1 - Alice Pevyhouse
... 17. The granulation seen in photographs of the Sun is the tops of convective cells (T/F) 18. The Sun is continuously losing mass due to nuclear reactions and to the solar wind (T/F) 21. The hotter region directly above the Sun’s visible surface(the part that we normally see is called what? 23. Not ...
... 17. The granulation seen in photographs of the Sun is the tops of convective cells (T/F) 18. The Sun is continuously losing mass due to nuclear reactions and to the solar wind (T/F) 21. The hotter region directly above the Sun’s visible surface(the part that we normally see is called what? 23. Not ...
Physics 2028: Great Ideas in Science: The Exobiology
... the growth in the population, though still expanding, has slowed a bit. viii) Unfortunately, the Earth is a rather small planet and the question still remains, will the day come when the earth is no longer able to support the human population? 4. Planetary Catastrophes — those that affect the whole ...
... the growth in the population, though still expanding, has slowed a bit. viii) Unfortunately, the Earth is a rather small planet and the question still remains, will the day come when the earth is no longer able to support the human population? 4. Planetary Catastrophes — those that affect the whole ...
Can you figure out which of the stars shown here have planets
... It's a big planet, with a mass like Jupiter, but it's located six times closer to its star than Mercury is to the Sun! Astronomers have since found many more such planets, and call them "Hot Jupiters" because of their size and high temperatures. ...
... It's a big planet, with a mass like Jupiter, but it's located six times closer to its star than Mercury is to the Sun! Astronomers have since found many more such planets, and call them "Hot Jupiters" because of their size and high temperatures. ...
Archaeologists Say the `Anthropocene` Is Here—But It Began Long
... haps even conceivable mission Imagination run free. Exoplanet Kepler-62f’s rising star and neighboring planet there.’ Kepler’s stars are too could show that this particular (bright point) are known; the presence of clouds, land, and sea are purely speculative. faint; the amount of informaexoplanet i ...
... haps even conceivable mission Imagination run free. Exoplanet Kepler-62f’s rising star and neighboring planet there.’ Kepler’s stars are too could show that this particular (bright point) are known; the presence of clouds, land, and sea are purely speculative. faint; the amount of informaexoplanet i ...
What is a planet?
... • planetary orbital angular momentum is close to direction of Sun s spin angular momentum (within 7o) • 3 of 4 terrestrial planets and 3 of 4 giant planets have obliquities (angle between spin and orbital angular momentum) < 30o; but Uranus is tipped at 98o • interplanetary space is virtually emp ...
... • planetary orbital angular momentum is close to direction of Sun s spin angular momentum (within 7o) • 3 of 4 terrestrial planets and 3 of 4 giant planets have obliquities (angle between spin and orbital angular momentum) < 30o; but Uranus is tipped at 98o • interplanetary space is virtually emp ...
File
... 7. What is a Jet Stream? Fast moving air that pushes the weather from West to East. 8. What is the Mesosphere? Coldest layer of the atmosphere temperatures reach a minimum of -100 degrees Celsius. Most meteors burn up in the mesosphere. 9. What is the Thermosphere? The temperature here increases due ...
... 7. What is a Jet Stream? Fast moving air that pushes the weather from West to East. 8. What is the Mesosphere? Coldest layer of the atmosphere temperatures reach a minimum of -100 degrees Celsius. Most meteors burn up in the mesosphere. 9. What is the Thermosphere? The temperature here increases due ...
Email Template - Personal.psu.edu
... 100 points = 100% Estimated to be this test: (1) (four points) If you were classifying the planets by size only, you might make three classes. What planets would be in each class? ...
... 100 points = 100% Estimated to be this test: (1) (four points) If you were classifying the planets by size only, you might make three classes. What planets would be in each class? ...
Jovian Planets
... • Four Galilean moons: easily seen even through amateur telescopes as little points of light. • Io: Erupting volcanoes! Geologically youngest surface (the “pizza” moon). Interior molten due to tidal forces during its elliptical orbit around Jupiter. • Europa: Smooth, narrow, dark stripes and few cra ...
... • Four Galilean moons: easily seen even through amateur telescopes as little points of light. • Io: Erupting volcanoes! Geologically youngest surface (the “pizza” moon). Interior molten due to tidal forces during its elliptical orbit around Jupiter. • Europa: Smooth, narrow, dark stripes and few cra ...
space - jennseymour
... Jupiter revolves around the Sun in 12 Earth years Pluto takes 248 Earth years to revolve around the Sun ...
... Jupiter revolves around the Sun in 12 Earth years Pluto takes 248 Earth years to revolve around the Sun ...
L1 Solar system
... •Solar composition (primordial): X0 0.71, Y0 0.27, Z0 0.015 •The gas giant planets (Jupiter, Saturn) are clearly enriched compared to solar composition. ...
... •Solar composition (primordial): X0 0.71, Y0 0.27, Z0 0.015 •The gas giant planets (Jupiter, Saturn) are clearly enriched compared to solar composition. ...
ORIGIN OF THE UNIVERSE
... - Collections of similar galaxies found within a cluster. Our galaxy is found in the “Local Group” which contains about 29 other galaxies Galaxy - A collection of similar stars found within a star group. Our galaxy is called the Milky Way and contains about 200 Billion Stars. - There may be about 10 ...
... - Collections of similar galaxies found within a cluster. Our galaxy is found in the “Local Group” which contains about 29 other galaxies Galaxy - A collection of similar stars found within a star group. Our galaxy is called the Milky Way and contains about 200 Billion Stars. - There may be about 10 ...
Bringing Our Solar System to Life Grade 5 Overview Since the Solar
... The classroom contains roughly 20 fifth graders. The genders in the classroom are about even. These students have had one prior lesson on the solar system and its planets which was presented in a lecture form, with pictures, by the teacher. The setting of the school is rural. 5.2.1 Recognize that ou ...
... The classroom contains roughly 20 fifth graders. The genders in the classroom are about even. These students have had one prior lesson on the solar system and its planets which was presented in a lecture form, with pictures, by the teacher. The setting of the school is rural. 5.2.1 Recognize that ou ...
Solar.System
... The direction they orbit around the Sun is the same as the Sun’s rotation on its axis The direction most planets rotate on their axes is the same as that for the Sun The direction of a planet’s moon orbits is the same as that planet’s direction of rotation The Terrestrial planets are very different ...
... The direction they orbit around the Sun is the same as the Sun’s rotation on its axis The direction most planets rotate on their axes is the same as that for the Sun The direction of a planet’s moon orbits is the same as that planet’s direction of rotation The Terrestrial planets are very different ...
Chapter 30
... A. They expand and become supergiants. B. They collapse and become white dwarfs. C. They switch to fission reactions. D. They contract and turn into neutron stars. ...
... A. They expand and become supergiants. B. They collapse and become white dwarfs. C. They switch to fission reactions. D. They contract and turn into neutron stars. ...
32) What spacecraft mission crashed because the NASA contractor
... B) Red light tends to be refracted more through the Earth’s atmosphere than blue light so the light reflected off the Moon appears red. C) Blue light tends to be refracted more through the Earth’s atmosphere than red light so the light reflected off the Moon appears blue. D) Solar flares tend to emi ...
... B) Red light tends to be refracted more through the Earth’s atmosphere than blue light so the light reflected off the Moon appears red. C) Blue light tends to be refracted more through the Earth’s atmosphere than red light so the light reflected off the Moon appears blue. D) Solar flares tend to emi ...
The Solar System - Teachers TryScience
... and nine known planets and the moons that orbit those planets. • The force of gravity keeps planets in orbit around the sun. ...
... and nine known planets and the moons that orbit those planets. • The force of gravity keeps planets in orbit around the sun. ...
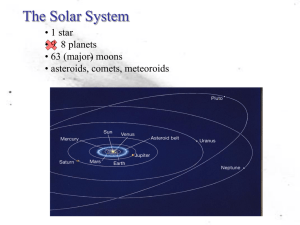
The Solar System
... – This model saw the solar system as perfect spheres with attached celestial bodies rotating around a fixed Earth. – The planets rotated around the Earth in perfect circles. – This model grew out of the ideas that: • Humans were at the center of a perfect universe created just for them. • Since Heav ...
... – This model saw the solar system as perfect spheres with attached celestial bodies rotating around a fixed Earth. – The planets rotated around the Earth in perfect circles. – This model grew out of the ideas that: • Humans were at the center of a perfect universe created just for them. • Since Heav ...
search for extrasolar planets
... life-bearing planets • Many sunlike stars have giant planets; the more metal-rich the better • Many of these are in places hostile to terrestrial planets • Moons may offer rich pickings, opening up faint, cool stars for habitable zones • Interstellar probes can start with significant knowledge of th ...
... life-bearing planets • Many sunlike stars have giant planets; the more metal-rich the better • Many of these are in places hostile to terrestrial planets • Moons may offer rich pickings, opening up faint, cool stars for habitable zones • Interstellar probes can start with significant knowledge of th ...
STARS
... • Most stars are between 1 billion and 10 billion years old. Some stars may even be close to 13.7 billion years old—the observed age of the universe. The oldest star yet discovered, HE 1523-0901, is an estimated 13.2 billion years old. • The more massive the star, the shorter its lifespan, primarily ...
... • Most stars are between 1 billion and 10 billion years old. Some stars may even be close to 13.7 billion years old—the observed age of the universe. The oldest star yet discovered, HE 1523-0901, is an estimated 13.2 billion years old. • The more massive the star, the shorter its lifespan, primarily ...
Quentin Parker Lecture 1b - PowerPoint file.
... This 2MASS image, covering a field roughly 10 X 8 degrees (about the area of your fist held out at arm's length) reveals multitudes of otherwise hidden stars, penetrating all the way to the central star cluster of the Galaxy. On a dark starry night, it seems as though we can see countless stars. In ...
... This 2MASS image, covering a field roughly 10 X 8 degrees (about the area of your fist held out at arm's length) reveals multitudes of otherwise hidden stars, penetrating all the way to the central star cluster of the Galaxy. On a dark starry night, it seems as though we can see countless stars. In ...
Astronomy 1400: Exam 3 version 1
... A. Greenhouse gases absorb X-rays and ultraviolet light from the Sun, and this absorbed radiation then heats the atmosphere and the surface. B. A planet’s surface absorbs visible sunlight and returns this absorbed energy to space as infrared light. Greenhouse gases slow the escape of this infrared r ...
... A. Greenhouse gases absorb X-rays and ultraviolet light from the Sun, and this absorbed radiation then heats the atmosphere and the surface. B. A planet’s surface absorbs visible sunlight and returns this absorbed energy to space as infrared light. Greenhouse gases slow the escape of this infrared r ...
Our Solar System
... black hole. Our sun is not on fire, it is just very hot. Its just too hot for anyone to touch with there own hands. The sun is the biggest star in our solar system. The sun gives a lot energy and life on earth. ...
... black hole. Our sun is not on fire, it is just very hot. Its just too hot for anyone to touch with there own hands. The sun is the biggest star in our solar system. The sun gives a lot energy and life on earth. ...
Unit 3: Understanding the Universe
... Enduring Understandings The solar system contains planets, dwarf planets, comets, asteroids, and other small solar system bodies. ...
... Enduring Understandings The solar system contains planets, dwarf planets, comets, asteroids, and other small solar system bodies. ...
How space is explored?
... everything in it 1. It is believed to be infinite in volume 2. The observable universe is a sphere around earth with a radius of 46 billion light years. B. The universe is ge@ng larger. 1. There ...
... everything in it 1. It is believed to be infinite in volume 2. The observable universe is a sphere around earth with a radius of 46 billion light years. B. The universe is ge@ng larger. 1. There ...
Planetary habitability

Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia. As the existence of life beyond Earth is unknown, planetary habitability is largely an extrapolation of conditions on Earth and the characteristics of the Sun and Solar System which appear favourable to life's flourishing—in particular those factors that have sustained complex, multicellular organisms and not just simpler, unicellular creatures. Research and theory in this regard is a component of planetary science and the emerging discipline of astrobiology.An absolute requirement for life is an energy source, and the notion of planetary habitability implies that many other geophysical, geochemical, and astrophysical criteria must be met before an astronomical body can support life. In its astrobiology roadmap, NASA has defined the principal habitability criteria as ""extended regions of liquid water, conditions favourable for the assembly of complex organic molecules, and energy sources to sustain metabolism.""In determining the habitability potential of a body, studies focus on its bulk composition, orbital properties, atmosphere, and potential chemical interactions. Stellar characteristics of importance include mass and luminosity, stable variability, and high metallicity. Rocky, terrestrial-type planets and moons with the potential for Earth-like chemistry are a primary focus of astrobiological research, although more speculative habitability theories occasionally examine alternative biochemistries and other types of astronomical bodies.The idea that planets beyond Earth might host life is an ancient one, though historically it was framed by philosophy as much as physical science. The late 20th century saw two breakthroughs in the field. The observation and robotic spacecraft exploration of other planets and moons within the Solar System has provided critical information on defining habitability criteria and allowed for substantial geophysical comparisons between the Earth and other bodies. The discovery of extrasolar planets, beginning in the early 1990s and accelerating thereafter, has provided further information for the study of possible extraterrestrial life. These findings confirm that the Sun is not unique among stars in hosting planets and expands the habitability research horizon beyond the Solar System.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently. On 4 November 2013, astronomers reported, based on Kepler space mission data, that there could be as many as 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of Sun-like stars and red dwarfs within the Milky Way. 11 billion of these estimated planets may be orbiting Sun-like stars. The nearest such planet may be 12 light-years away, according to the scientists.