Weekly Class Newsletter
... come without P.E shoes or towels during P.E. Parents are kindly requested to double check their bags to make sure all required items are provided. ...
... come without P.E shoes or towels during P.E. Parents are kindly requested to double check their bags to make sure all required items are provided. ...
Slide 1
... 6.1 An Inventory of the Solar System Now known: Solar system has 165 moons, one star, eight planets (added Uranus and Neptune), eight asteroids and more than 100 Kuiper belt objects more than 300 km in diameter, smaller asteroids, comets, and meteoroids ...
... 6.1 An Inventory of the Solar System Now known: Solar system has 165 moons, one star, eight planets (added Uranus and Neptune), eight asteroids and more than 100 Kuiper belt objects more than 300 km in diameter, smaller asteroids, comets, and meteoroids ...
Components of Universe
... What can you see with the naked eye? [outside of the Solar System] - Milky Way stars! (meaning only stars in our own galaxy) i.e., you cannot see any individual stars in any other galaxy;-- they’re just too far and too faint ...
... What can you see with the naked eye? [outside of the Solar System] - Milky Way stars! (meaning only stars in our own galaxy) i.e., you cannot see any individual stars in any other galaxy;-- they’re just too far and too faint ...
The Copernican Cosmos
... Copernican systems. Geocentric universe with the planets revolving around the sun. Why? He could not observe a stellar parallax (shifting of the stars) which would involve great distances of empty space which was an implausible notion (horror vacui-nature abhors a vacuum). Made and used a sextan ...
... Copernican systems. Geocentric universe with the planets revolving around the sun. Why? He could not observe a stellar parallax (shifting of the stars) which would involve great distances of empty space which was an implausible notion (horror vacui-nature abhors a vacuum). Made and used a sextan ...
History of astronomy - Part I.
... The Chinese, Egyptians, Britons, Mayans, and others have left us evidence of their interest in astronomy. ...
... The Chinese, Egyptians, Britons, Mayans, and others have left us evidence of their interest in astronomy. ...
A Solar System - Cloudfront.net
... The Milky Way: Our galaxy containing up to 400 billion solar systems. Earth is located on one spiral arm. ...
... The Milky Way: Our galaxy containing up to 400 billion solar systems. Earth is located on one spiral arm. ...
Revolving and Rotating
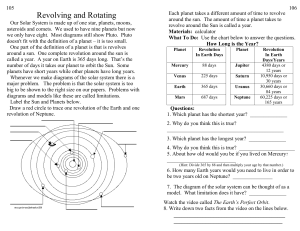
... Revolving and Rotating Our Solar System is made up of one star, planets, moons, asteroids and comets. We used to have nine planets but now we only have eight. Most diagrams still show Pluto. Pluto doesn't fit with the definition of a planet – it is too small. One part of the definition of a planet i ...
... Revolving and Rotating Our Solar System is made up of one star, planets, moons, asteroids and comets. We used to have nine planets but now we only have eight. Most diagrams still show Pluto. Pluto doesn't fit with the definition of a planet – it is too small. One part of the definition of a planet i ...
How much do we make
... Revolving and Rotating Our Solar System is made up of one star, planets, moons, asteroids and comets. We used to have nine planets but now we only have eight. Most diagrams still show Pluto. Pluto doesn't fit with the definition of a planet – it is too small. One part of the definition of a planet i ...
... Revolving and Rotating Our Solar System is made up of one star, planets, moons, asteroids and comets. We used to have nine planets but now we only have eight. Most diagrams still show Pluto. Pluto doesn't fit with the definition of a planet – it is too small. One part of the definition of a planet i ...
Q: Do other planets have summer? A:
... is no chance of them ever colliding—so its seasons, such as they are, really are due to the change in distance from the Sun (a common misconception that people have about the cause of the Earth’s seasons). During its 248-year trip around the Sun, Pluto receives almost three times more solar energy w ...
... is no chance of them ever colliding—so its seasons, such as they are, really are due to the change in distance from the Sun (a common misconception that people have about the cause of the Earth’s seasons). During its 248-year trip around the Sun, Pluto receives almost three times more solar energy w ...
The search for exoplanets
... On April 17th 2014 NASA’s Kepler-telescope discovered the first Earth-size planet Kepler186f in a habitable zone, which is also accompanied by four other planets. It orbits its star (a red dwarf) once every 130 days and receives one-third of the energy that the earth gets from the sun. Not much is k ...
... On April 17th 2014 NASA’s Kepler-telescope discovered the first Earth-size planet Kepler186f in a habitable zone, which is also accompanied by four other planets. It orbits its star (a red dwarf) once every 130 days and receives one-third of the energy that the earth gets from the sun. Not much is k ...
For Chapter 16 on November 26, 2012
... • The Kuiper Belt extends just beyond the orbit of Neptune and into the space of Eris. • Consists of comet and cometary material and other small objects – Trans Neptunian Objects • Many astronomers put the edge of the solar system to be at about 100 AU. • Voyager 1, launched in 1977, and in 2004 rea ...
... • The Kuiper Belt extends just beyond the orbit of Neptune and into the space of Eris. • Consists of comet and cometary material and other small objects – Trans Neptunian Objects • Many astronomers put the edge of the solar system to be at about 100 AU. • Voyager 1, launched in 1977, and in 2004 rea ...
planets suitable for life
... A wide range of uncertainty suggests a tremendous difficulty involved in making an estimation of NHP. The number 4 x 106 still seems to be an optimistic estimate, if giant Moon is necessary to make Earth suitable for life. The same number could well be a pessimistic estimate, if migration of Jovian ...
... A wide range of uncertainty suggests a tremendous difficulty involved in making an estimation of NHP. The number 4 x 106 still seems to be an optimistic estimate, if giant Moon is necessary to make Earth suitable for life. The same number could well be a pessimistic estimate, if migration of Jovian ...
PTYS/ASTR 206 – Section 2 – Fall 2004 Activity #1: 8/25/04
... B) a rotating disk of dense gas surrounding a young newly formed star, like our Sun around the time the solar system formed C) another name for the asteroid belt that exists between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter D) the plane in which moons orbit their parent planet (e.g. Jupiter’s moons) 4. When Ve ...
... B) a rotating disk of dense gas surrounding a young newly formed star, like our Sun around the time the solar system formed C) another name for the asteroid belt that exists between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter D) the plane in which moons orbit their parent planet (e.g. Jupiter’s moons) 4. When Ve ...
24. Life Beyond Earth: Prospects for Microbes, Civilizations, and
... • going faster requires more fuel, which make the ship more massive and harder to accelerate ...
... • going faster requires more fuel, which make the ship more massive and harder to accelerate ...
Planets Beyond the Solar System
... Van de Kamp’s planet finding was overturned, but, after years of searching, NASA astronomers at Palomar Observatory identified an exoplanet using astrometry in 2009. It is a gas giant (about 6x Jupiter’s mass) called VB 10b and is about 20 light-years away in the constellation Aquila. It is orbit ...
... Van de Kamp’s planet finding was overturned, but, after years of searching, NASA astronomers at Palomar Observatory identified an exoplanet using astrometry in 2009. It is a gas giant (about 6x Jupiter’s mass) called VB 10b and is about 20 light-years away in the constellation Aquila. It is orbit ...
Planets Beyond the Solar System
... Van de Kamp’s planet finding was overturned, but, after years of searching, NASA astronomers at Palomar Observatory identified an exoplanet using astrometry in 2009. It is a gas giant (about 6x Jupiter’s mass) called VB 10b and is about 20 light-years away in the constellation Aquila. It is orbit ...
... Van de Kamp’s planet finding was overturned, but, after years of searching, NASA astronomers at Palomar Observatory identified an exoplanet using astrometry in 2009. It is a gas giant (about 6x Jupiter’s mass) called VB 10b and is about 20 light-years away in the constellation Aquila. It is orbit ...
Chapter 13
... The more massive a white dwarf, the smaller it is. Eventually, white dwarf will run out of fuel and form a black dwarf. ...
... The more massive a white dwarf, the smaller it is. Eventually, white dwarf will run out of fuel and form a black dwarf. ...
Chapter 11 - USD Home Pages
... 10,000 times as luminous as our sun will have a mass of about 10 M . Chap 12 will show that explains its short life of only 10 million years. b. A star with a mass of 10−1 M will have a luminosity of about 10−3 L . That’s why its life will be 1000 billion years. 44. What if? The Sun were a B-type ...
... 10,000 times as luminous as our sun will have a mass of about 10 M . Chap 12 will show that explains its short life of only 10 million years. b. A star with a mass of 10−1 M will have a luminosity of about 10−3 L . That’s why its life will be 1000 billion years. 44. What if? The Sun were a B-type ...
Astronomy Midterm Review Sheet
... c. An object in motion remains in motion. d. The parabola is a kind of conic section. 58. What object is located at one focus of the orbit of the planet Mars? a) the Sun b) the Earth c) Mars d) Jupiter 59. According to Kepler’s laws, a planet moves fastest in its orbit when it is a) nearest the Eart ...
... c. An object in motion remains in motion. d. The parabola is a kind of conic section. 58. What object is located at one focus of the orbit of the planet Mars? a) the Sun b) the Earth c) Mars d) Jupiter 59. According to Kepler’s laws, a planet moves fastest in its orbit when it is a) nearest the Eart ...
Kepler - STScI
... •Giant planets, as a class, are enriched in heavy elements •Enriched compared to the Sun •Enriched compared to their parent stars •Enrichment is a strong inverse function of mass, but with an apparent “floor” at high mass •The heavy element mass of an inflated planet could be estimated only from its ...
... •Giant planets, as a class, are enriched in heavy elements •Enriched compared to the Sun •Enriched compared to their parent stars •Enrichment is a strong inverse function of mass, but with an apparent “floor” at high mass •The heavy element mass of an inflated planet could be estimated only from its ...
Document
... to the distant fixed stars (i.e. its ‘true’ orbital period) is called its sidereal period. However, during this time, the Earth has also been moving in its orbit: after one planetary sidereal period, the planet still appears to be in a different position relative to the Sun, as viewed from the Earth ...
... to the distant fixed stars (i.e. its ‘true’ orbital period) is called its sidereal period. However, during this time, the Earth has also been moving in its orbit: after one planetary sidereal period, the planet still appears to be in a different position relative to the Sun, as viewed from the Earth ...
Structure of the Universe
... by combining smaller elements to form a larger one, specifically two hydrogen atoms form a helium atom, ...
... by combining smaller elements to form a larger one, specifically two hydrogen atoms form a helium atom, ...
Early Observers (The Beginnings of Astronomy)
... Many buildings were aligned with celestial bodies during certain astronomical events ...
... Many buildings were aligned with celestial bodies during certain astronomical events ...
Earth in Space
... There are two major motions of the earth…. • Rotation - the spinning of the earth on its axis resulting in daily changes such as the rising and setting of the sun and moon. • Revolution - the movement of the earth in its orbit around the sun resulting in yearly changes such as the changing ...
... There are two major motions of the earth…. • Rotation - the spinning of the earth on its axis resulting in daily changes such as the rising and setting of the sun and moon. • Revolution - the movement of the earth in its orbit around the sun resulting in yearly changes such as the changing ...
Planetary habitability

Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia. As the existence of life beyond Earth is unknown, planetary habitability is largely an extrapolation of conditions on Earth and the characteristics of the Sun and Solar System which appear favourable to life's flourishing—in particular those factors that have sustained complex, multicellular organisms and not just simpler, unicellular creatures. Research and theory in this regard is a component of planetary science and the emerging discipline of astrobiology.An absolute requirement for life is an energy source, and the notion of planetary habitability implies that many other geophysical, geochemical, and astrophysical criteria must be met before an astronomical body can support life. In its astrobiology roadmap, NASA has defined the principal habitability criteria as ""extended regions of liquid water, conditions favourable for the assembly of complex organic molecules, and energy sources to sustain metabolism.""In determining the habitability potential of a body, studies focus on its bulk composition, orbital properties, atmosphere, and potential chemical interactions. Stellar characteristics of importance include mass and luminosity, stable variability, and high metallicity. Rocky, terrestrial-type planets and moons with the potential for Earth-like chemistry are a primary focus of astrobiological research, although more speculative habitability theories occasionally examine alternative biochemistries and other types of astronomical bodies.The idea that planets beyond Earth might host life is an ancient one, though historically it was framed by philosophy as much as physical science. The late 20th century saw two breakthroughs in the field. The observation and robotic spacecraft exploration of other planets and moons within the Solar System has provided critical information on defining habitability criteria and allowed for substantial geophysical comparisons between the Earth and other bodies. The discovery of extrasolar planets, beginning in the early 1990s and accelerating thereafter, has provided further information for the study of possible extraterrestrial life. These findings confirm that the Sun is not unique among stars in hosting planets and expands the habitability research horizon beyond the Solar System.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently. On 4 November 2013, astronomers reported, based on Kepler space mission data, that there could be as many as 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of Sun-like stars and red dwarfs within the Milky Way. 11 billion of these estimated planets may be orbiting Sun-like stars. The nearest such planet may be 12 light-years away, according to the scientists.