Exam 2
... example, some of the heavy elements (such as carbon, nitrogen and oxygen) that form in a star’s core move into its outer layers. The abundance of these elements in a planetary nebula can show how material mixes through the various parts of a star’s interior. The expanding nebula merges with the inte ...
... example, some of the heavy elements (such as carbon, nitrogen and oxygen) that form in a star’s core move into its outer layers. The abundance of these elements in a planetary nebula can show how material mixes through the various parts of a star’s interior. The expanding nebula merges with the inte ...
stars - acpsd
... and planetary systems. Time scales of Stellar Fuel Consumption The time scales of stellar evolution depend on the mass of the star. The rule governing stellar evolution is the more mass present, the faster the evolution for the star through the fuel consumption stages. Another property directly link ...
... and planetary systems. Time scales of Stellar Fuel Consumption The time scales of stellar evolution depend on the mass of the star. The rule governing stellar evolution is the more mass present, the faster the evolution for the star through the fuel consumption stages. Another property directly link ...
- Schwab`s Writings
... both. The newly created universe appears to have produced an asymmetrical amount of those two types, allowing the existence of the world as we know it after most opposite particles annihilated themselves and only the not-matched ones were left over. The resulting “matter” makes up about 5% of our un ...
... both. The newly created universe appears to have produced an asymmetrical amount of those two types, allowing the existence of the world as we know it after most opposite particles annihilated themselves and only the not-matched ones were left over. The resulting “matter” makes up about 5% of our un ...
The Science of Astronomy 3.1 Multiple
... E) We don't know how he did it since all his writings were destroyed. Answer: C 16) Which of the following statements about scientific models is true? A) A model tries to represent all aspects of nature. B) A model tries to represent only one aspect of nature. C) A model can be used to explain and p ...
... E) We don't know how he did it since all his writings were destroyed. Answer: C 16) Which of the following statements about scientific models is true? A) A model tries to represent all aspects of nature. B) A model tries to represent only one aspect of nature. C) A model can be used to explain and p ...
Untitled
... atmosphere by turbulent heat exchanges, so that the ground temperature cannot deviate much from that of the immediately overlying air. Thus, Ts = T (ps ). If the atmosphere were transparent to infrared, as is very nearly the case for nitrogen or oxygen, the OLR would be σ Ts4 . Now, let’s stir an ad ...
... atmosphere by turbulent heat exchanges, so that the ground temperature cannot deviate much from that of the immediately overlying air. Thus, Ts = T (ps ). If the atmosphere were transparent to infrared, as is very nearly the case for nitrogen or oxygen, the OLR would be σ Ts4 . Now, let’s stir an ad ...
View PDF - Sara Seager
... Abstract. The Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) will search for planets transiting bright and nearby stars. TESS has been selected by NASA for launch in 2017 as an Astrophysics Explorer mission. The spacecraft will be placed into a highly elliptical 13.7-day orbit around the Earth. During ...
... Abstract. The Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) will search for planets transiting bright and nearby stars. TESS has been selected by NASA for launch in 2017 as an Astrophysics Explorer mission. The spacecraft will be placed into a highly elliptical 13.7-day orbit around the Earth. During ...
Compartive Planetology I: Our Solar. System
... vian planets would be futile, because the materials of which these planets are made are mostly gaseous or liquid. The visible “surface” features of a Jovian planet are actually cloud forma— tions in the planet’s atmosphere. The photographs in Figure 7-2 show the distinctive appearances of the two cl ...
... vian planets would be futile, because the materials of which these planets are made are mostly gaseous or liquid. The visible “surface” features of a Jovian planet are actually cloud forma— tions in the planet’s atmosphere. The photographs in Figure 7-2 show the distinctive appearances of the two cl ...
Problem 1. Marking scheme Lagrange Point
... You may use the following data: T 272 K / the temperature of the ice in the can, p s 550 Pa - the pressure of the saturated water vapors at the temperature T 272 K ; R 8300 J/(kmol K) - the constant of perfect gas; 18 kg/kmol - the molar mass of the water. ...
... You may use the following data: T 272 K / the temperature of the ice in the can, p s 550 Pa - the pressure of the saturated water vapors at the temperature T 272 K ; R 8300 J/(kmol K) - the constant of perfect gas; 18 kg/kmol - the molar mass of the water. ...
Why do Earth satellites stay up?
... physical explanation for this stability. In asking our colleagues we have received a variety of answers, such as “there are only periodic oscillations in the perigee and these are too small to be important” or “the orbits are unstable but on timescales much longer than the satellite lifetime”. We sh ...
... physical explanation for this stability. In asking our colleagues we have received a variety of answers, such as “there are only periodic oscillations in the perigee and these are too small to be important” or “the orbits are unstable but on timescales much longer than the satellite lifetime”. We sh ...
Kepler File
... begin with, the relative distance between the spheres will remain the same. Kepler found to his great delight that the relative distance between the planetary orbits that he found after nesting all these regular solids and spheres was pretty close to the distances that had been calculated from the C ...
... begin with, the relative distance between the spheres will remain the same. Kepler found to his great delight that the relative distance between the planetary orbits that he found after nesting all these regular solids and spheres was pretty close to the distances that had been calculated from the C ...
Planets, Moons, and Stars
... of its lighted side. The Sun shines on and lights half of the Moon’s surface. The other half faces away from the Sun. It is in darkness. As the Moon revolves around Earth, different amounts of the Moon’s lighted half face Earth. The lighted parts are the phases you see. When the Moon is between Eart ...
... of its lighted side. The Sun shines on and lights half of the Moon’s surface. The other half faces away from the Sun. It is in darkness. As the Moon revolves around Earth, different amounts of the Moon’s lighted half face Earth. The lighted parts are the phases you see. When the Moon is between Eart ...
12.1 Introduction
... Particularly useful in this respect are the H-R diagrams of halo globular clusters which, being among the oldest stellar systems known, give us a view of the late stages in the evolution of long-lived stars with masses comparable to that of the Sun (see Figure 12.3). The combination of computer mode ...
... Particularly useful in this respect are the H-R diagrams of halo globular clusters which, being among the oldest stellar systems known, give us a view of the late stages in the evolution of long-lived stars with masses comparable to that of the Sun (see Figure 12.3). The combination of computer mode ...
Ben R. Oppenheimer1,2 and Sasha Hinkley1,2
... (commonly defined as objects below roughly 13 MJ where MJ is the mass of Jupiter; see Side Bar), one need only take a very superficial look at the objects in our solar system to see a vast diversity. Indeed, the giant planets of our solar system are all roughly of the same radius, of nearly the sam ...
... (commonly defined as objects below roughly 13 MJ where MJ is the mass of Jupiter; see Side Bar), one need only take a very superficial look at the objects in our solar system to see a vast diversity. Indeed, the giant planets of our solar system are all roughly of the same radius, of nearly the sam ...
Mar 2016 - Bays Mountain Park
... used. Early scientific instruments were fancy sticks, such as the astrolabe and armillary. The Best Man: America’s Pioneering Astrophysicist, J.E. Keeler Tom English, professor of astronomy at Guilford Technical Community College, gave an in-depth biography of American astrophysicist James Edward Ke ...
... used. Early scientific instruments were fancy sticks, such as the astrolabe and armillary. The Best Man: America’s Pioneering Astrophysicist, J.E. Keeler Tom English, professor of astronomy at Guilford Technical Community College, gave an in-depth biography of American astrophysicist James Edward Ke ...
Life as a Low Mass Red Giant
... – As core temperature rises, fusion rate rises, so luminosity increases somewhat. – This is very important for understanding origin of life on earth. Sun's luminosity has grown at least 50% since birth of Earth. Planetary scientists having difficult time understanding why Earth was not in permanent ...
... – As core temperature rises, fusion rate rises, so luminosity increases somewhat. – This is very important for understanding origin of life on earth. Sun's luminosity has grown at least 50% since birth of Earth. Planetary scientists having difficult time understanding why Earth was not in permanent ...
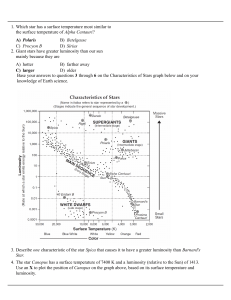
A) Polaris B) Betelgeuse C) Procyon B D) Sirius 1. Which star has a
... 38. Compared to other groups of stars, the group that has 44. The schematic below shows the number of stars relatively low luminosities and relatively low formed in each mass range for each star more temperatures is the massive than 10 M Sun . A) Red Dwarfs B) White Dwarfs C) Red Giants D) Blue Supe ...
... 38. Compared to other groups of stars, the group that has 44. The schematic below shows the number of stars relatively low luminosities and relatively low formed in each mass range for each star more temperatures is the massive than 10 M Sun . A) Red Dwarfs B) White Dwarfs C) Red Giants D) Blue Supe ...
L87 THE b PICTORIS MOVING GROUP B. ZUCkERMAN AND
... Notes.—Units of right ascension are hours, minutes, and seconds, and units of declination are degrees, arcminutes, and arcseconds. (1) On A star zero-age main sequence (Jura et al. 1998). (2) Binary: listed ROSAT flux and LX/Lbol are for the secondary. (3) See Table 2 for additional details. (4) See ...
... Notes.—Units of right ascension are hours, minutes, and seconds, and units of declination are degrees, arcminutes, and arcseconds. (1) On A star zero-age main sequence (Jura et al. 1998). (2) Binary: listed ROSAT flux and LX/Lbol are for the secondary. (3) See Table 2 for additional details. (4) See ...
10. Atmospheres of Planets and of Exoplanets - ETH E
... The Atmosphere of Mercury - 1 So far it was a riddle: How is it possible that the low-mass intermost and hottest Planet can keep a permant Atmosphere, even though this Atmosphere is extremely thin? On the day side, the surface temperature of Mercury is over 400oC (s. p. 419). Due to the strong radi ...
... The Atmosphere of Mercury - 1 So far it was a riddle: How is it possible that the low-mass intermost and hottest Planet can keep a permant Atmosphere, even though this Atmosphere is extremely thin? On the day side, the surface temperature of Mercury is over 400oC (s. p. 419). Due to the strong radi ...
Lecture 30 Solar System Formation and Early Evolution
... 7. Why are Earth’s two close neighbors Venus and Mars so different, especially in surface temperature? For answers to such questions, one of the most important sources of clues is the meteorites and their compositions. GG325 L30, F2013 ...
... 7. Why are Earth’s two close neighbors Venus and Mars so different, especially in surface temperature? For answers to such questions, one of the most important sources of clues is the meteorites and their compositions. GG325 L30, F2013 ...
01_test_bank
... A) It contains between 100 billion and 1 trillion stars. B) Our solar system is located very close to the center of the Milky Way Galaxy. C) Our view of distant objects is obscured by gas and dust when we look into the galactic plane. D) The galaxy is about 100,000 light-years in diameter. E) One ro ...
... A) It contains between 100 billion and 1 trillion stars. B) Our solar system is located very close to the center of the Milky Way Galaxy. C) Our view of distant objects is obscured by gas and dust when we look into the galactic plane. D) The galaxy is about 100,000 light-years in diameter. E) One ro ...
Chapter-by-Chapter Guide
... much younger than they are today. This statement makes sense because when we look far into space, we also see far back in time. Thus, we see distant galaxies as they were in the distant past, when they were younger than they are today. At a nearby park, I built a scale model of our solar system in w ...
... much younger than they are today. This statement makes sense because when we look far into space, we also see far back in time. Thus, we see distant galaxies as they were in the distant past, when they were younger than they are today. At a nearby park, I built a scale model of our solar system in w ...
Identifying the rotation rate and the presence of dynamic
... We simulate several time series of the Earth’s scattered light towards a hypothetical observer. For each time series, we perform an autocorrelation analysis. For example, in Figure 3, the black curve shows the autocorrelation as a function of the time lag based on a simulated data series for an Eart ...
... We simulate several time series of the Earth’s scattered light towards a hypothetical observer. For each time series, we perform an autocorrelation analysis. For example, in Figure 3, the black curve shows the autocorrelation as a function of the time lag based on a simulated data series for an Eart ...
The Chemical Composition of an Extrasolar Kuiper-Belt
... The Kuiper Belt of our solar system is a source of short-period comets that may have delivered water and other volatiles to Earth and the other terrestrial planets. However, the distribution of water and other volatiles in extrasolar planetary systems is largely unknown. We report the discovery of a ...
... The Kuiper Belt of our solar system is a source of short-period comets that may have delivered water and other volatiles to Earth and the other terrestrial planets. However, the distribution of water and other volatiles in extrasolar planetary systems is largely unknown. We report the discovery of a ...
Grade 8 Earth/Space Posttest
... ____ 23. The heliocentric model over time replaced the geocentric model as the explanation that astronomers accepted for their observed movements of planet, stars, and other objects in the sky. Which statement best explains the basic principles of the heliocentric model? A. The heliocentric model sh ...
... ____ 23. The heliocentric model over time replaced the geocentric model as the explanation that astronomers accepted for their observed movements of planet, stars, and other objects in the sky. Which statement best explains the basic principles of the heliocentric model? A. The heliocentric model sh ...
Planetary habitability

Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia. As the existence of life beyond Earth is unknown, planetary habitability is largely an extrapolation of conditions on Earth and the characteristics of the Sun and Solar System which appear favourable to life's flourishing—in particular those factors that have sustained complex, multicellular organisms and not just simpler, unicellular creatures. Research and theory in this regard is a component of planetary science and the emerging discipline of astrobiology.An absolute requirement for life is an energy source, and the notion of planetary habitability implies that many other geophysical, geochemical, and astrophysical criteria must be met before an astronomical body can support life. In its astrobiology roadmap, NASA has defined the principal habitability criteria as ""extended regions of liquid water, conditions favourable for the assembly of complex organic molecules, and energy sources to sustain metabolism.""In determining the habitability potential of a body, studies focus on its bulk composition, orbital properties, atmosphere, and potential chemical interactions. Stellar characteristics of importance include mass and luminosity, stable variability, and high metallicity. Rocky, terrestrial-type planets and moons with the potential for Earth-like chemistry are a primary focus of astrobiological research, although more speculative habitability theories occasionally examine alternative biochemistries and other types of astronomical bodies.The idea that planets beyond Earth might host life is an ancient one, though historically it was framed by philosophy as much as physical science. The late 20th century saw two breakthroughs in the field. The observation and robotic spacecraft exploration of other planets and moons within the Solar System has provided critical information on defining habitability criteria and allowed for substantial geophysical comparisons between the Earth and other bodies. The discovery of extrasolar planets, beginning in the early 1990s and accelerating thereafter, has provided further information for the study of possible extraterrestrial life. These findings confirm that the Sun is not unique among stars in hosting planets and expands the habitability research horizon beyond the Solar System.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently. On 4 November 2013, astronomers reported, based on Kepler space mission data, that there could be as many as 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of Sun-like stars and red dwarfs within the Milky Way. 11 billion of these estimated planets may be orbiting Sun-like stars. The nearest such planet may be 12 light-years away, according to the scientists.