* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Astronomy Midterm Review Sheet
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy on Mars wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
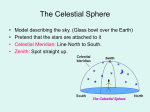
Astronomy Midterm Review Sheet 1. a. b. 2. a) 3. The Greek astronomer Thales is reported to have predicted discovery of Uranus c. appearance of a comet total solar eclipse d. discovery of variable stars Which civilization worshipped the sun god, Ra? Assyrians b) Babylonians c) China d) Egypt e) India Precession can be detected by noting the a. changes in the celestial coordinates of stars over many years b. the westward motion of the stars during a night c. the motion of the Sun relative to that of the Earth d. the motion of the planets during retrograde motion 4. In Ptolemy’s model of the solar system, the circle on which the center of the epicycle moved about the Earth was called the a) Equant b) Eccentric c) Orbit d) Epicycle e) Parallax 5. Which civilization first had astrologer priest that used the zodiac constellations to predict when to plant and harvest crops? a) Assyrians b) Australians c) Chinese d) Egyptians e) Indians 6. Mass has a property called _________ that causes it to move in a straight line unless acted on by a force. a) weight b) inertia c)momentum d) density e) volume 7. Unlike most other Egyptian temples, the pyramids of Giza are aligned with the ________. a) cardinal points b) Moon c) Sun d) Sirius e) Solstice 8. You observe a star today at 9:00p.m, to observe the same star tomorrow in the same location you would have to look at the star at 9:04p.m. a. True b. False 9. If an object exceeds a critical size of ___________ gravity begins to round it. a. 350 miles b. 350Km c. 3500 miles d. 3500Km e. 350m 10. The distance from the Earth to the Sun is _______ _______. a. 4 A.U. b. 3 A.U. c. 2 A.U. d. 1 A.U. e. 1,000 Km 11. An imaginary line about which the Earth spins is called __________. a. revolution b. rotation c. tilt d. gravity e. axis 12. Sidereal day is defined according to the _____________, and it is __________. a. sun, 24 hours b. sun, 23 hr 56 min c. star, 24 hours d. star, 23 hr 56 min 13. The Earth’s axis tilt is ______? a. 15.5 b. 23.5 c. 30 d. 45 e. There is no tilt 14. The initial velocity needed to escape a massive body’s gravitational influence is called _________. a. low velocity b. high velocity c. escape velocity d. caught velocity 15. The seasons of the Earth are due to ____________. a. speed of the Earth in its orbit c. rotation of Earth e. none of the above b. precession d. tilt of axis 16. In a few thousand years the Earth’s north star will not be Polaris because of ___. a. tilt b. rotation c. precession d. revolution e. parallax Math the following for 26-35 a. Circumpolar constellation b. Constellation c. Apparent magnitude d. Solstice e. Celestial Horizon f. Equinox g. Celestial Equator h. Altitude i. Azimuth j. Degree 17. When the ecliptic crosses the celestial equator, day, and night hours are equal. 18. The point where the ecliptic is highest or lowest above the celestial equator, Sun is greatest distance north or south of the celestial equator. 19. Star patterns or easily recognized groups of stars formed because the individual stars appear in the same direction as viewed from Earth. 20. Visible from the Northern Hemisphere all year long, and appear to rotate around Polaris. 21. Observed brightness as seen from Earth. 22. Occurs at 0 degrees declination, from the observer’s position. 23. Circle where the Earth’s equator, if extended outward into space, would intersect the celestial sphere. 24. The angular distance from the north point on the horizon eastward around the horizon to the point nearest the direction of the celestial body. 25. A unit used to measure angle 26. The angular distance between the direction of the object and the horizon 27. How much of the sky can we see in one night. a. 1/4 b. 1/3 c. 1/2 d. 2/3 e. 3/4 28. On Earth, the Prime Meridian runs through what country? a. Portugal b. France c. England d. U.S.A. e. India 29. ______ degrees is the measurement of Zenith. a. 45 b. 60 c. 75 d. 90 e. 120 30. The angular distance above or below the celestial equator is called ______. a. right ascension b. declination c. equator d. longitude e. latitude 31. The point at which the R.A. and Dec. are both zero is called ______. a. Summer Solstice b. Winter Solstice c. Autumnal Equinox d. Vernal Equinox 32. In a constellation, the brightest star is assigned what Greek letter? a. Alpha b. Beta c. Lambda d. Delta e. Sigma 33. How many constellations can we see in Georgia? a. 37 b. 45 c. 22 d. 88 e. 102 34. How many constellations are there? a. 37 b. 45 c. 22 d. 88 e. 102 35. Which part of the Electromagnetic Spectrum causes cancer. a. Visible Light b. UltraViolet c. Infrared d. Microwaves 36. Electromagnetic radiation encompasses _______, ________, and _________. 37. The speed of light is ___________. 38. The distance between two crest is called _______. 39. Hertz is the measurement for ________. 40. A particle of electromagnetic radiation is called a ________. 41. Light has both properties of a ______ and a ________. 42. What is a reflecting telescope? 43. What is a refracting telescope? 44. Know the parts of a telescope. 45. A continuous array of rainbow colors is called a ______ spectrum. 46. A pattern of bright-colored lines of different wavelengths is called a _____ spectrum. 47. A _____ spectrum is a pattern of dark-lines across a spectrum. 48. In a reflector telescope the angle of incidence is _____ angle of reflection. 49. The point on the optical axis where the images are focused is called the ______. 50. Light gathering power in a telescope depends on what two things. 51. Know the disadvantages of reflector telescopes. 52. Who invented the 1st telescope? 53. Know what some of the famous telescopes are. 54. Geocentric means that everything goes around the ____________. a) Earth b) Moon c) Stars d) Sun e) Mars 55. Who discovered the moons of Jupiter? a) Aristarchus b) Copernicus c) Galileo d) Newton e) Ptolemy 56. Which of the following describes Tycho’s model of the solar system? a. Sun orbits Earth, planets orbit the Sun c. Earth orbits Sun, planets orbit Earth b. Sun and planets orbit Earth d. Planets and Earth orbit Sun 57. Which of the following is one of Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion? a. The planet’s distance cubed is proportional to its distance squared. b. Acceleration is proportional to unbalanced force. c. An object in motion remains in motion. d. The parabola is a kind of conic section. 58. What object is located at one focus of the orbit of the planet Mars? a) the Sun b) the Earth c) Mars d) Jupiter 59. According to Kepler’s laws, a planet moves fastest in its orbit when it is a) nearest the Earth in the Earth’s orbital plane. b) Nearest the Sun c) Midway between the foci of its orbit d) Farthest from the ecliptic 60. Kepler’s Second Law states that a) A planet moves more rapidly when near the Sun b) Planets close to the Sun have longer periods than those further away. c) An object in motion remains in motion d) A planet’s mass increases with distance from the Sun