Gravitation 4, and the Waltz of the Planets
... arrangement of the planets without ambiguity. Copernicus realized that because Mercury and Venus are al ways observed fairly near the Sun in the sky, their orbits must be smaller than Earth’s. Planets in such orbits are called inferior planets (Figure 4-6). The other visible planets—Mars, Jupiter, a ...
... arrangement of the planets without ambiguity. Copernicus realized that because Mercury and Venus are al ways observed fairly near the Sun in the sky, their orbits must be smaller than Earth’s. Planets in such orbits are called inferior planets (Figure 4-6). The other visible planets—Mars, Jupiter, a ...
Senior thesis - University of Texas Astronomy Home Page
... Fig. 3.—: Simulations of pulsations in the DBV star GD 358. Changes in the observed flux of the white dwarf on the left corresponds to surface brightness changes modeled on the right. Calculations and figure courtesy of Mike Montgomery white dwarf, slight changes in temperature and pressure cause th ...
... Fig. 3.—: Simulations of pulsations in the DBV star GD 358. Changes in the observed flux of the white dwarf on the left corresponds to surface brightness changes modeled on the right. Calculations and figure courtesy of Mike Montgomery white dwarf, slight changes in temperature and pressure cause th ...
PSCI1030-CHAP016-The Solar System
... or Jovian Planets • Pluto is the only planet that has not been visited by a space probe Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. ...
... or Jovian Planets • Pluto is the only planet that has not been visited by a space probe Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. ...
Inti didn`t form in the X wind (and neither did most CAIs)
... "upstream" and limited (Cuzzi & Hogan 2003; Cuzzi et al. 2003). In a decretion disk, outward radial diffusion goes "with the flow": the majority of material can be transported outward. Enables outward transport of crystalline silicates and even CAI-like materials produced in inner solar system, out ...
... "upstream" and limited (Cuzzi & Hogan 2003; Cuzzi et al. 2003). In a decretion disk, outward radial diffusion goes "with the flow": the majority of material can be transported outward. Enables outward transport of crystalline silicates and even CAI-like materials produced in inner solar system, out ...
Lecture 13 Main Sequence and Low Mass Evolution
... young as they only live for a few Million years. • You can’t tell how old an M dwarf is because their lives can be so long. • The Sun is ~ 5 Billion years old, so it will last only for ~ 5 Billion years longer. ...
... young as they only live for a few Million years. • You can’t tell how old an M dwarf is because their lives can be so long. • The Sun is ~ 5 Billion years old, so it will last only for ~ 5 Billion years longer. ...
PHYS3380_102815_bw - The University of Texas at Dallas
... Stellar Model For isolated, static, and spherically symmetric stars – these laws lead to four basic equations to describe structure. All physical quantities depend on the distance from the centre of the star ...
... Stellar Model For isolated, static, and spherically symmetric stars – these laws lead to four basic equations to describe structure. All physical quantities depend on the distance from the centre of the star ...
Planet Building Part 4
... Saturn and then somehow were shifted outward by gravitational interactions. – This seems to be a rather complex explanation. – Remember, in science, the more complex an explanation, the less likely it is true. ...
... Saturn and then somehow were shifted outward by gravitational interactions. – This seems to be a rather complex explanation. – Remember, in science, the more complex an explanation, the less likely it is true. ...
Sky Maps Teacher`s Guide - Northern Stars Planetarium
... Friction and compression between rock and the air create enough heat to make the object burn. Most meteors never reach the ground. Instead, they burn up high in the atmosphere. Nebulae are large interstellar gas clouds. There are several types of nebulae. The so called hydrogen II clouds are regions ...
... Friction and compression between rock and the air create enough heat to make the object burn. Most meteors never reach the ground. Instead, they burn up high in the atmosphere. Nebulae are large interstellar gas clouds. There are several types of nebulae. The so called hydrogen II clouds are regions ...
The Origin, Structure, and Evolution of the Stars
... the galaxy is so huge that the total mass of this material accounts for about one-tenth the mass of the galaxy—quite enough to provide material for the formation of new stars. Astronomers believe that initially the galaxy was an ellipsoid of gas that tended to flatten to its present form because of ...
... the galaxy is so huge that the total mass of this material accounts for about one-tenth the mass of the galaxy—quite enough to provide material for the formation of new stars. Astronomers believe that initially the galaxy was an ellipsoid of gas that tended to flatten to its present form because of ...
13.1 Introduction 13.2 The Red Giant Branch
... An important process experienced by stars while they are in the red giant phase is mass loss. As the stellar luminosity and radius increase while a star evolves along the giant branch, the envelope becomes loosely bound and it is relatively easy for the large photon flux to remove mass from the stel ...
... An important process experienced by stars while they are in the red giant phase is mass loss. As the stellar luminosity and radius increase while a star evolves along the giant branch, the envelope becomes loosely bound and it is relatively easy for the large photon flux to remove mass from the stel ...
Low mass stars
... Nearby stars: main-sequence appears. Most stars are less luminous and cooler than the Sun (alpha Centauri, nearest to us and a triple system, is similar). Note the hot small stars: the white dwarfs. ...
... Nearby stars: main-sequence appears. Most stars are less luminous and cooler than the Sun (alpha Centauri, nearest to us and a triple system, is similar). Note the hot small stars: the white dwarfs. ...
Astronomy and the Coal Age of Alabama
... would. Relative patterns on a solid object are maintained as the object rotates. In the Milky Way, stars farther from the center take longer to go around than stars closer in. Also, orbits are generally not closed. This changes all relative patterns, like constellations. ...
... would. Relative patterns on a solid object are maintained as the object rotates. In the Milky Way, stars farther from the center take longer to go around than stars closer in. Also, orbits are generally not closed. This changes all relative patterns, like constellations. ...
takes its time doing so. The coolest white dwarfs
... Figure 3: : White Dwarf Luminosity Distribution: log of the number of white dwarfs observed at a certain luminosity. The circles show the number observed, while the solid line represent the theoretical distribution. The observed points in the above graph come from several sources. The hotter sources ...
... Figure 3: : White Dwarf Luminosity Distribution: log of the number of white dwarfs observed at a certain luminosity. The circles show the number observed, while the solid line represent the theoretical distribution. The observed points in the above graph come from several sources. The hotter sources ...
IDENTIFYING THE ROTATION RATE AND THE PRESENCE OF
... (e.g., the blue curve for the cloudy Earth has no significant amplitude at 12 hr) but rather is due to the distribution of continents and oceans on the Earth. For this data set, the difference in the amplitude between the local maxima at 12 hr and 24 hr would indicate that the peak at 24 hr correspo ...
... (e.g., the blue curve for the cloudy Earth has no significant amplitude at 12 hr) but rather is due to the distribution of continents and oceans on the Earth. For this data set, the difference in the amplitude between the local maxima at 12 hr and 24 hr would indicate that the peak at 24 hr correspo ...
Earth Science - Bryn Mawr Elementary School - Index
... The curriculum for the competency-based Credit-Recovery Program was developed by committees of high school teachers. The curriculum was designed to focus solely on essential State Standards as defined by the blueprints for the California Standards Tests and the California High School Exit Exam. With ...
... The curriculum for the competency-based Credit-Recovery Program was developed by committees of high school teachers. The curriculum was designed to focus solely on essential State Standards as defined by the blueprints for the California Standards Tests and the California High School Exit Exam. With ...
The Essential Cosmic Perspective, 6e
... percent of this material into heavier elements, including all the elements of which we and Earth are made. Stars expel this material through winds and explosions, and the galaxy recycles it into new generations of stars. When a new star system forms, it therefore contains the ingredients needed to m ...
... percent of this material into heavier elements, including all the elements of which we and Earth are made. Stars expel this material through winds and explosions, and the galaxy recycles it into new generations of stars. When a new star system forms, it therefore contains the ingredients needed to m ...
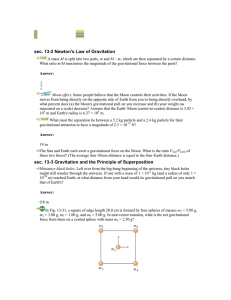
Halliday 9th chapter 13
... Certain neutron stars (extremely dense stars) are believed to be rotating at about 1 rev/s. If such a star has a radius of 20 km, what must be its minimum mass so that material on its surface remains in place during the rapid rotation? Answer: 5 × 1024 kg ••22The radius Rh and mass Mh of a black hol ...
... Certain neutron stars (extremely dense stars) are believed to be rotating at about 1 rev/s. If such a star has a radius of 20 km, what must be its minimum mass so that material on its surface remains in place during the rapid rotation? Answer: 5 × 1024 kg ••22The radius Rh and mass Mh of a black hol ...
PSU/TCfA search for planets around evolved stars
... Proper interpretation of results obtained from precision RV studies of GK giants also requires detailed knowledge of their physical parameters. Effective temperatures and gravitational accelerations are needed to obtain luminosities and in turn, with additional knowledge of metallicities, an estimat ...
... Proper interpretation of results obtained from precision RV studies of GK giants also requires detailed knowledge of their physical parameters. Effective temperatures and gravitational accelerations are needed to obtain luminosities and in turn, with additional knowledge of metallicities, an estimat ...
Stars and Stellar Evolution The Hertzsprung
... Nearby stars: main-sequence appears. Most stars are less luminous and cooler than the Sun (alpha Centauri, nearest to us and a triple system, is similar). Note the hot small stars: the white dwarfs. ...
... Nearby stars: main-sequence appears. Most stars are less luminous and cooler than the Sun (alpha Centauri, nearest to us and a triple system, is similar). Note the hot small stars: the white dwarfs. ...
Quarton Name Hull Class Disposition After Cimtar
... speculated that this may refer to the enigmatic "Count Iblis", a being who bedeviled the Fleet for the first several years of our journey. After fleeing beyond the Home System, the Twilight Guardians settled on a remote, unexplored world. They had escaped with several warships, as well as three gene ...
... speculated that this may refer to the enigmatic "Count Iblis", a being who bedeviled the Fleet for the first several years of our journey. After fleeing beyond the Home System, the Twilight Guardians settled on a remote, unexplored world. They had escaped with several warships, as well as three gene ...
The figure below shows what scientists over 1000 years ago thought
... Over 300 years ago, the famous scientist Isaac Newton proposed, with a ‘thought experiment’, the idea of satellites. Newton suggested that if an object was fired at the right speed from the top of a high mountain, it would circle the Earth. Why did many people accept Isaac Newton’s idea as being pos ...
... Over 300 years ago, the famous scientist Isaac Newton proposed, with a ‘thought experiment’, the idea of satellites. Newton suggested that if an object was fired at the right speed from the top of a high mountain, it would circle the Earth. Why did many people accept Isaac Newton’s idea as being pos ...
The Moon and the Origin of Life on Earth
... Figure 1: The change of seasons depends on the Earth’s obliquity (a) and on the precession of the equinoxes (b). In summer, the amount of solar heat received in the northern hemisphere is greater than that received in the southern hemisphere. Depending on the angle of precession, the Earth may be at ...
... Figure 1: The change of seasons depends on the Earth’s obliquity (a) and on the precession of the equinoxes (b). In summer, the amount of solar heat received in the northern hemisphere is greater than that received in the southern hemisphere. Depending on the angle of precession, the Earth may be at ...
The masses of stars
... brightness (stars shine with luminosities that are tens of thousands of times fainter and over a million times brighter than our Sun); of surface temperature (from below 3,000K to greater than 30,000K); of size (with diameters of about ten km for neutron stars, about 1.4 million km for our Sun, and ...
... brightness (stars shine with luminosities that are tens of thousands of times fainter and over a million times brighter than our Sun); of surface temperature (from below 3,000K to greater than 30,000K); of size (with diameters of about ten km for neutron stars, about 1.4 million km for our Sun, and ...
A dust ring around Epsilon Eridani: analogue to the young Solar
... 1984; Jayawardhana et al. 1998; Koerner et al. 1998). Unexpected features are now emerging, including secondary dust spots around Vega and β Pic (Holland et al. 1998a), and these have yet to be explained by planet formation theories. So far, there is little evidence for analogues of the Solar System ...
... 1984; Jayawardhana et al. 1998; Koerner et al. 1998). Unexpected features are now emerging, including secondary dust spots around Vega and β Pic (Holland et al. 1998a), and these have yet to be explained by planet formation theories. So far, there is little evidence for analogues of the Solar System ...
Planetary habitability

Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia. As the existence of life beyond Earth is unknown, planetary habitability is largely an extrapolation of conditions on Earth and the characteristics of the Sun and Solar System which appear favourable to life's flourishing—in particular those factors that have sustained complex, multicellular organisms and not just simpler, unicellular creatures. Research and theory in this regard is a component of planetary science and the emerging discipline of astrobiology.An absolute requirement for life is an energy source, and the notion of planetary habitability implies that many other geophysical, geochemical, and astrophysical criteria must be met before an astronomical body can support life. In its astrobiology roadmap, NASA has defined the principal habitability criteria as ""extended regions of liquid water, conditions favourable for the assembly of complex organic molecules, and energy sources to sustain metabolism.""In determining the habitability potential of a body, studies focus on its bulk composition, orbital properties, atmosphere, and potential chemical interactions. Stellar characteristics of importance include mass and luminosity, stable variability, and high metallicity. Rocky, terrestrial-type planets and moons with the potential for Earth-like chemistry are a primary focus of astrobiological research, although more speculative habitability theories occasionally examine alternative biochemistries and other types of astronomical bodies.The idea that planets beyond Earth might host life is an ancient one, though historically it was framed by philosophy as much as physical science. The late 20th century saw two breakthroughs in the field. The observation and robotic spacecraft exploration of other planets and moons within the Solar System has provided critical information on defining habitability criteria and allowed for substantial geophysical comparisons between the Earth and other bodies. The discovery of extrasolar planets, beginning in the early 1990s and accelerating thereafter, has provided further information for the study of possible extraterrestrial life. These findings confirm that the Sun is not unique among stars in hosting planets and expands the habitability research horizon beyond the Solar System.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently. On 4 November 2013, astronomers reported, based on Kepler space mission data, that there could be as many as 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of Sun-like stars and red dwarfs within the Milky Way. 11 billion of these estimated planets may be orbiting Sun-like stars. The nearest such planet may be 12 light-years away, according to the scientists.