A1 3.4* 10**(-11) N Q13: A moon is moving in a circular orbit around a planet with a period of 2.75* 10**4 s. Find the MASS of the planet if the radius of the orbit is 9.4* ...
Solar System: Planets Asteroids Comets
... 1.524 AU, Jupiter at 5.204 AU, Saturn at 9.582AU. Amazingly, Uranus at 19.23AU was determined in 1781 to be a planet an not a star. The gap at 2.8 is located in the belt of asteroids between Mars and Jupiter. The dwarf planet Ceres at 2.766AU was discovered in 1801 at almost exactly the predicted lo ...
... 1.524 AU, Jupiter at 5.204 AU, Saturn at 9.582AU. Amazingly, Uranus at 19.23AU was determined in 1781 to be a planet an not a star. The gap at 2.8 is located in the belt of asteroids between Mars and Jupiter. The dwarf planet Ceres at 2.766AU was discovered in 1801 at almost exactly the predicted lo ...
New Indivisible Planetary Science Paradigm J. Marvin Herndon
... steps settled at the center of the Earth where it engaged in self-sustaining nuclear fission chain reactions [5, 20, 37-40]. The gaseous portion of primordial Solar System matter, as is the Sun’s photosphere today, was about 300 times as massive as all of its rock-plus-metal forming elements. I posi ...
... steps settled at the center of the Earth where it engaged in self-sustaining nuclear fission chain reactions [5, 20, 37-40]. The gaseous portion of primordial Solar System matter, as is the Sun’s photosphere today, was about 300 times as massive as all of its rock-plus-metal forming elements. I posi ...
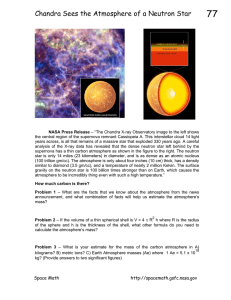
Chandra Sees the Atmosphere of a Neutron Star - Chandra X
... star is only 14 miles (23 kilometers) in diameter, and is as dense as an atomic nucleus (100 trillion gm/cc). The atmosphere is only about four inches (10 cm) thick, has a density similar to diamond (3.5 gm/cc), and a temperature of nearly 2 million Kelvin. The surface gravity on the neutron star is ...
... star is only 14 miles (23 kilometers) in diameter, and is as dense as an atomic nucleus (100 trillion gm/cc). The atmosphere is only about four inches (10 cm) thick, has a density similar to diamond (3.5 gm/cc), and a temperature of nearly 2 million Kelvin. The surface gravity on the neutron star is ...
Constellations appear to move across the sky at night because
... a) stars don’t seem to show any parallax. ...
... a) stars don’t seem to show any parallax. ...
Mercury_Orbit_Lab_1_(better_than_2)
... How do we know what the orbit of a planet is like? At first glance this appears to be a difficult question, but in many cases it is surprisingly easy to derive an orbit from basic observations. In this exercise you will use a set of simple observations, which you could have made yourself, to discove ...
... How do we know what the orbit of a planet is like? At first glance this appears to be a difficult question, but in many cases it is surprisingly easy to derive an orbit from basic observations. In this exercise you will use a set of simple observations, which you could have made yourself, to discove ...
Stellar Physics - Craigie High School
... The development of what we know about the Earth, Solar System and Universe is a fascinating study in its own right. From earliest times Man has wondered at and speculated over the ‘Nature of the Heavens’. It is hardly surprising that most people (until around 1500 A.D.) thought that the Sun revolved ...
... The development of what we know about the Earth, Solar System and Universe is a fascinating study in its own right. From earliest times Man has wondered at and speculated over the ‘Nature of the Heavens’. It is hardly surprising that most people (until around 1500 A.D.) thought that the Sun revolved ...
S1_LectureOutlines
... • Difference between a planet’s orbital (sidereal) and synodic period depends on how far planet moves in one Earth year for outer planets ...
... • Difference between a planet’s orbital (sidereal) and synodic period depends on how far planet moves in one Earth year for outer planets ...
Earth at Aphelion - Stargazers Lounge
... In 2016, the Moon reaches New on July 4th at 11:01 Universal Time (UT) just over five hours prior to aphelion, marking the start of lunation 1157. The sighting of the waxing crescent Moon also marks the end of the Muslim fasting month of Ramadan. Earth reaches aphelion at 16:24 UT today, 1.0168 AU ...
... In 2016, the Moon reaches New on July 4th at 11:01 Universal Time (UT) just over five hours prior to aphelion, marking the start of lunation 1157. The sighting of the waxing crescent Moon also marks the end of the Muslim fasting month of Ramadan. Earth reaches aphelion at 16:24 UT today, 1.0168 AU ...
Jupiter
... naked eye. Just outside the main ring is the broad and exceedingly faint "Gossamer" ring, which extends out beyond the orbit of the moon Amalthea. It is probably composed of dust particles less than 10 microns in diameter about the size of cigarette smoke particles. It extends to an outer edge of ab ...
... naked eye. Just outside the main ring is the broad and exceedingly faint "Gossamer" ring, which extends out beyond the orbit of the moon Amalthea. It is probably composed of dust particles less than 10 microns in diameter about the size of cigarette smoke particles. It extends to an outer edge of ab ...
STAR FORMATION
... T > 6 x 106 K then ordinary H fusion can begin. • This is official definition of stellar birth -- the star is on the Zero Age MS (ZAMS) now. • The star's location on the ZAMS is determined almost completely by its MASS (there are lesser effects from composition and rotation that you should know exis ...
... T > 6 x 106 K then ordinary H fusion can begin. • This is official definition of stellar birth -- the star is on the Zero Age MS (ZAMS) now. • The star's location on the ZAMS is determined almost completely by its MASS (there are lesser effects from composition and rotation that you should know exis ...
The Outer Planets and Their Moons
... geologically varied than Jupiter’s. They are less dense, icier, and brighter, perhaps because Saturn is farther from Sun. Saturn’s satellites can be placed into four groups, in order of their distance from Saturn: the small innermost satellites near Saturn’s rings, the larger Saturnian satellites, t ...
... geologically varied than Jupiter’s. They are less dense, icier, and brighter, perhaps because Saturn is farther from Sun. Saturn’s satellites can be placed into four groups, in order of their distance from Saturn: the small innermost satellites near Saturn’s rings, the larger Saturnian satellites, t ...
what`s up this month – april 2017
... Virgo is not a very distinctive constellation but it is easy to locate this year because it is host the planet Jupiter. With Jupiter as a guide the bright star Spica can be located to the south. The recognised shape of Virgo may be difficult to identify from a light polluted area because most the s ...
... Virgo is not a very distinctive constellation but it is easy to locate this year because it is host the planet Jupiter. With Jupiter as a guide the bright star Spica can be located to the south. The recognised shape of Virgo may be difficult to identify from a light polluted area because most the s ...
Ch. 17 (RGs & WDs)
... These stars are all more luminous than the Sun. Three new categories appear here – the red giants & supergiants and the blue giants. Clearly, the brightest stars in the sky appear bright because of their enormous luminosities, not their proximity. ...
... These stars are all more luminous than the Sun. Three new categories appear here – the red giants & supergiants and the blue giants. Clearly, the brightest stars in the sky appear bright because of their enormous luminosities, not their proximity. ...
The Copernican Revolution
... contemplating the stars in a clear sky. I noticed that a new and unusual star, surpassing the other stars in brilliancy, was shining almost directly above my head; and since I had, from boyhood, known all the stars of the heavens perfectly, it was quite evident to me that there had never been any st ...
... contemplating the stars in a clear sky. I noticed that a new and unusual star, surpassing the other stars in brilliancy, was shining almost directly above my head; and since I had, from boyhood, known all the stars of the heavens perfectly, it was quite evident to me that there had never been any st ...
PHYS-638-07f: Problem set #0 Solutions
... being refected by, e.g. clouds, snow, etc., without contributing any heat to Earth. So now redo the calculation in (a) reducing the solar input energy by this amount. If only a fraction 0.367 of Sun’s luminosity is actually absorbed by Earth, then the equilibrium temperature should be reduced by a f ...
... being refected by, e.g. clouds, snow, etc., without contributing any heat to Earth. So now redo the calculation in (a) reducing the solar input energy by this amount. If only a fraction 0.367 of Sun’s luminosity is actually absorbed by Earth, then the equilibrium temperature should be reduced by a f ...
Gemini - Sochias
... 40-200 AU separation Second epoch observations of 48 stars confirm all candidates as unrelated background stars 95% upper limit of fractions of star with at least one planet of 0.5 - 13 MJup are – 0.28 for 10-25 AU – 0.13 for 25-50 AU ...
... 40-200 AU separation Second epoch observations of 48 stars confirm all candidates as unrelated background stars 95% upper limit of fractions of star with at least one planet of 0.5 - 13 MJup are – 0.28 for 10-25 AU – 0.13 for 25-50 AU ...
What is a planet? - X-ray and Observational Astronomy Group
... planet survivability, if they both form at same time – Planets interior to a migrating giant planet will be disrupted and lost – Of course, these small planets may also migrate into star! ...
... planet survivability, if they both form at same time – Planets interior to a migrating giant planet will be disrupted and lost – Of course, these small planets may also migrate into star! ...
Powerpoint file
... There are only two astronomical bodies that have a radius ~ 1 REarth: 1. White Dwarf 2. A terrestrial planet White Dwarfs have a mass of ~ 1 Solar Mass, so the radial velocity amplitude should be ~ 100s km/s. This is excluded by low precision radial velocity measurements. ...
... There are only two astronomical bodies that have a radius ~ 1 REarth: 1. White Dwarf 2. A terrestrial planet White Dwarfs have a mass of ~ 1 Solar Mass, so the radial velocity amplitude should be ~ 100s km/s. This is excluded by low precision radial velocity measurements. ...
Stellar Evolution: the Death of Stars
... expel most stellar material outward • Shock wave produces a series of nuclear reaction, the only place elements heavier than iron (such as silver, gold) are produced in the universe ...
... expel most stellar material outward • Shock wave produces a series of nuclear reaction, the only place elements heavier than iron (such as silver, gold) are produced in the universe ...
Planetary habitability

Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia. As the existence of life beyond Earth is unknown, planetary habitability is largely an extrapolation of conditions on Earth and the characteristics of the Sun and Solar System which appear favourable to life's flourishing—in particular those factors that have sustained complex, multicellular organisms and not just simpler, unicellular creatures. Research and theory in this regard is a component of planetary science and the emerging discipline of astrobiology.An absolute requirement for life is an energy source, and the notion of planetary habitability implies that many other geophysical, geochemical, and astrophysical criteria must be met before an astronomical body can support life. In its astrobiology roadmap, NASA has defined the principal habitability criteria as ""extended regions of liquid water, conditions favourable for the assembly of complex organic molecules, and energy sources to sustain metabolism.""In determining the habitability potential of a body, studies focus on its bulk composition, orbital properties, atmosphere, and potential chemical interactions. Stellar characteristics of importance include mass and luminosity, stable variability, and high metallicity. Rocky, terrestrial-type planets and moons with the potential for Earth-like chemistry are a primary focus of astrobiological research, although more speculative habitability theories occasionally examine alternative biochemistries and other types of astronomical bodies.The idea that planets beyond Earth might host life is an ancient one, though historically it was framed by philosophy as much as physical science. The late 20th century saw two breakthroughs in the field. The observation and robotic spacecraft exploration of other planets and moons within the Solar System has provided critical information on defining habitability criteria and allowed for substantial geophysical comparisons between the Earth and other bodies. The discovery of extrasolar planets, beginning in the early 1990s and accelerating thereafter, has provided further information for the study of possible extraterrestrial life. These findings confirm that the Sun is not unique among stars in hosting planets and expands the habitability research horizon beyond the Solar System.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently. On 4 November 2013, astronomers reported, based on Kepler space mission data, that there could be as many as 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of Sun-like stars and red dwarfs within the Milky Way. 11 billion of these estimated planets may be orbiting Sun-like stars. The nearest such planet may be 12 light-years away, according to the scientists.