Slides for Earth and the Solar System Unit #1
... "Clearing the Orbit" That third requirement can be tricky to understand so let's imagine a crowded school hallway. ...
... "Clearing the Orbit" That third requirement can be tricky to understand so let's imagine a crowded school hallway. ...
Lec10_ch12_deathofstars
... combine with protons, we are left with a neutron core--a neutron star! – Core about 10-20 km in diameter! – Gas layers completely blown away – Star now supported by neutron ...
... combine with protons, we are left with a neutron core--a neutron star! – Core about 10-20 km in diameter! – Gas layers completely blown away – Star now supported by neutron ...
Dynamical evolution of planetary systems
... There are two possible mechanisms by which we envision that giant planets can form. The first is nicknamed the “core-accretion mechanism”: the coagulation of solid particles forms a core typically of about 10 Earth masses (M⊕ ) while the gas is still present in the proto-planetary disk; the core the ...
... There are two possible mechanisms by which we envision that giant planets can form. The first is nicknamed the “core-accretion mechanism”: the coagulation of solid particles forms a core typically of about 10 Earth masses (M⊕ ) while the gas is still present in the proto-planetary disk; the core the ...
Nebula
... Other nebulae may form as planetary nebulae. This is the final stage of a low-mass star's life, like Earth's Sun. Stars with a mass up to 8-10 solar masses evolve into red giants and slowly lose their outer layers during pulsations in their atmospheres. When a star has lost a sufficient amount of m ...
... Other nebulae may form as planetary nebulae. This is the final stage of a low-mass star's life, like Earth's Sun. Stars with a mass up to 8-10 solar masses evolve into red giants and slowly lose their outer layers during pulsations in their atmospheres. When a star has lost a sufficient amount of m ...
Article PDF - IOPscience
... Neptune and other hypothetical massive planetary embryos or of its temporary capture in a resonance with one of the other planets, although these scenarios have never been quantitatively simulated. In this section we investigate the effects that an eccentric Neptune would have on the formation of th ...
... Neptune and other hypothetical massive planetary embryos or of its temporary capture in a resonance with one of the other planets, although these scenarios have never been quantitatively simulated. In this section we investigate the effects that an eccentric Neptune would have on the formation of th ...
@let@token Stellar Oscillations: Pulsations of Stars Throughout the
... zone impedes the passage of Ñux perturbations from the base of the convection zone to the photosphere. Thus the photometric variation of a mode with constant velocity amplitude decreases. These factors account for the observed trend that longer period modes are found in cooler DA variables. Overstab ...
... zone impedes the passage of Ñux perturbations from the base of the convection zone to the photosphere. Thus the photometric variation of a mode with constant velocity amplitude decreases. These factors account for the observed trend that longer period modes are found in cooler DA variables. Overstab ...
FOSS Sun, Moon, and Planets Module Glossary 3 Edition © 2012
... planet a large, round object orbiting a star (SRB, IG) planetarium a theater with a dome-shaped ceiling that represents the sky (SRB) predict to estimate accurately in advance based on a pattern or previous knowledge (SRB) reflect to bounce off an object or surface (SRB) revolution to travel around ...
... planet a large, round object orbiting a star (SRB, IG) planetarium a theater with a dome-shaped ceiling that represents the sky (SRB) predict to estimate accurately in advance based on a pattern or previous knowledge (SRB) reflect to bounce off an object or surface (SRB) revolution to travel around ...
starwalk2 manual en - Vito Technology Inc.
... The highlighted parameter will start changing accordingly. To make any parameter elapse automatically, tap one of them and drag the Time slider. The map sky will rotate. In order to stop that, tap the Time slider again. To return to the current time zone, tap ...
... The highlighted parameter will start changing accordingly. To make any parameter elapse automatically, tap one of them and drag the Time slider. The map sky will rotate. In order to stop that, tap the Time slider again. To return to the current time zone, tap ...
Indications for an influence of Hot Jupiters
... of two lower than in the previous full band (0.2-5 keV) observations performed with XMM-Newton. This is not surprising, because τ Boo A’s spectrum has been found to have a mean coronal temperature of T = 3 MK in the XMM-Newton observations, which corresponds to a flux reduction of ca. 50% when movin ...
... of two lower than in the previous full band (0.2-5 keV) observations performed with XMM-Newton. This is not surprising, because τ Boo A’s spectrum has been found to have a mean coronal temperature of T = 3 MK in the XMM-Newton observations, which corresponds to a flux reduction of ca. 50% when movin ...
Bayesian mass and age estimates for transiting exoplanet host stars⋆
... subscript “obs”, their standard errors are σT , σlog L , etc., and other quantities are derived from the model, as described above. In cases where asymmetric error bars are quoted on values we use either the upper or lower error bar, as appropriate, depending on whether the model value is greater th ...
... subscript “obs”, their standard errors are σT , σlog L , etc., and other quantities are derived from the model, as described above. In cases where asymmetric error bars are quoted on values we use either the upper or lower error bar, as appropriate, depending on whether the model value is greater th ...
Chapter 1: The Sun - New Hampshire Public Television
... The Sun’s energy is generated by nuclear fusion. At very high temperatures, in the hearts of stars like our Sun, the nuclei of small atoms are fused together to make the nuclei of larger ones. Deep inside the Sun’s core, a “fusion reactor” has been in continuous operation since firing up some five b ...
... The Sun’s energy is generated by nuclear fusion. At very high temperatures, in the hearts of stars like our Sun, the nuclei of small atoms are fused together to make the nuclei of larger ones. Deep inside the Sun’s core, a “fusion reactor” has been in continuous operation since firing up some five b ...
SUN, MOON, AND PLANETS Overview
... • Ask questions about objects, organisms, systems, and events in thee natural and human-made world (science). • Ask questions to define and clarify a problem, determine criteria for solutions, and identify constraints (engineering). Planning and carrying out investigations • Plan and conduct investi ...
... • Ask questions about objects, organisms, systems, and events in thee natural and human-made world (science). • Ask questions to define and clarify a problem, determine criteria for solutions, and identify constraints (engineering). Planning and carrying out investigations • Plan and conduct investi ...
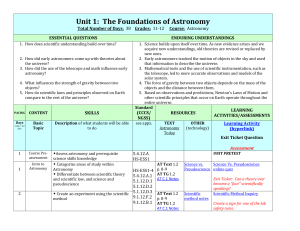
Unit 1: The Foundations of Astronomy
... 1. Science builds upon itself over time. As new evidence arises and we acquire new understandings, old theories are revised or replaced by new ones. 2. Early astronomers tracked the motion of objects in the sky and used that information to describe the universe. 3. Mathematical tools and the use of ...
... 1. Science builds upon itself over time. As new evidence arises and we acquire new understandings, old theories are revised or replaced by new ones. 2. Early astronomers tracked the motion of objects in the sky and used that information to describe the universe. 3. Mathematical tools and the use of ...
Solaria Binaria - The Grazian Archive
... belt that may be called “Apollo” represents a planet that exploded. Nor can we exclude from the common experience this scared Earth. Consistent with the panorama of catastrophes, and additionally supplying a new dynamic form in cosmogony, there has been developed a body of knowledge and speculation ...
... belt that may be called “Apollo” represents a planet that exploded. Nor can we exclude from the common experience this scared Earth. Consistent with the panorama of catastrophes, and additionally supplying a new dynamic form in cosmogony, there has been developed a body of knowledge and speculation ...
Astrophysical and astrochemical insights into the origin of life
... The clouds, which are thought to occupy only a minor volume fraction of the overall ISM, are in turn divisible into the so-called diffuse clouds which are characterized by visual extinctions Av ∼ 1 mag, densities of the order of 100 atoms cm−3 , and temperatures ∼100 K; dense clouds with Av > 5 mag, ...
... The clouds, which are thought to occupy only a minor volume fraction of the overall ISM, are in turn divisible into the so-called diffuse clouds which are characterized by visual extinctions Av ∼ 1 mag, densities of the order of 100 atoms cm−3 , and temperatures ∼100 K; dense clouds with Av > 5 mag, ...
Understanding Uranus - Lewis Center for
... But it was not until 1781 that English astronomer William Herschel recognized it as a planet. Uranus travels in a nearly circular orbit at an average distance of almost 3 billion kilometers (1.9 billion miles) from the Sun (about nineteen times the distance from Earth to the Sun). The earliest obser ...
... But it was not until 1781 that English astronomer William Herschel recognized it as a planet. Uranus travels in a nearly circular orbit at an average distance of almost 3 billion kilometers (1.9 billion miles) from the Sun (about nineteen times the distance from Earth to the Sun). The earliest obser ...
Grade 9 Space Review 50KB Nov 18 2009 10:52:00 AM
... 31. The Sun emits not only visible light but also other forms of radiation. List some of these other forms and their effect on living things on Earth. Write your answer in complete sentences. 32. What advice would you give to dedicated sunbathers? Why? Publish your advice in the school newspaper. 33 ...
... 31. The Sun emits not only visible light but also other forms of radiation. List some of these other forms and their effect on living things on Earth. Write your answer in complete sentences. 32. What advice would you give to dedicated sunbathers? Why? Publish your advice in the school newspaper. 33 ...
The Magellan 20 Telescope Science Goals
... in the plane of the sky. A 3D tomographic reconstruction of the mass distribution and kinematics of the IGM becomes possible, mapping tenuous structures with densities down to the mean density of the universe. A combination with a traditional galaxy redshift survey of the same volume sampled by the ...
... in the plane of the sky. A 3D tomographic reconstruction of the mass distribution and kinematics of the IGM becomes possible, mapping tenuous structures with densities down to the mean density of the universe. A combination with a traditional galaxy redshift survey of the same volume sampled by the ...
16_Testbank
... A) 100 molecules per cubic centimeter, 10-30 Kelvin. B) 300 molecules per cubic centimeter, 10-30 Kelvin. C) 1000 molecules per cubic centimeter, 10-30 Kelvin. D) 100 molecules per cubic centimeter, 100-300 Kelvin. E) 300 molecules per cubic centimeter, 100-300 Kelvin. Answer: B 5) The most abundant ...
... A) 100 molecules per cubic centimeter, 10-30 Kelvin. B) 300 molecules per cubic centimeter, 10-30 Kelvin. C) 1000 molecules per cubic centimeter, 10-30 Kelvin. D) 100 molecules per cubic centimeter, 100-300 Kelvin. E) 300 molecules per cubic centimeter, 100-300 Kelvin. Answer: B 5) The most abundant ...
Determining the mass loss limit for close
... Erkaev et al. (2007) showed that Eqs. (1) and (4) can be applied for close-in gas giants at orbital distances ≤ 0.15 AU, because due to the Roche lobe effect the upper atmospheres of such planets can also experience hydrodynamic blow-off conditions even if their exobase temperatures are lower than t ...
... Erkaev et al. (2007) showed that Eqs. (1) and (4) can be applied for close-in gas giants at orbital distances ≤ 0.15 AU, because due to the Roche lobe effect the upper atmospheres of such planets can also experience hydrodynamic blow-off conditions even if their exobase temperatures are lower than t ...
Pluto Reading
... Pluto has one large moon, named Charon; two small moons (called Nix and Hydra) were discovered in 2005 and another was discovered in 2011 (it is called P4). Although Charon is small, about 1,172 km (728 miles) in diameter, it about half of the size of Pluto itself. Charon orbits about 19,640 km from ...
... Pluto has one large moon, named Charon; two small moons (called Nix and Hydra) were discovered in 2005 and another was discovered in 2011 (it is called P4). Although Charon is small, about 1,172 km (728 miles) in diameter, it about half of the size of Pluto itself. Charon orbits about 19,640 km from ...
Planet Hunters Education Guide
... them particularly adept at identifying faces, objects, words and sounds. Computers are now sometimes being used to identify faces, but this extremely expensive technology still only works in ideal conditions and generally fails where lighting is poor or where faces are turned to the side. Images use ...
... them particularly adept at identifying faces, objects, words and sounds. Computers are now sometimes being used to identify faces, but this extremely expensive technology still only works in ideal conditions and generally fails where lighting is poor or where faces are turned to the side. Images use ...
The Age Distribution of Potential Intelligent Life in the Milky Way
... From this equation we can see that the gas mass lost as it is turned into stars (per parsec squared per year) is proportional to the total mass of gas (per parsec squared) to the power n. Observations of distant galaxies have found this relationship to hold consistently, just with varying values of ...
... From this equation we can see that the gas mass lost as it is turned into stars (per parsec squared per year) is proportional to the total mass of gas (per parsec squared) to the power n. Observations of distant galaxies have found this relationship to hold consistently, just with varying values of ...
Dynamics of small bodies in planetary systems
... comets are confined to relatively narrow rings known as the asteroid belt and the Kuiper belt (see chapters by Nakamura and Jewitt). These belts are the source of the majority of the smaller objects seen in the solar system, since such objects are inevitably created in collisions between objects wit ...
... comets are confined to relatively narrow rings known as the asteroid belt and the Kuiper belt (see chapters by Nakamura and Jewitt). These belts are the source of the majority of the smaller objects seen in the solar system, since such objects are inevitably created in collisions between objects wit ...
Planetary habitability

Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia. As the existence of life beyond Earth is unknown, planetary habitability is largely an extrapolation of conditions on Earth and the characteristics of the Sun and Solar System which appear favourable to life's flourishing—in particular those factors that have sustained complex, multicellular organisms and not just simpler, unicellular creatures. Research and theory in this regard is a component of planetary science and the emerging discipline of astrobiology.An absolute requirement for life is an energy source, and the notion of planetary habitability implies that many other geophysical, geochemical, and astrophysical criteria must be met before an astronomical body can support life. In its astrobiology roadmap, NASA has defined the principal habitability criteria as ""extended regions of liquid water, conditions favourable for the assembly of complex organic molecules, and energy sources to sustain metabolism.""In determining the habitability potential of a body, studies focus on its bulk composition, orbital properties, atmosphere, and potential chemical interactions. Stellar characteristics of importance include mass and luminosity, stable variability, and high metallicity. Rocky, terrestrial-type planets and moons with the potential for Earth-like chemistry are a primary focus of astrobiological research, although more speculative habitability theories occasionally examine alternative biochemistries and other types of astronomical bodies.The idea that planets beyond Earth might host life is an ancient one, though historically it was framed by philosophy as much as physical science. The late 20th century saw two breakthroughs in the field. The observation and robotic spacecraft exploration of other planets and moons within the Solar System has provided critical information on defining habitability criteria and allowed for substantial geophysical comparisons between the Earth and other bodies. The discovery of extrasolar planets, beginning in the early 1990s and accelerating thereafter, has provided further information for the study of possible extraterrestrial life. These findings confirm that the Sun is not unique among stars in hosting planets and expands the habitability research horizon beyond the Solar System.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently. On 4 November 2013, astronomers reported, based on Kepler space mission data, that there could be as many as 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of Sun-like stars and red dwarfs within the Milky Way. 11 billion of these estimated planets may be orbiting Sun-like stars. The nearest such planet may be 12 light-years away, according to the scientists.