May 8, 2012 - Plummer Pumas Science
... Consider the four characteristics (1) Temperature, (2) color, (3) distance, and (4) class or spectral type. Which characteristics most strongly influence the size and location of the habitable zone? Explain your reasoning for each. ____________________________________________________________________ ...
... Consider the four characteristics (1) Temperature, (2) color, (3) distance, and (4) class or spectral type. Which characteristics most strongly influence the size and location of the habitable zone? Explain your reasoning for each. ____________________________________________________________________ ...
Astro 1050 HW #2
... 24. Discuss similarities and differences in the way terrestrial planets and giant planets formed in our Solar System. 25. Many of the giant exoplanets are quite close to their parent stars. If they initially formed farther out, how could they have ended up and their observed positions? 26. What was ...
... 24. Discuss similarities and differences in the way terrestrial planets and giant planets formed in our Solar System. 25. Many of the giant exoplanets are quite close to their parent stars. If they initially formed farther out, how could they have ended up and their observed positions? 26. What was ...
Homework #5 Chapter 3: Solar System Due
... highly elliptical orbits. Many of these worlds are very close to their stars, some within 0.1 AU, even planets massive enough to be "gas giants." It is possible, however, that planetary systems such as our own would not produce enough motion in their stars to detect from Earth. The effects of such s ...
... highly elliptical orbits. Many of these worlds are very close to their stars, some within 0.1 AU, even planets massive enough to be "gas giants." It is possible, however, that planetary systems such as our own would not produce enough motion in their stars to detect from Earth. The effects of such s ...
Review Sheet
... The material on this exam can be broken down into four broad catagories: a quick introduction to the night sky, astronomy as a case history of science, some notes on physics, and an overview of the planets. From the quick introduction to the night sky you should understand: • What the celestial sphe ...
... The material on this exam can be broken down into four broad catagories: a quick introduction to the night sky, astronomy as a case history of science, some notes on physics, and an overview of the planets. From the quick introduction to the night sky you should understand: • What the celestial sphe ...
Our Solar System
... Discovered through math 7 known moons Triton largest moon Great Dark Spot thought to be a hole, similar to the hole in the ozone layer on Earth ...
... Discovered through math 7 known moons Triton largest moon Great Dark Spot thought to be a hole, similar to the hole in the ozone layer on Earth ...
Planet Earth - ThinkChemistry
... Describe what makes up our solar system. Describe the difference between a galaxy and The Universe. Name our galaxy. Name our next closest galaxy. ...
... Describe what makes up our solar system. Describe the difference between a galaxy and The Universe. Name our galaxy. Name our next closest galaxy. ...
Uninhabitableearth
... http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/kepler/overview/index.html#.Uj6eiMaThnQ NASA Science Learn about recent discoveries by the Kepler Space Telescope of three super-Earth planets that lie within the habitable zones of other star systems. http://science.nasa.gov/science-news/science-at-nasa/2013/18apr_ ...
... http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/kepler/overview/index.html#.Uj6eiMaThnQ NASA Science Learn about recent discoveries by the Kepler Space Telescope of three super-Earth planets that lie within the habitable zones of other star systems. http://science.nasa.gov/science-news/science-at-nasa/2013/18apr_ ...
An earthllke planet would have a rocky mantle surround
... little more than 100 years ago. the great British scientist Lord Kelvin proposed that radio waves had no practical use, X rays were a hoax. and heavier-than-air flight was Impossible. Only 25 years before the development of the nuclear bomb. Nobel Laureate Robert Millikan said that humans would neve ...
... little more than 100 years ago. the great British scientist Lord Kelvin proposed that radio waves had no practical use, X rays were a hoax. and heavier-than-air flight was Impossible. Only 25 years before the development of the nuclear bomb. Nobel Laureate Robert Millikan said that humans would neve ...
File - Ms. Feffer 6th and 7th Grade Science
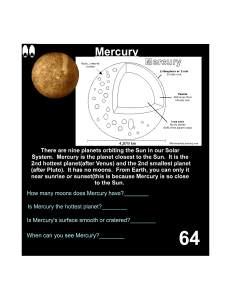
... Planets have two kinds of motion. One is rotation, where the planet spins on its axis (day). The other type of motion is revolution, where it revolves around another body. The planet with the smallest revolution is Mercury and the largest is Neptune. Time it takes for a planet to rotate one complete ...
... Planets have two kinds of motion. One is rotation, where the planet spins on its axis (day). The other type of motion is revolution, where it revolves around another body. The planet with the smallest revolution is Mercury and the largest is Neptune. Time it takes for a planet to rotate one complete ...
The Solar System. The Inner Planets.
... Venus has very similar parameters to those of the Earth. However, it spins backwards (clockwise if looking from its north pole). Its atmosphere has 96% CO2, surface temperature 400740 K, surface pressure is 90 times the Earth’s one. It has volcanic activity, but probably no tectonic activity. The S ...
... Venus has very similar parameters to those of the Earth. However, it spins backwards (clockwise if looking from its north pole). Its atmosphere has 96% CO2, surface temperature 400740 K, surface pressure is 90 times the Earth’s one. It has volcanic activity, but probably no tectonic activity. The S ...
ASTR101 Unit 14 Assessment Answer Key 1. It is believed that the
... paradox. If other technological civilizations exist, they would tend to spread out and colonize the galaxy. It is estimated that this would take about a million years, a negligible fraction of the age of the galaxy. Since the galaxy does not seem to be colonized, Fermi argued that other technologica ...
... paradox. If other technological civilizations exist, they would tend to spread out and colonize the galaxy. It is estimated that this would take about a million years, a negligible fraction of the age of the galaxy. Since the galaxy does not seem to be colonized, Fermi argued that other technologica ...
1 - WordPress.com
... 22. An astronomical unit (AU) is the average distance between Earth and the Sun. Explain why the distances between bodies in the solar system are measured using AUs. ...
... 22. An astronomical unit (AU) is the average distance between Earth and the Sun. Explain why the distances between bodies in the solar system are measured using AUs. ...
SMART Notebook
... dioxide. Venus is slightly smaller than the Earth. It has no moons. Venus is known as the "morning star" since it is visible and quite bright at dawn or dusk(this is because Venus is closer to the Sun How many moons does Venus have?_________ ...
... dioxide. Venus is slightly smaller than the Earth. It has no moons. Venus is known as the "morning star" since it is visible and quite bright at dawn or dusk(this is because Venus is closer to the Sun How many moons does Venus have?_________ ...
Benchmark One Study Guide: Science Benchmark Wed
... 4. What unit of measurement do we use to measure distance within the Milky Way Galaxy? ____________________________ What unit of measurement do we use to measure within our solar system? _____________________________ 5. Identify each type of galaxy below. ...
... 4. What unit of measurement do we use to measure distance within the Milky Way Galaxy? ____________________________ What unit of measurement do we use to measure within our solar system? _____________________________ 5. Identify each type of galaxy below. ...
Astronomy powerpoint
... Stars that have burnt most of the hydrogen. The last shining phase of an average star. Hot on surface but not bright. Can be any color. ...
... Stars that have burnt most of the hydrogen. The last shining phase of an average star. Hot on surface but not bright. Can be any color. ...
Physical Attributes of Stars
... • Do you know why we experience seasons? • It’s because of the Earth’s tilt! ...
... • Do you know why we experience seasons? • It’s because of the Earth’s tilt! ...
Old Sample Exam #2
... _____ 3) How long can a star run on gravity without nuclear fusion? (in years) a) 1031 b) 1012 c) 1010 d) 107 e) 100 _____ 4) What element cannot be nuclear burned to release energy? a) oxygen b) iron c) hydrogen d) uranium e) helium _____ 5) Planetary nebulae are often shaped like a(n) a) hourglass ...
... _____ 3) How long can a star run on gravity without nuclear fusion? (in years) a) 1031 b) 1012 c) 1010 d) 107 e) 100 _____ 4) What element cannot be nuclear burned to release energy? a) oxygen b) iron c) hydrogen d) uranium e) helium _____ 5) Planetary nebulae are often shaped like a(n) a) hourglass ...
etlife_douglas_ewart_short
... Could some of those planets be like the Earth? Most planets we’ve found so far are ‘hot Jupiters’: gas giants, much bigger and closer to their parent star than the Earth is to the Sun. ...
... Could some of those planets be like the Earth? Most planets we’ve found so far are ‘hot Jupiters’: gas giants, much bigger and closer to their parent star than the Earth is to the Sun. ...
signatures of life on other worlds
... liquid water. In our Solar System, Earth sits snugly inside the inner boundary of Kasting’s habitable zone, whereas Venus orbits too close to the Sun, dooming our near twin to be waterless and lifeless. The case of Mars illustrates that there is more to habitability than a planet’s distance from a s ...
... liquid water. In our Solar System, Earth sits snugly inside the inner boundary of Kasting’s habitable zone, whereas Venus orbits too close to the Sun, dooming our near twin to be waterless and lifeless. The case of Mars illustrates that there is more to habitability than a planet’s distance from a s ...
File
... closer to the Sun overtake planets further away, indicating heliocentric model • Calculated distances to other planets based on an astronomical unit (AU) • Showed that the universe was much, much larger than thought. People began thinking other stars might be suns with other planets orbiting them. ...
... closer to the Sun overtake planets further away, indicating heliocentric model • Calculated distances to other planets based on an astronomical unit (AU) • Showed that the universe was much, much larger than thought. People began thinking other stars might be suns with other planets orbiting them. ...
Solar System Basics 1 - Usk Astronomical Society
... to freeze carbon dioxide. Venus also orbits the Sun inside our orbit and it too is only seen close to the Sun from our vantage point. It is known as the evening or the morning star when seen setting after or rising before the Sun. Venus is just a little smaller than Earth, but it is a most inhospita ...
... to freeze carbon dioxide. Venus also orbits the Sun inside our orbit and it too is only seen close to the Sun from our vantage point. It is known as the evening or the morning star when seen setting after or rising before the Sun. Venus is just a little smaller than Earth, but it is a most inhospita ...
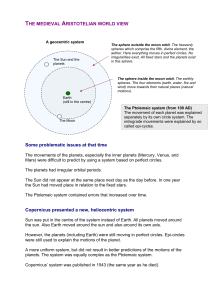
THE MEDIEVAL ARISTOTELIAN WORLD VIEW Some
... How could Earth move around the Sun? A tremendous force is needed to cause this movement. Such a force cannot exist. There were other astronomical observations that contradicted the new system. These contradictions could be explained if the distance to the stars was substantially increased; however, ...
... How could Earth move around the Sun? A tremendous force is needed to cause this movement. Such a force cannot exist. There were other astronomical observations that contradicted the new system. These contradictions could be explained if the distance to the stars was substantially increased; however, ...
Planetary habitability

Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia. As the existence of life beyond Earth is unknown, planetary habitability is largely an extrapolation of conditions on Earth and the characteristics of the Sun and Solar System which appear favourable to life's flourishing—in particular those factors that have sustained complex, multicellular organisms and not just simpler, unicellular creatures. Research and theory in this regard is a component of planetary science and the emerging discipline of astrobiology.An absolute requirement for life is an energy source, and the notion of planetary habitability implies that many other geophysical, geochemical, and astrophysical criteria must be met before an astronomical body can support life. In its astrobiology roadmap, NASA has defined the principal habitability criteria as ""extended regions of liquid water, conditions favourable for the assembly of complex organic molecules, and energy sources to sustain metabolism.""In determining the habitability potential of a body, studies focus on its bulk composition, orbital properties, atmosphere, and potential chemical interactions. Stellar characteristics of importance include mass and luminosity, stable variability, and high metallicity. Rocky, terrestrial-type planets and moons with the potential for Earth-like chemistry are a primary focus of astrobiological research, although more speculative habitability theories occasionally examine alternative biochemistries and other types of astronomical bodies.The idea that planets beyond Earth might host life is an ancient one, though historically it was framed by philosophy as much as physical science. The late 20th century saw two breakthroughs in the field. The observation and robotic spacecraft exploration of other planets and moons within the Solar System has provided critical information on defining habitability criteria and allowed for substantial geophysical comparisons between the Earth and other bodies. The discovery of extrasolar planets, beginning in the early 1990s and accelerating thereafter, has provided further information for the study of possible extraterrestrial life. These findings confirm that the Sun is not unique among stars in hosting planets and expands the habitability research horizon beyond the Solar System.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently. On 4 November 2013, astronomers reported, based on Kepler space mission data, that there could be as many as 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of Sun-like stars and red dwarfs within the Milky Way. 11 billion of these estimated planets may be orbiting Sun-like stars. The nearest such planet may be 12 light-years away, according to the scientists.