Science 3rd prep. 1st term unit 3 lesson 2 The Solar System Millions
... 8 – the scientist who found Nebular theory about the evolution of the solar system is called……………………. 9 – according to nebular theory, the gaseous rings cooled down and frozen forming the …………………………………. , while the flaming mass remained is the ………………………… 10 – the scientist who established ………………………… ...
... 8 – the scientist who found Nebular theory about the evolution of the solar system is called……………………. 9 – according to nebular theory, the gaseous rings cooled down and frozen forming the …………………………………. , while the flaming mass remained is the ………………………… 10 – the scientist who established ………………………… ...
Star Types
... sun, an O star, a white dwarf, or a red giant? Which of these star is the hottest? What are Sun-like stars (0.4 Msun < M < 8 Msun) in common? What about red dwarfs (0.08 Msun < M < 0.4 Msun) ? Where do stars spend most of their time? ...
... sun, an O star, a white dwarf, or a red giant? Which of these star is the hottest? What are Sun-like stars (0.4 Msun < M < 8 Msun) in common? What about red dwarfs (0.08 Msun < M < 0.4 Msun) ? Where do stars spend most of their time? ...
Starry Monday at Otterbein
... F = ma = G Mm/r2 (m cancels out) – From the weight of objects (i.e., the force of gravity) near the surface of the Earth, and known radius of Earth RE = 6.4103 km, we find ME = 61024 kg – Your weight on another planet is F = m GM/r2 • E.g., on the Moon your weight would be 1/6 of what it is on E ...
... F = ma = G Mm/r2 (m cancels out) – From the weight of objects (i.e., the force of gravity) near the surface of the Earth, and known radius of Earth RE = 6.4103 km, we find ME = 61024 kg – Your weight on another planet is F = m GM/r2 • E.g., on the Moon your weight would be 1/6 of what it is on E ...
Issue #87 of Lunar and Planetary Information Bulletin
... (through “direct detection” methods) may one day reveal these characteristics; the same methods may one day reveal, through the detection of significant quantities of life-related gases such as oxygen and methane, whether a planet is habitable or possibly inhabited. ...
... (through “direct detection” methods) may one day reveal these characteristics; the same methods may one day reveal, through the detection of significant quantities of life-related gases such as oxygen and methane, whether a planet is habitable or possibly inhabited. ...
ALUMINIUM-26 IN THE EARLY SOLAR SYSTEM : A PROBABILITY
... Fe (T1/2 = 2.6 Myr) in the early Solar System [1] have helped for some time to answer that important question [2]. Because in a large cluster dynamical encounters are more frequent and disruptive than in a small one, the dynamically cold orbital distribution of giant planets and the mere existence o ...
... Fe (T1/2 = 2.6 Myr) in the early Solar System [1] have helped for some time to answer that important question [2]. Because in a large cluster dynamical encounters are more frequent and disruptive than in a small one, the dynamically cold orbital distribution of giant planets and the mere existence o ...
The Science of Astronomy - Ohio Wesleyan University
... – He was taken by aesthetic appeal of a concentric pattern of uniform circular motion – His mathematical model was no more accurate than that of Ptolemy, but it was more elegant – He was forced to introduce epicycles to account for some of the irregularities of planetary speeds and distances ...
... – He was taken by aesthetic appeal of a concentric pattern of uniform circular motion – His mathematical model was no more accurate than that of Ptolemy, but it was more elegant – He was forced to introduce epicycles to account for some of the irregularities of planetary speeds and distances ...
strange new Worlds - Scholars at Princeton
... swells up to become a gas giant. However, this threshold mass can only be achieved in distant, colder regions of the disk, where the supply of solid materials is enhanced by ices of water, methane, and ammonia. In other words, giant planets only form beyond the star system’s “snow line,” where there ...
... swells up to become a gas giant. However, this threshold mass can only be achieved in distant, colder regions of the disk, where the supply of solid materials is enhanced by ices of water, methane, and ammonia. In other words, giant planets only form beyond the star system’s “snow line,” where there ...
Charting The Universe - University of Windsor
... Pleiades from Orion, Greek gods placed them among the stars. Orion nightly stalks them across the sky! ...
... Pleiades from Orion, Greek gods placed them among the stars. Orion nightly stalks them across the sky! ...
File
... • Is it the final stage for medium size stars? • For our Sun- YES. • For stars that are part of a binary system or star cluster- NO (on next slide) • The white dwarf is the dense core left behind from the previous red giant. • 1 tsp. of white dwarf matter would have a mass of several tons. • This wi ...
... • Is it the final stage for medium size stars? • For our Sun- YES. • For stars that are part of a binary system or star cluster- NO (on next slide) • The white dwarf is the dense core left behind from the previous red giant. • 1 tsp. of white dwarf matter would have a mass of several tons. • This wi ...
Planet Jupiter - Rocky View Schools
... storms. While storms are constantly forming and dissipating on Jupiter, the Great Red Spot is a huge storm that has been visible for hundreds of years. It is about three times the size of the Earth and is the most recognizable feature on Jupiter, visible even in amateur telescopes. The rotational ra ...
... storms. While storms are constantly forming and dissipating on Jupiter, the Great Red Spot is a huge storm that has been visible for hundreds of years. It is about three times the size of the Earth and is the most recognizable feature on Jupiter, visible even in amateur telescopes. The rotational ra ...
Introduction This book will teach you all you need to know about the
... The picture to the left is a protostar. You can still see the rings of gases surrounding it. A nebula is the first stage in the life cycle of a star. A nebula is a large cloud of dust, gas hydrogen gas, and plasma. Over long periods of time the gas and dust do to gravitational force pull towards eac ...
... The picture to the left is a protostar. You can still see the rings of gases surrounding it. A nebula is the first stage in the life cycle of a star. A nebula is a large cloud of dust, gas hydrogen gas, and plasma. Over long periods of time the gas and dust do to gravitational force pull towards eac ...
Birth of Stars
... The dust-shrouded interiors of molecular clouds where stellar births are thought to take place cannot be observed with visible light, but only with infrared and radio telescopes The timescale for the initial collapse is estimated to be very short astronomically (thousands of years), implying that st ...
... The dust-shrouded interiors of molecular clouds where stellar births are thought to take place cannot be observed with visible light, but only with infrared and radio telescopes The timescale for the initial collapse is estimated to be very short astronomically (thousands of years), implying that st ...
Stars and Galaxies
... have a life cycle and evolve over time. The mass of a star controls its Evolution Lifespan Ultimate fate (how it dies) ...
... have a life cycle and evolve over time. The mass of a star controls its Evolution Lifespan Ultimate fate (how it dies) ...
Stellar Evolution: After the Main Sequence
... ceases when the hydrogen has been exhausted in the core of a main-sequence star • This leaves a core of nearly pure helium surrounded by a shell through which hydrogen fusion works its way outward in the star • The core shrinks and becomes hotter, while the star’s outer layers expand and cool • The ...
... ceases when the hydrogen has been exhausted in the core of a main-sequence star • This leaves a core of nearly pure helium surrounded by a shell through which hydrogen fusion works its way outward in the star • The core shrinks and becomes hotter, while the star’s outer layers expand and cool • The ...
Stellar Remnants
... • An object as big as the Sun with a onemonth rotation period will rotate more than 1000 times a second if squeezed down to the size of a neutron star – This happens when a massive star’s iron core collapses – magnetic field beams radiation energy in ...
... • An object as big as the Sun with a onemonth rotation period will rotate more than 1000 times a second if squeezed down to the size of a neutron star – This happens when a massive star’s iron core collapses – magnetic field beams radiation energy in ...
Recap: High Mass Stars
... Low Mass 4.2 light years Stars away! • From ½ all the way down to 0.075% of the Sun’s mass • Burn cool, less than 3500 K. Dim light. • Can live a REALLY long time. 10,000,000,000,000 years? • Our nearest star neighbor is Proxima Centauri, a red dwarf. • Most numerous stars in the entire Universe! ...
... Low Mass 4.2 light years Stars away! • From ½ all the way down to 0.075% of the Sun’s mass • Burn cool, less than 3500 K. Dim light. • Can live a REALLY long time. 10,000,000,000,000 years? • Our nearest star neighbor is Proxima Centauri, a red dwarf. • Most numerous stars in the entire Universe! ...
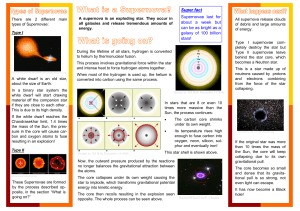
What is a supernova - University of Warwick
... This is a star made up of neutrons caused by protons and electrons combining from the force of the star collapsing. ...
... This is a star made up of neutrons caused by protons and electrons combining from the force of the star collapsing. ...
ph507lecnote07
... outer planets are not prograde, but these are believed to be captured satellites) All planets except Venus and Uranus have prograde rotation The sun contains essentially all the mass The planets (especially Jupiter and Saturn) contain most of the angular momentum in the solar system Small, dense, ir ...
... outer planets are not prograde, but these are believed to be captured satellites) All planets except Venus and Uranus have prograde rotation The sun contains essentially all the mass The planets (especially Jupiter and Saturn) contain most of the angular momentum in the solar system Small, dense, ir ...
Our Solar System LEVELED BOOK • S www.readinga-z.com
... Mars is almost as long as two Earth years. A day on Mars lasts only one-half hour longer than a day on Earth. ...
... Mars is almost as long as two Earth years. A day on Mars lasts only one-half hour longer than a day on Earth. ...
www.NewYorkScienceTeacher.org/review
... Under the right conditions, when the CME arrived at Earth’s magnetosphere, energy would be released in the form of an intense auroral display. For an intense auroral display, the emission must encounter Earth’s magnetic field directly, as opposed to a glancing blow, and the magnetosphere must alread ...
... Under the right conditions, when the CME arrived at Earth’s magnetosphere, energy would be released in the form of an intense auroral display. For an intense auroral display, the emission must encounter Earth’s magnetic field directly, as opposed to a glancing blow, and the magnetosphere must alread ...
Document
... • A computer program that simulates the vision of the sky during day and night Things to observe: • Position on Earth: observe how the view of sky changes as you move E,W, N,S • Note the distribution of sunlight on Earth! • Rotation is around Polaris which is not in zenith ...
... • A computer program that simulates the vision of the sky during day and night Things to observe: • Position on Earth: observe how the view of sky changes as you move E,W, N,S • Note the distribution of sunlight on Earth! • Rotation is around Polaris which is not in zenith ...
Lecture 5 Astronomy
... 29. During the course of a year and relative to the Sun, the Earth’s axis A. Always away from the Sun B. Always toward the Sun C. Toward the Sun for half a day and away from the Sun the other half D. Toward the Sun half of the year and away the other half. 30. During the equinoxes? A. A vertical st ...
... 29. During the course of a year and relative to the Sun, the Earth’s axis A. Always away from the Sun B. Always toward the Sun C. Toward the Sun for half a day and away from the Sun the other half D. Toward the Sun half of the year and away the other half. 30. During the equinoxes? A. A vertical st ...
Lars Bildsten - nnpss
... Massive, most luminous stars burn their fuel the fastest, so we get the age of an Open Cluster like Pleiades from the absence of even brighter stars ==> 120 Myr ...
... Massive, most luminous stars burn their fuel the fastest, so we get the age of an Open Cluster like Pleiades from the absence of even brighter stars ==> 120 Myr ...
Stars
... A sphere (like the Sun) will be 1/2° across when its distance is 115 times its diameter. ...
... A sphere (like the Sun) will be 1/2° across when its distance is 115 times its diameter. ...
Biblical Astrophysics - The Call of the Bride
... (Amos 8:8-9) The earth will tremble for your deeds, and everyone will mourn. The ground will rise like the Nile River at floodtime; it will heave up, then sink again. "In that day," says the Sovereign LORD, "I will make the sun go down at noon and darken the earth while it is still day. (The Earth's ...
... (Amos 8:8-9) The earth will tremble for your deeds, and everyone will mourn. The ground will rise like the Nile River at floodtime; it will heave up, then sink again. "In that day," says the Sovereign LORD, "I will make the sun go down at noon and darken the earth while it is still day. (The Earth's ...
Planetary habitability

Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia. As the existence of life beyond Earth is unknown, planetary habitability is largely an extrapolation of conditions on Earth and the characteristics of the Sun and Solar System which appear favourable to life's flourishing—in particular those factors that have sustained complex, multicellular organisms and not just simpler, unicellular creatures. Research and theory in this regard is a component of planetary science and the emerging discipline of astrobiology.An absolute requirement for life is an energy source, and the notion of planetary habitability implies that many other geophysical, geochemical, and astrophysical criteria must be met before an astronomical body can support life. In its astrobiology roadmap, NASA has defined the principal habitability criteria as ""extended regions of liquid water, conditions favourable for the assembly of complex organic molecules, and energy sources to sustain metabolism.""In determining the habitability potential of a body, studies focus on its bulk composition, orbital properties, atmosphere, and potential chemical interactions. Stellar characteristics of importance include mass and luminosity, stable variability, and high metallicity. Rocky, terrestrial-type planets and moons with the potential for Earth-like chemistry are a primary focus of astrobiological research, although more speculative habitability theories occasionally examine alternative biochemistries and other types of astronomical bodies.The idea that planets beyond Earth might host life is an ancient one, though historically it was framed by philosophy as much as physical science. The late 20th century saw two breakthroughs in the field. The observation and robotic spacecraft exploration of other planets and moons within the Solar System has provided critical information on defining habitability criteria and allowed for substantial geophysical comparisons between the Earth and other bodies. The discovery of extrasolar planets, beginning in the early 1990s and accelerating thereafter, has provided further information for the study of possible extraterrestrial life. These findings confirm that the Sun is not unique among stars in hosting planets and expands the habitability research horizon beyond the Solar System.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently. On 4 November 2013, astronomers reported, based on Kepler space mission data, that there could be as many as 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of Sun-like stars and red dwarfs within the Milky Way. 11 billion of these estimated planets may be orbiting Sun-like stars. The nearest such planet may be 12 light-years away, according to the scientists.