il 3 ~ )
... (a) What is this in absolute units (Kelvin)? What is the peak wavelength emitted by a person with this temperature? (b) In what region of the spectrum is this wavelength? Is this consistent with the fact that humans do not appear to glow (optically) in the dark? (c) Estimate the surface area of your ...
... (a) What is this in absolute units (Kelvin)? What is the peak wavelength emitted by a person with this temperature? (b) In what region of the spectrum is this wavelength? Is this consistent with the fact that humans do not appear to glow (optically) in the dark? (c) Estimate the surface area of your ...
Unit Review Name
... B. The limited technology of the period could not prove it invalid. C. For a long period of time, no one offered a better explanation. D. Scientists lost interest in space studies as other discoveries were made. 12. What is the main advantage to having the Hubble Space Telescope located in space ...
... B. The limited technology of the period could not prove it invalid. C. For a long period of time, no one offered a better explanation. D. Scientists lost interest in space studies as other discoveries were made. 12. What is the main advantage to having the Hubble Space Telescope located in space ...
Models of the Solar System
... Components of the Solar System The ancients knew of six planets. Three more planets were discovered with the aid of telescopes: • Uranus in 1781 • Neptune in 1846 • Pluto in 1930 (Pluto was later reclassified as a dwarf ...
... Components of the Solar System The ancients knew of six planets. Three more planets were discovered with the aid of telescopes: • Uranus in 1781 • Neptune in 1846 • Pluto in 1930 (Pluto was later reclassified as a dwarf ...
Quiz 1 Review, Astronomy 1144 - astronomy.ohio
... 1. Law of Inertia: A body either stays at rest or moves in a straight line unless acted upon by an external force. Mass is a measure of this inertia. 2. Law of Acceleration: For a given mass, its acceleration is proportional to the force applied F = ma. More massive objects are more resistant to acc ...
... 1. Law of Inertia: A body either stays at rest or moves in a straight line unless acted upon by an external force. Mass is a measure of this inertia. 2. Law of Acceleration: For a given mass, its acceleration is proportional to the force applied F = ma. More massive objects are more resistant to acc ...
ESSAY - First Earth-Like Exoplanet Found in Habitable Zone
... Carnegie's Alan Boss, has discovered what could be a large, rocky planet with a surface temperature of about 22 degrees Celsius (72 degrees Fahrenheit), comparable to a comfortable spring day on Earth. This landmark finding will be published in The Astrophysical Journal. The discovery team, led by W ...
... Carnegie's Alan Boss, has discovered what could be a large, rocky planet with a surface temperature of about 22 degrees Celsius (72 degrees Fahrenheit), comparable to a comfortable spring day on Earth. This landmark finding will be published in The Astrophysical Journal. The discovery team, led by W ...
Final Exam Review (Word doc)
... 96. If I make the analogy of the universe to a rocket leaving the earth, the rocket would be accelerating away from the earth. 97. Supernova Ia’s, which provide good standard candles, can only be seen out to 11 billion light years away. 98. The MAP satellite has confirmed the age of the universe to ...
... 96. If I make the analogy of the universe to a rocket leaving the earth, the rocket would be accelerating away from the earth. 97. Supernova Ia’s, which provide good standard candles, can only be seen out to 11 billion light years away. 98. The MAP satellite has confirmed the age of the universe to ...
"It`s increasingly seeming that the solar system is
... spheres of gas surrounded by rings. In between lies the asteroid belt like a cosmic moat. It's a tidy configuration, and for about a century and a half, it was all we knew about planets. Then, in 1995, everything changed. That's when astronomers discovered the first planet orbiting another star, a J ...
... spheres of gas surrounded by rings. In between lies the asteroid belt like a cosmic moat. It's a tidy configuration, and for about a century and a half, it was all we knew about planets. Then, in 1995, everything changed. That's when astronomers discovered the first planet orbiting another star, a J ...
Our Habitable Earth
... through observation the presence of a global salt water ocean containing more water than is present on Earth covered in a thick, ice shell Tidal forces on Europa (gravity interaction between Jupiter, Europa and the other moons) would be enough to keep the interior of Europa liquid ...
... through observation the presence of a global salt water ocean containing more water than is present on Earth covered in a thick, ice shell Tidal forces on Europa (gravity interaction between Jupiter, Europa and the other moons) would be enough to keep the interior of Europa liquid ...
The Origin of Our Solar System
... substance is a solid or a gas. – Above the condensation temperature, gas state – Below the condensation temperature, solid sate • Hydrogen and Helium: always in gas state, because concentration temperatures close to absolute zero • Substance such as water (H2O), methane (CH4) and ammonia (NH3) have ...
... substance is a solid or a gas. – Above the condensation temperature, gas state – Below the condensation temperature, solid sate • Hydrogen and Helium: always in gas state, because concentration temperatures close to absolute zero • Substance such as water (H2O), methane (CH4) and ammonia (NH3) have ...
Solar System: 3rd Grade
... Put students into groups of 2 or 3 Have each group sign into www.tinkercad.com using one computer per group. Go over what a plane is in geometry and have discuss how to use a plane and what it is for. Have them discuss how big each square is in the plane. Ask how many millimeters are in a centimeter ...
... Put students into groups of 2 or 3 Have each group sign into www.tinkercad.com using one computer per group. Go over what a plane is in geometry and have discuss how to use a plane and what it is for. Have them discuss how big each square is in the plane. Ask how many millimeters are in a centimeter ...
Supernovae - Cloudfront.net
... the amount of energy created in a Type Ia Supernova is always about the same. Thus its luminosity is always the same. A Type Ia Supernova in another galaxy is thus a good standard candle to use to find the distance to the galaxy ...
... the amount of energy created in a Type Ia Supernova is always about the same. Thus its luminosity is always the same. A Type Ia Supernova in another galaxy is thus a good standard candle to use to find the distance to the galaxy ...
Earths Place in the Universe
... As the core runs out of hydrogen and then helium, the core contacts and the outer layers expand, cool, and become less bright. It will eventually collapse and explode. Its fate is determined by the original mass of the star; it will become either a black dwarf, ...
... As the core runs out of hydrogen and then helium, the core contacts and the outer layers expand, cool, and become less bright. It will eventually collapse and explode. Its fate is determined by the original mass of the star; it will become either a black dwarf, ...
Activity 12: Solar System
... composed of mostly rock and iron. Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune make up the outer planets, which are much larger and consist mainly of hydrogen, helium and ice. Because Pluto is the farthest planet from Earth, astronomers know very little about it. Some believe it should not even be considere ...
... composed of mostly rock and iron. Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune make up the outer planets, which are much larger and consist mainly of hydrogen, helium and ice. Because Pluto is the farthest planet from Earth, astronomers know very little about it. Some believe it should not even be considere ...
16-6 How do astronomers measure distance?
... ____________________ 2. One light-year is equal to a distance of about 10 trillion kilometers. ____________________ 3. An astronomical unit is equal to the distance between Earth and the Moon. ____________________ 4. Proxima Centauri is the closest star to Earth other than the Sun. _________________ ...
... ____________________ 2. One light-year is equal to a distance of about 10 trillion kilometers. ____________________ 3. An astronomical unit is equal to the distance between Earth and the Moon. ____________________ 4. Proxima Centauri is the closest star to Earth other than the Sun. _________________ ...
File
... densities and compositions. 6. The 4 outer planets that are gas giants have similar densities and compositions. ...
... densities and compositions. 6. The 4 outer planets that are gas giants have similar densities and compositions. ...
Do you ever wonder why when you jump up, you always come back
... things – the mass of each object, and the distance between the objects. The more mass a star – like our Sun – has, and the closer a planet is to that star, the greater the star’s abilit ...
... things – the mass of each object, and the distance between the objects. The more mass a star – like our Sun – has, and the closer a planet is to that star, the greater the star’s abilit ...
Document
... Asteroids are mainly made of materials left over from the formation of the inner Solar System. Asteroids come in three composition classes. C-types are made of clay and silicate. S-types are made of silicate rocks and nickeliron mixtures. M-types are made of metallic nickel-iron. ...
... Asteroids are mainly made of materials left over from the formation of the inner Solar System. Asteroids come in three composition classes. C-types are made of clay and silicate. S-types are made of silicate rocks and nickeliron mixtures. M-types are made of metallic nickel-iron. ...
WHERE DO WE SEARCH FOR LIFE IN THE UNIVERSE?
... Sun’s, then we eliminate nearly 75% of all stars in the Milky Way! ...
... Sun’s, then we eliminate nearly 75% of all stars in the Milky Way! ...
Which object is a meteor?
... • Not Option A (Nebular Star? What the heck is that?) • Not Option C (A Binary Star isn’t formed as a result of a star dying) • Not Option D (A supernova can be created when a star dies, but nothing is left -like with a the other options listed) • CORRECT ANSWER: Option B must be correct. A Black H ...
... • Not Option A (Nebular Star? What the heck is that?) • Not Option C (A Binary Star isn’t formed as a result of a star dying) • Not Option D (A supernova can be created when a star dies, but nothing is left -like with a the other options listed) • CORRECT ANSWER: Option B must be correct. A Black H ...
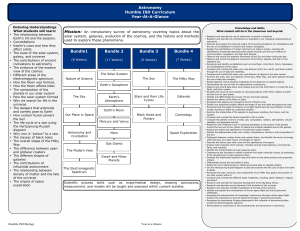
Astronomy Humble ISD Curriculum Year-At-A
... • Identify the characteristics of main sequence stars. • Characterize star formation in stellar nurseries from giant molecular clouds, to protostars, to the development of main sequence stars. • Evaluate the relationship between mass and fusion on the dying process and properties of stars. • Differe ...
... • Identify the characteristics of main sequence stars. • Characterize star formation in stellar nurseries from giant molecular clouds, to protostars, to the development of main sequence stars. • Evaluate the relationship between mass and fusion on the dying process and properties of stars. • Differe ...
Earth and the Universe -The Meaning of Life
... sun, like all others suns, is a star. The sun, and other stars, are luminous objects All other objects in the solar system orbit the sun ...
... sun, like all others suns, is a star. The sun, and other stars, are luminous objects All other objects in the solar system orbit the sun ...
White Dwarfs - Astronomy - The University of Texas at Austin
... White dwarfs have about the same mass as the Sun and about the same radius as the Earth. How does the gravity of a white dwarf compare to the Sun and the Earth, and why? ...
... White dwarfs have about the same mass as the Sun and about the same radius as the Earth. How does the gravity of a white dwarf compare to the Sun and the Earth, and why? ...
Article - Iowa State University
... If you were traveling in a spaceship at 10 miles per second (36,000 miles per hour) it would take you 70,000 years to get to the next closest one. Could Earth be hit by an asteroid or meteor? For the most part, our atmosphere protects us by burning up the majority of space material as it enters. In ...
... If you were traveling in a spaceship at 10 miles per second (36,000 miles per hour) it would take you 70,000 years to get to the next closest one. Could Earth be hit by an asteroid or meteor? For the most part, our atmosphere protects us by burning up the majority of space material as it enters. In ...
Third Nine Weeks Review – Sky Patterns
... Planets: Order of the planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune All planets orbit around the sun. Inner Planets – the planets that are closets to the sun (Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars)—they are small and rocky Outer Planets – these planets are farther away fro ...
... Planets: Order of the planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune All planets orbit around the sun. Inner Planets – the planets that are closets to the sun (Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars)—they are small and rocky Outer Planets – these planets are farther away fro ...
Planetary habitability

Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia. As the existence of life beyond Earth is unknown, planetary habitability is largely an extrapolation of conditions on Earth and the characteristics of the Sun and Solar System which appear favourable to life's flourishing—in particular those factors that have sustained complex, multicellular organisms and not just simpler, unicellular creatures. Research and theory in this regard is a component of planetary science and the emerging discipline of astrobiology.An absolute requirement for life is an energy source, and the notion of planetary habitability implies that many other geophysical, geochemical, and astrophysical criteria must be met before an astronomical body can support life. In its astrobiology roadmap, NASA has defined the principal habitability criteria as ""extended regions of liquid water, conditions favourable for the assembly of complex organic molecules, and energy sources to sustain metabolism.""In determining the habitability potential of a body, studies focus on its bulk composition, orbital properties, atmosphere, and potential chemical interactions. Stellar characteristics of importance include mass and luminosity, stable variability, and high metallicity. Rocky, terrestrial-type planets and moons with the potential for Earth-like chemistry are a primary focus of astrobiological research, although more speculative habitability theories occasionally examine alternative biochemistries and other types of astronomical bodies.The idea that planets beyond Earth might host life is an ancient one, though historically it was framed by philosophy as much as physical science. The late 20th century saw two breakthroughs in the field. The observation and robotic spacecraft exploration of other planets and moons within the Solar System has provided critical information on defining habitability criteria and allowed for substantial geophysical comparisons between the Earth and other bodies. The discovery of extrasolar planets, beginning in the early 1990s and accelerating thereafter, has provided further information for the study of possible extraterrestrial life. These findings confirm that the Sun is not unique among stars in hosting planets and expands the habitability research horizon beyond the Solar System.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently. On 4 November 2013, astronomers reported, based on Kepler space mission data, that there could be as many as 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of Sun-like stars and red dwarfs within the Milky Way. 11 billion of these estimated planets may be orbiting Sun-like stars. The nearest such planet may be 12 light-years away, according to the scientists.