The birth of stars and planets - School of Physics
... for those who’d like to know more about the subject. It’s written by two experts in the field, is entirely non-technical, and has fantastic illustrations all the way through. • “The Story of the Solar System” by Mark Garlick (Cambridge, 2002) is by that rarest of creatures, an artist who is also a s ...
... for those who’d like to know more about the subject. It’s written by two experts in the field, is entirely non-technical, and has fantastic illustrations all the way through. • “The Story of the Solar System” by Mark Garlick (Cambridge, 2002) is by that rarest of creatures, an artist who is also a s ...
FREE Sample Here
... 2 percent of this material into heavier elements, including all the elements of which we and Earth are made. Stars expel this material through winds and explosions, and the galaxy recycles it into new generations of stars. When a new star system forms, it therefore contains the ingredients needed to ...
... 2 percent of this material into heavier elements, including all the elements of which we and Earth are made. Stars expel this material through winds and explosions, and the galaxy recycles it into new generations of stars. When a new star system forms, it therefore contains the ingredients needed to ...
Chapter 1 - Pearson Education
... as galaxies and clusters of galaxies occupy regions where gravity has won out against the overall expansion That is, while the universe as a whole continues to expand, individual galaxies and their contents do not expand. Most galaxies, including our own Milky Way, probably formed within a few billi ...
... as galaxies and clusters of galaxies occupy regions where gravity has won out against the overall expansion That is, while the universe as a whole continues to expand, individual galaxies and their contents do not expand. Most galaxies, including our own Milky Way, probably formed within a few billi ...
What causes the moon to change in appearance
... all may have been caused by the crust cracking and wind erosion. On Earth, many valleys are caused by erosion when water flows downhill, so we can make an inference—a conclusion based on evidence and reasoning--that there was a lot of water on the planet long ago. There are areas in the southern hem ...
... all may have been caused by the crust cracking and wind erosion. On Earth, many valleys are caused by erosion when water flows downhill, so we can make an inference—a conclusion based on evidence and reasoning--that there was a lot of water on the planet long ago. There are areas in the southern hem ...
Radial Velocity - Yale Exoplanet
... The unknown inclination angle i prevents us from meaIn this equation, v is the velocity of the source relative suring the true mass of the companion m2 . While this is an important limitation of the RV technique for individual to the observer, k is the unit vector pointing from the obsystems, this f ...
... The unknown inclination angle i prevents us from meaIn this equation, v is the velocity of the source relative suring the true mass of the companion m2 . While this is an important limitation of the RV technique for individual to the observer, k is the unit vector pointing from the obsystems, this f ...
PHYS3380_110215_bw - The University of Texas at Dallas
... •In stars of less than about 10 solar masses, the outer envelope of the star contains a region where partial ionization of hydrogen and helium raises the heat capacity. The relatively low temperature in this region simultaneously causes the opacity due to heavier elements to be high enough to produc ...
... •In stars of less than about 10 solar masses, the outer envelope of the star contains a region where partial ionization of hydrogen and helium raises the heat capacity. The relatively low temperature in this region simultaneously causes the opacity due to heavier elements to be high enough to produc ...
ELED 303
... Weathering occurs all around us, but because it is such a slow process, we don't always notice its effects. All materials are susceptible to weathering, which is the physical breakdown of rock into smaller pieces or the chemical decomposition of rock into different materials, taking place at or near ...
... Weathering occurs all around us, but because it is such a slow process, we don't always notice its effects. All materials are susceptible to weathering, which is the physical breakdown of rock into smaller pieces or the chemical decomposition of rock into different materials, taking place at or near ...
The Time of Perihelion Passage and the Longitude of Perihelion of
... perturbed the orbits of the planets substantially, especially near times of perihelion passage. Yet almost no such perturbations have been detected. This can be explained if Nemesis is comprised of two stars with complementary orbits such that their perturbing accelerations tend to cancel at the Sun ...
... perturbed the orbits of the planets substantially, especially near times of perihelion passage. Yet almost no such perturbations have been detected. This can be explained if Nemesis is comprised of two stars with complementary orbits such that their perturbing accelerations tend to cancel at the Sun ...
Appendix A - Government of Newfoundland and Labrador
... systems around stars other than our own sun. Most of the planets we have found orbiting other stars have been large gas giants like Jupiter. Some of them have also been found very close to their parent star, unlike our own solar system. However, for the first time, we have been able to detect earth ...
... systems around stars other than our own sun. Most of the planets we have found orbiting other stars have been large gas giants like Jupiter. Some of them have also been found very close to their parent star, unlike our own solar system. However, for the first time, we have been able to detect earth ...
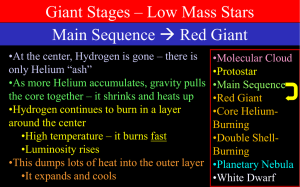
Giant Stars
... •For stars from 0.5 to 3 MSun, it is qualitatively the same •Heavy stars do everything faster •For heavier stars, some details are different •Higher temperature and lower density •Core isn’t so compact •No dramatic increase in luminosity •Motion on the H-R diagram is mostly ...
... •For stars from 0.5 to 3 MSun, it is qualitatively the same •Heavy stars do everything faster •For heavier stars, some details are different •Higher temperature and lower density •Core isn’t so compact •No dramatic increase in luminosity •Motion on the H-R diagram is mostly ...
Slide 1
... Observations find hot, dusty discs within tidal radius Can we link the two populations? Maybe the Kuiper-belts provide the reservoir of material required to replenish the hot discs? We just need a mechanism to move the material inwards ….. ...
... Observations find hot, dusty discs within tidal radius Can we link the two populations? Maybe the Kuiper-belts provide the reservoir of material required to replenish the hot discs? We just need a mechanism to move the material inwards ….. ...
Course Description: This is an introductory course in Descriptive
... d) Distinguishing four separate types of rocks and describing how each is formed. e) Explaining the process of radioactive dating of rocks. f) Describing the general properties of oceans and other bodies of water on Earth and how they interact with continents and the atmosphere. g) Labeling Earth’s ...
... d) Distinguishing four separate types of rocks and describing how each is formed. e) Explaining the process of radioactive dating of rocks. f) Describing the general properties of oceans and other bodies of water on Earth and how they interact with continents and the atmosphere. g) Labeling Earth’s ...
Document
... D • A is incorrect because star A has a negative apparent magnitude, which means it is a brighter star. • B is incorrect because even though star B has a big apparent magnitude, it does not have the biggest apparent magnitude of the stars listed. • C is incorrect because stars that have smaller appa ...
... D • A is incorrect because star A has a negative apparent magnitude, which means it is a brighter star. • B is incorrect because even though star B has a big apparent magnitude, it does not have the biggest apparent magnitude of the stars listed. • C is incorrect because stars that have smaller appa ...
ASTR 1020 Homework Solutions Chapter 1
... each photon’s energy = 0.8 × 10–13 J. We know from Chapter 5 that E = hc/λ or λ = hc/E, so the wavelength of each photon is λ = (6.63 ×10–34 J s)(3 ×108 m/s) / (0.8 × 10–13 J) = 2.5 × 10–12 m = 2.5 × 10–3 nm which is in the gamma-ray portion of the electromagnetic spectrum (see Figure 5-7). 36. Sinc ...
... each photon’s energy = 0.8 × 10–13 J. We know from Chapter 5 that E = hc/λ or λ = hc/E, so the wavelength of each photon is λ = (6.63 ×10–34 J s)(3 ×108 m/s) / (0.8 × 10–13 J) = 2.5 × 10–12 m = 2.5 × 10–3 nm which is in the gamma-ray portion of the electromagnetic spectrum (see Figure 5-7). 36. Sinc ...
The Life of the Sun
... get nice solid Star formation going on and to get our Planets formed and to get everything lined up so that we have a Solar System that looked like the Solar System we live in today although the terrestrial surfaces were very different. ...
... get nice solid Star formation going on and to get our Planets formed and to get everything lined up so that we have a Solar System that looked like the Solar System we live in today although the terrestrial surfaces were very different. ...
The Sun and Stars
... night, about 6,000 stars can be seen without a telescope. Ancient astronomers believed that the sun and the stars were different from each other. Today we know that the sun is just one star like all the others in the night sky. The others appear to be so dim because they are incredibly far away. The ...
... night, about 6,000 stars can be seen without a telescope. Ancient astronomers believed that the sun and the stars were different from each other. Today we know that the sun is just one star like all the others in the night sky. The others appear to be so dim because they are incredibly far away. The ...
The Star Finder Book - Starpath School of Navigation
... patches of clear sky. Such stars may be in view for a few minutes only, just long enough to get a sextant sight of them. New navigators soon learn that these unknown stars may offer the only sights available for several days, and that this can occur much more often than was suspected. This is not ju ...
... patches of clear sky. Such stars may be in view for a few minutes only, just long enough to get a sextant sight of them. New navigators soon learn that these unknown stars may offer the only sights available for several days, and that this can occur much more often than was suspected. This is not ju ...
Video Lesson Information Astronomy: Observations & Theories Astronomy 1
... Lesson 1 - The Study of the Universe This lesson takes students on a journey from planet Earth to the distant galaxies and superclusters. It is illustrated with stunning computer animation and photographs from NASA, the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), and astronomical observatories. This journey in ...
... Lesson 1 - The Study of the Universe This lesson takes students on a journey from planet Earth to the distant galaxies and superclusters. It is illustrated with stunning computer animation and photographs from NASA, the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), and astronomical observatories. This journey in ...
Extrasolar planets - Astronomisk Ungdom
... As mentioned above a macula can disappear and reappear. However, planets do not vanish from their orbit without a trace or a caveat, except if it is a free planet passing the star, but those are rare and not yet accurately proven. All work around extra solar planets is fairly new and current. At pre ...
... As mentioned above a macula can disappear and reappear. However, planets do not vanish from their orbit without a trace or a caveat, except if it is a free planet passing the star, but those are rare and not yet accurately proven. All work around extra solar planets is fairly new and current. At pre ...
The Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite
... The study of exoplanets—planets outside our Solar System—is one of the most exciting and rapidly advancing fields of science. Especially valuable are systems in which a planet’s orbit carries it directly across the face of its host star. For such a “transiting” planet, it is possible to determine th ...
... The study of exoplanets—planets outside our Solar System—is one of the most exciting and rapidly advancing fields of science. Especially valuable are systems in which a planet’s orbit carries it directly across the face of its host star. For such a “transiting” planet, it is possible to determine th ...
LESSON 8: STARS
... 7. Composition of Stars In composition and size, the Sun is an average star and is in the middle of its hydrogen-burning stage. It will continue to process hydrogen for another few billion years before swelling into a red giant. Although the Sun is an averagesized star, it is still huge by Earthly s ...
... 7. Composition of Stars In composition and size, the Sun is an average star and is in the middle of its hydrogen-burning stage. It will continue to process hydrogen for another few billion years before swelling into a red giant. Although the Sun is an averagesized star, it is still huge by Earthly s ...
m/s
... David Fabricius (1564_1617), an amateur astronomer and native of Friesland, The Netherlands, is recognized as the first to have discovered a long period variable in 1596, later called o (omicron) Ceti by Johann Bayer in 1603. Fabricius (Wolf 1877) observed the star from August 3, when he had used it ...
... David Fabricius (1564_1617), an amateur astronomer and native of Friesland, The Netherlands, is recognized as the first to have discovered a long period variable in 1596, later called o (omicron) Ceti by Johann Bayer in 1603. Fabricius (Wolf 1877) observed the star from August 3, when he had used it ...
STELLAR FORMATION AND EVOLUTION
... The central region is denser and forms the protostar. The nebular disk forms slower to become a planetary system. As the temperature and pressure in the center begin to increase, the pressure from the core stops the infalling of gas into the core and the object becomes stable as a protostar. If a pr ...
... The central region is denser and forms the protostar. The nebular disk forms slower to become a planetary system. As the temperature and pressure in the center begin to increase, the pressure from the core stops the infalling of gas into the core and the object becomes stable as a protostar. If a pr ...
Untitled
... From what is understood about our known universe is that, it may be infinitely large and the one that we are familiar with might as well be one of many universes that are possibly our there in the vast regions of space and time. So life would pop up only on planet Earth and no where else in this mas ...
... From what is understood about our known universe is that, it may be infinitely large and the one that we are familiar with might as well be one of many universes that are possibly our there in the vast regions of space and time. So life would pop up only on planet Earth and no where else in this mas ...
Planetary habitability

Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia. As the existence of life beyond Earth is unknown, planetary habitability is largely an extrapolation of conditions on Earth and the characteristics of the Sun and Solar System which appear favourable to life's flourishing—in particular those factors that have sustained complex, multicellular organisms and not just simpler, unicellular creatures. Research and theory in this regard is a component of planetary science and the emerging discipline of astrobiology.An absolute requirement for life is an energy source, and the notion of planetary habitability implies that many other geophysical, geochemical, and astrophysical criteria must be met before an astronomical body can support life. In its astrobiology roadmap, NASA has defined the principal habitability criteria as ""extended regions of liquid water, conditions favourable for the assembly of complex organic molecules, and energy sources to sustain metabolism.""In determining the habitability potential of a body, studies focus on its bulk composition, orbital properties, atmosphere, and potential chemical interactions. Stellar characteristics of importance include mass and luminosity, stable variability, and high metallicity. Rocky, terrestrial-type planets and moons with the potential for Earth-like chemistry are a primary focus of astrobiological research, although more speculative habitability theories occasionally examine alternative biochemistries and other types of astronomical bodies.The idea that planets beyond Earth might host life is an ancient one, though historically it was framed by philosophy as much as physical science. The late 20th century saw two breakthroughs in the field. The observation and robotic spacecraft exploration of other planets and moons within the Solar System has provided critical information on defining habitability criteria and allowed for substantial geophysical comparisons between the Earth and other bodies. The discovery of extrasolar planets, beginning in the early 1990s and accelerating thereafter, has provided further information for the study of possible extraterrestrial life. These findings confirm that the Sun is not unique among stars in hosting planets and expands the habitability research horizon beyond the Solar System.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently. On 4 November 2013, astronomers reported, based on Kepler space mission data, that there could be as many as 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of Sun-like stars and red dwarfs within the Milky Way. 11 billion of these estimated planets may be orbiting Sun-like stars. The nearest such planet may be 12 light-years away, according to the scientists.