July 2014 BRAS Newsletter - The Baton Rouge Astronomical Society
... Computing Earth’s twin NASA’s Kepler spacecraft, launched into an Earth-trailing orbit in 2009, stared at some 156,000 stars in the constellation Cygnus, monitoring their brightness photometrically every 30 minutes for four years. It was searching for any minute decreases in brightness that might in ...
... Computing Earth’s twin NASA’s Kepler spacecraft, launched into an Earth-trailing orbit in 2009, stared at some 156,000 stars in the constellation Cygnus, monitoring their brightness photometrically every 30 minutes for four years. It was searching for any minute decreases in brightness that might in ...
Stars and Nebulae
... Nebula in Taurus (M1), shown in the image above. The light of the inner core is from synchrotron radiation, while the outer regions glow in many colors from emission of many gases, including red for hydrogen. ...
... Nebula in Taurus (M1), shown in the image above. The light of the inner core is from synchrotron radiation, while the outer regions glow in many colors from emission of many gases, including red for hydrogen. ...
Asynchronous rotation of Earth-mass planets in the habitable zone
... an important fraction of planets in the habitable zone of lower mass stars. This is especially true in the outer habitable zone where planets are expected to build massive CO2 atmospheres (7). This has many implications. On one hand, all the threats to habitability created by the presence of a perma ...
... an important fraction of planets in the habitable zone of lower mass stars. This is especially true in the outer habitable zone where planets are expected to build massive CO2 atmospheres (7). This has many implications. On one hand, all the threats to habitability created by the presence of a perma ...
Procedurally Generating an Artificial Galaxy
... method. It will take a seed of up to four digits, square it into an eight digit number, adding zeroes in front if necessary, and output the four middle digits of this new number (Introduction to Random Number Generators 2007). Like all PRNG's, this algorithm will always generate the same output from ...
... method. It will take a seed of up to four digits, square it into an eight digit number, adding zeroes in front if necessary, and output the four middle digits of this new number (Introduction to Random Number Generators 2007). Like all PRNG's, this algorithm will always generate the same output from ...
MAPPING THE SOLAR SYSTEM
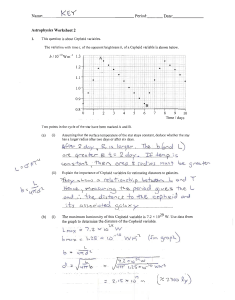
... The average radius of the moons orbit around the earth is 384 748 km and has a period of 27.3 days. A Direct TV satellite has a period of exactly one day. What is the radius of the satellites orbit? How far is the satellite above the Earths surface? ...
... The average radius of the moons orbit around the earth is 384 748 km and has a period of 27.3 days. A Direct TV satellite has a period of exactly one day. What is the radius of the satellites orbit? How far is the satellite above the Earths surface? ...
Volume 1 (Issue 7), July 2012
... shown in the Figure 1. It is clear from the figure that weather of Karachi on the given day is partly cloudy with a temperature of 34 C and a wind speed of 30km/hr. The figure informs about the sunrise/set times and phase of moon also. Additionally, a 5 day forecast has been presented mentioning the ...
... shown in the Figure 1. It is clear from the figure that weather of Karachi on the given day is partly cloudy with a temperature of 34 C and a wind speed of 30km/hr. The figure informs about the sunrise/set times and phase of moon also. Additionally, a 5 day forecast has been presented mentioning the ...
Star Formation - Leslie Looney
... http://homepage.smc.edu/balm_simon/images/astro%205/spock.jpg ...
... http://homepage.smc.edu/balm_simon/images/astro%205/spock.jpg ...
notes
... Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2) for ten consecutive days between December 18 and 28, 1995. 1,500 galaxies at various stages of evolution. Most of the galaxies are so faint (nearly 30th magnitude or about four-billion times fainter than can be seen by the human eye) they have never before b ...
... Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2) for ten consecutive days between December 18 and 28, 1995. 1,500 galaxies at various stages of evolution. Most of the galaxies are so faint (nearly 30th magnitude or about four-billion times fainter than can be seen by the human eye) they have never before b ...
The Stars: Distance, Luminosity, Size
... Suppose two stars are at equal distance and have the same radius, but one has a temperature that is twice as great as the other. The apparent brightness of the hotter star is ____ as the other. ...
... Suppose two stars are at equal distance and have the same radius, but one has a temperature that is twice as great as the other. The apparent brightness of the hotter star is ____ as the other. ...
Lecture 12, PPT version
... Galaxy). All of the stars formed at roughly the same time. Globular clusters have lots of RED stars, but no BLUE stars (because they died long ago and were not “replenished”). ...
... Galaxy). All of the stars formed at roughly the same time. Globular clusters have lots of RED stars, but no BLUE stars (because they died long ago and were not “replenished”). ...
of the outer planets are gas
... Absolute magnitude tell us how much light is given off by a star. Apparent magnitude tells us how bright a star appears to be due to how far or close it is. A large group of stars that are held together by gravity are called a __________________. "Inner Planets" are called 'inner' because they have ...
... Absolute magnitude tell us how much light is given off by a star. Apparent magnitude tells us how bright a star appears to be due to how far or close it is. A large group of stars that are held together by gravity are called a __________________. "Inner Planets" are called 'inner' because they have ...
The Astrophysics of Planetary Habitability
... P2.13. Characteristics of solar coronal mass ejections . . . . . . . . . . . P2.14. Stellar high-energy luminosity evolution for pre-main sequence and main-sequence stars . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . P2.15. The ultimate fate of planetary systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . P2.16. ...
... P2.13. Characteristics of solar coronal mass ejections . . . . . . . . . . . P2.14. Stellar high-energy luminosity evolution for pre-main sequence and main-sequence stars . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . P2.15. The ultimate fate of planetary systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . P2.16. ...
The Prospective Aspect of the Cosmogonic Models in Laozi and T
... some metal and non-metal elements. Studies have found organic radicals such as OH, CO and CH4, and even molecules of up to 8-9 atoms. • Interstellar matter is of two kinds: – Insterstellar gas includes gaseous atoms, molecules, electrons and ions. Elements present are largely consistent with those w ...
... some metal and non-metal elements. Studies have found organic radicals such as OH, CO and CH4, and even molecules of up to 8-9 atoms. • Interstellar matter is of two kinds: – Insterstellar gas includes gaseous atoms, molecules, electrons and ions. Elements present are largely consistent with those w ...
starway of heaven - Conscious Evolution
... The ruling deities of this constellation are the Ashwins, the twin-gods, the divine physicians born of Sun in his form as a horse. These twins are ever youthful, the lords of bliss and healing and are the most ready of all gods to come to the aid of humans. They are fleetfooted and faster than thoug ...
... The ruling deities of this constellation are the Ashwins, the twin-gods, the divine physicians born of Sun in his form as a horse. These twins are ever youthful, the lords of bliss and healing and are the most ready of all gods to come to the aid of humans. They are fleetfooted and faster than thoug ...
The Bible, Science and Creation
... Since 1996, over 1,000 planets outside our solar system have been found Only 5% of stars have planets The planets are either too large, too close to their star, or with too erratic an orbit to harbor life Have the probabilities changed? ...
... Since 1996, over 1,000 planets outside our solar system have been found Only 5% of stars have planets The planets are either too large, too close to their star, or with too erratic an orbit to harbor life Have the probabilities changed? ...
The Bible, Science and Creation
... Since 1996, over 1,000 planets outside our solar system have been found Only 5% of stars have planets The planets are either too large, too close to their star, or with too erratic an orbit to harbor life Have the probabilities changed? ...
... Since 1996, over 1,000 planets outside our solar system have been found Only 5% of stars have planets The planets are either too large, too close to their star, or with too erratic an orbit to harbor life Have the probabilities changed? ...
+(J - cloudfront.net
... spectrum and temperature of a certain star are used to determine its luminosity to be approximately 5.0 x 1031 W. The '!Pparent brightness of the star is 1.4 x 10-9 W m-2. These data can be used to detennine the distance ofihe'staifromEarth~------""----..-.--..---- - - ..(i) ...
... spectrum and temperature of a certain star are used to determine its luminosity to be approximately 5.0 x 1031 W. The '!Pparent brightness of the star is 1.4 x 10-9 W m-2. These data can be used to detennine the distance ofihe'staifromEarth~------""----..-.--..---- - - ..(i) ...
The star Betelgeuse is about 500 light years away from us. If this star
... c. the photoelectric effect d. the large look back times of distant galaxies From the spectrum of a starts light we can learn about a. the CBR b. Planck's constant c. the elements in the star d. its look back time An electron in an atom can go to a higher, more energetic orbit by a. absorbing a phot ...
... c. the photoelectric effect d. the large look back times of distant galaxies From the spectrum of a starts light we can learn about a. the CBR b. Planck's constant c. the elements in the star d. its look back time An electron in an atom can go to a higher, more energetic orbit by a. absorbing a phot ...
File - Adriana Romo
... Interviewer: How much mass do white dwarfs contain? Scientific: They contain as much mass as the sun. Interviewer: How much volume do white dwarfs contain? Scientist: They could contain as much as earth. Interviewer: What is the ultimate fate for the stars like the sun? Scientist: Upon its dead, a ...
... Interviewer: How much mass do white dwarfs contain? Scientific: They contain as much mass as the sun. Interviewer: How much volume do white dwarfs contain? Scientist: They could contain as much as earth. Interviewer: What is the ultimate fate for the stars like the sun? Scientist: Upon its dead, a ...
1. Introduction
... very many, stars pulsate in more complicated manners than the Cepheids. In many instances more than one mode of oscillation is excited simultaneously in a star; these modes may include both radial overtones, in addition to the fundamental, and nonradial modes, where the motion does not preserve sphe ...
... very many, stars pulsate in more complicated manners than the Cepheids. In many instances more than one mode of oscillation is excited simultaneously in a star; these modes may include both radial overtones, in addition to the fundamental, and nonradial modes, where the motion does not preserve sphe ...
Lecture Nine (Powerpoint format) - Flash
... Survey, led an expedition through the Grand Canyon and estimated its age -- today known to be nearly 2 billion years old. Today we know from crater records of the moon and radioactive dating of meteorites that the solar system is about 4.6 billion years old. ...
... Survey, led an expedition through the Grand Canyon and estimated its age -- today known to be nearly 2 billion years old. Today we know from crater records of the moon and radioactive dating of meteorites that the solar system is about 4.6 billion years old. ...
ACTIVITIES for Grades 3-5 (Continued)
... • What kinds of energy does the Sun provide for Earth? Answers may include: The Sun provides heat and light. Plants capture this energy through the process of photosynthesis, create sugars and starches, and store them for later use. • Where do a plant, a grasshopper, a chicken, and a human get their ...
... • What kinds of energy does the Sun provide for Earth? Answers may include: The Sun provides heat and light. Plants capture this energy through the process of photosynthesis, create sugars and starches, and store them for later use. • Where do a plant, a grasshopper, a chicken, and a human get their ...
A Reappraisal of The Habitability of Planets around M Dwarf Stars
... lengths nearly a century ago. It was later understood that the observable spectral features provide information about stellar surface temperatures and mass, but by then the classification alphabet was well established, requiring the ordering OBAFGKML from the hottest most massive star to the coolest ...
... lengths nearly a century ago. It was later understood that the observable spectral features provide information about stellar surface temperatures and mass, but by then the classification alphabet was well established, requiring the ordering OBAFGKML from the hottest most massive star to the coolest ...
A re-appraisal of the habitability of planets around M dwarf
... lengths nearly a century ago. It was later understood that the observable spectral features provide information about stellar surface temperatures and mass, but by then the classification alphabet was well established, requiring the ordering OBAFGKML from the hottest most massive star to the coolest ...
... lengths nearly a century ago. It was later understood that the observable spectral features provide information about stellar surface temperatures and mass, but by then the classification alphabet was well established, requiring the ordering OBAFGKML from the hottest most massive star to the coolest ...
here - ESA Science
... Information from Hipparcos has enabled astronomers to trace the Sun’s passage through the Galaxy back in time. This has shown that over the last 500 million years the Sun has passed through four of the Milky Way’s spiral arms. The times that these traverses occurred appear to coincide with extended ...
... Information from Hipparcos has enabled astronomers to trace the Sun’s passage through the Galaxy back in time. This has shown that over the last 500 million years the Sun has passed through four of the Milky Way’s spiral arms. The times that these traverses occurred appear to coincide with extended ...
Planetary habitability

Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia. As the existence of life beyond Earth is unknown, planetary habitability is largely an extrapolation of conditions on Earth and the characteristics of the Sun and Solar System which appear favourable to life's flourishing—in particular those factors that have sustained complex, multicellular organisms and not just simpler, unicellular creatures. Research and theory in this regard is a component of planetary science and the emerging discipline of astrobiology.An absolute requirement for life is an energy source, and the notion of planetary habitability implies that many other geophysical, geochemical, and astrophysical criteria must be met before an astronomical body can support life. In its astrobiology roadmap, NASA has defined the principal habitability criteria as ""extended regions of liquid water, conditions favourable for the assembly of complex organic molecules, and energy sources to sustain metabolism.""In determining the habitability potential of a body, studies focus on its bulk composition, orbital properties, atmosphere, and potential chemical interactions. Stellar characteristics of importance include mass and luminosity, stable variability, and high metallicity. Rocky, terrestrial-type planets and moons with the potential for Earth-like chemistry are a primary focus of astrobiological research, although more speculative habitability theories occasionally examine alternative biochemistries and other types of astronomical bodies.The idea that planets beyond Earth might host life is an ancient one, though historically it was framed by philosophy as much as physical science. The late 20th century saw two breakthroughs in the field. The observation and robotic spacecraft exploration of other planets and moons within the Solar System has provided critical information on defining habitability criteria and allowed for substantial geophysical comparisons between the Earth and other bodies. The discovery of extrasolar planets, beginning in the early 1990s and accelerating thereafter, has provided further information for the study of possible extraterrestrial life. These findings confirm that the Sun is not unique among stars in hosting planets and expands the habitability research horizon beyond the Solar System.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently. On 4 November 2013, astronomers reported, based on Kepler space mission data, that there could be as many as 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of Sun-like stars and red dwarfs within the Milky Way. 11 billion of these estimated planets may be orbiting Sun-like stars. The nearest such planet may be 12 light-years away, according to the scientists.