The Sun and the Origin of the Solar System
... – Envelope is ejected as a "planetary nebula" – The core remains as a "white dwarf" ...
... – Envelope is ejected as a "planetary nebula" – The core remains as a "white dwarf" ...
The Solar System
... the strongest hurricane-force winds on Earth top out at about 110 meters, or (360 feet), per second. These super-fast winds, combined with heat rising from within the planet's interior, cause the yellow and gold bands visible in the atmosphere. ...
... the strongest hurricane-force winds on Earth top out at about 110 meters, or (360 feet), per second. These super-fast winds, combined with heat rising from within the planet's interior, cause the yellow and gold bands visible in the atmosphere. ...
Is There Life in Space?
... to their distance. This is called "Hubble's Law," named after Edwin Hubble (1889-1953) who discovered this phenomenon in 1929. This observation supports the expansion of the universe and suggests that the universe was ...
... to their distance. This is called "Hubble's Law," named after Edwin Hubble (1889-1953) who discovered this phenomenon in 1929. This observation supports the expansion of the universe and suggests that the universe was ...
tata-surya
... There was encounter between the Sun and another star. In this scenario, the gravity of the passing star tears a succession of bolts from the solar surface. Bolts coming from the side nearer the star are thrown out to distances comparable with those of the giant plants, while those from the far side ...
... There was encounter between the Sun and another star. In this scenario, the gravity of the passing star tears a succession of bolts from the solar surface. Bolts coming from the side nearer the star are thrown out to distances comparable with those of the giant plants, while those from the far side ...
Solar_System - UF :: Astronomy
... Jovian Planets •Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune •Far from Sun •Large masses and radii •Gaseous surface •Low densities •Fast rotation •Strong magnetic field •Many rings •Many moons ...
... Jovian Planets •Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune •Far from Sun •Large masses and radii •Gaseous surface •Low densities •Fast rotation •Strong magnetic field •Many rings •Many moons ...
Unit Test - Dnyansagar Coaching Classes, Ahmednagar
... (D) Find odd man out. 1) Mercury, Venus, Mars, Sirius 2) Mercury, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn 3) Sun, Sirius, Pole Star, Venus 4) Mriga, Punarvasu, Ashlesha, Jupiter (A) Answer the following in short (any two) 1) What is period of rotation? 2) What is GMRT? 3) What are asteroids? 4) Name any four nakshatr ...
... (D) Find odd man out. 1) Mercury, Venus, Mars, Sirius 2) Mercury, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn 3) Sun, Sirius, Pole Star, Venus 4) Mriga, Punarvasu, Ashlesha, Jupiter (A) Answer the following in short (any two) 1) What is period of rotation? 2) What is GMRT? 3) What are asteroids? 4) Name any four nakshatr ...
Planet Flash Cards
... smaller than Jupiter and Saturn ► Many moons (13) ► Gas Giant – No Solid Surface ► Has a few rings ► 1 day = 19 hours ► 1 year = 168.8 years – longest year ...
... smaller than Jupiter and Saturn ► Many moons (13) ► Gas Giant – No Solid Surface ► Has a few rings ► 1 day = 19 hours ► 1 year = 168.8 years – longest year ...
Science – Chapter 9, Lesson 1 telescope – a tool that makes far
... made of gases with many moons and rings 3. ***Pluto – small and made of rocks and frozen gases with one moon and no rings asteroid – piece of rock that orbits the sun (can be as small as a grain or as large as California) asteroid belt – an area between inner planets and outer planets ...
... made of gases with many moons and rings 3. ***Pluto – small and made of rocks and frozen gases with one moon and no rings asteroid – piece of rock that orbits the sun (can be as small as a grain or as large as California) asteroid belt – an area between inner planets and outer planets ...
Grade 9 Applied Science – Space
... Jupiter has 67 moons. Jupiter has the shortest day of all the planets. It turns on its axis once every 9 hours and 55 minutes. The rapid rotation flattens the planet slightly, giving it an oblate shape. Jupiter has the Great Red Spot that is visible on its surface. It is a huge storm that has raged ...
... Jupiter has 67 moons. Jupiter has the shortest day of all the planets. It turns on its axis once every 9 hours and 55 minutes. The rapid rotation flattens the planet slightly, giving it an oblate shape. Jupiter has the Great Red Spot that is visible on its surface. It is a huge storm that has raged ...
ExamView - Untitled.tst
... a. their size and density. b. their rates of rotation. c. their atmospheres. d. their direction of rotation. 14. Which is the smallest terrestrial planet? a. Mars b. Mercury c. Venus d. Earth 15. The atmospheres of the gas giant planets cannot escape into space because a. the gases are too heavy. b. ...
... a. their size and density. b. their rates of rotation. c. their atmospheres. d. their direction of rotation. 14. Which is the smallest terrestrial planet? a. Mars b. Mercury c. Venus d. Earth 15. The atmospheres of the gas giant planets cannot escape into space because a. the gases are too heavy. b. ...
Solar System Vocab terms geocentric — discredited theory that
... gibbous phase — when a moon or planet shows more than half, but not all, of its face. gravity — seeming force of attraction felt between two or more objects with mass. heliocentric — theory that the sun is in the center of the solar system. infrared — invisible part of light, with longer wavelengths ...
... gibbous phase — when a moon or planet shows more than half, but not all, of its face. gravity — seeming force of attraction felt between two or more objects with mass. heliocentric — theory that the sun is in the center of the solar system. infrared — invisible part of light, with longer wavelengths ...
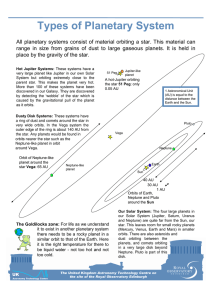
Types of Planetary System
... a ring of dust and comets around the star in very wide orbits. In the Vega system the outer edge of the ring is about 140 AU from the star. Any planets would be found in orbits nearer the star such as the Neptune-like planet in orbit around Vega. Orbit of Neptune-like planet around the star Vega: 65 ...
... a ring of dust and comets around the star in very wide orbits. In the Vega system the outer edge of the ring is about 140 AU from the star. Any planets would be found in orbits nearer the star such as the Neptune-like planet in orbit around Vega. Orbit of Neptune-like planet around the star Vega: 65 ...
The Solar System
... them => growth of first clumps of matter. 2) Accretion: Clumps collide and stick => larger clumps. Eventually, small-moon sized objects: "planetesimals". ...
... them => growth of first clumps of matter. 2) Accretion: Clumps collide and stick => larger clumps. Eventually, small-moon sized objects: "planetesimals". ...
Review Handout - Sturgeon Moodle
... 5. Match each of the planets with the description that best fits. Put the letters beside the right planet. a) cold, small, rocky, used to be a planet. ...
... 5. Match each of the planets with the description that best fits. Put the letters beside the right planet. a) cold, small, rocky, used to be a planet. ...
Geocentric Model of the Solar System
... Astronomers noticed that some celestial bodies did change position relative to the constellations. They called these “wandering stars” planets. Notice the planet Mars moving across the constellations Gemini and Leo over the course of 11 months. ...
... Astronomers noticed that some celestial bodies did change position relative to the constellations. They called these “wandering stars” planets. Notice the planet Mars moving across the constellations Gemini and Leo over the course of 11 months. ...
The Solar System
... The Solar System is located within one of the outer arms of Milky Way which contains about 200 billion stars. For many thousands of years, humanity, with a few notable exceptions, did not recognize the existence of the Solar System. People believed the Earth to be stationary at the centre ...
... The Solar System is located within one of the outer arms of Milky Way which contains about 200 billion stars. For many thousands of years, humanity, with a few notable exceptions, did not recognize the existence of the Solar System. People believed the Earth to be stationary at the centre ...
Name: Date: Period: ______ Unit 9
... 22. What are auroras? What causes them? Where do you normally see them? 23. How do sunspots form? 24. What is nuclear fusion? 25. How long is a sunspot cycle? 26. What is a coronal mass ejection? 27. Although the trigger for a solar flare is unknown, scientists know that… 28. The sun is composed mai ...
... 22. What are auroras? What causes them? Where do you normally see them? 23. How do sunspots form? 24. What is nuclear fusion? 25. How long is a sunspot cycle? 26. What is a coronal mass ejection? 27. Although the trigger for a solar flare is unknown, scientists know that… 28. The sun is composed mai ...
Name the eight planets in order by increasing distance from the sun:
... 1. Name the eight planets in order by increasing distance from the sun: A: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune 2. What are two pieces of technology that have helped scientists explore the solar system? A: space shuttles, probes, telescopes 3. What two things combine/balance ...
... 1. Name the eight planets in order by increasing distance from the sun: A: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune 2. What are two pieces of technology that have helped scientists explore the solar system? A: space shuttles, probes, telescopes 3. What two things combine/balance ...
The History of Astronomy
... 200 A .D. Librarian of Alexandria Believed Heraclides’ geocentric model of the solar system to be correct His model seemed to adequately explain the motion of the planets, but it was complicated. ...
... 200 A .D. Librarian of Alexandria Believed Heraclides’ geocentric model of the solar system to be correct His model seemed to adequately explain the motion of the planets, but it was complicated. ...
Astronomy Name Solar System Fact Sheet – A Closer Look Use the
... 9. How long would it take a radio signal (traveling at light speed) to reach the Moon? ____sec 10.Name the planet whose day is longer than its year. ____________ 11.Look at the orbital velocities for the planets. What pattern do you notice? ...
... 9. How long would it take a radio signal (traveling at light speed) to reach the Moon? ____sec 10.Name the planet whose day is longer than its year. ____________ 11.Look at the orbital velocities for the planets. What pattern do you notice? ...
The_Cosmic_Landscape
... quarter million miiles away. -Held in orbin by the Earth's gravity. -much smaller than the Earth, about 1/4 of Earth's diameter (3,474 km) -Its surface is made up of airless, rock -We only see one face of the moon because of synchronous rotation. (which means it spins and rotates at the same rate, ...
... quarter million miiles away. -Held in orbin by the Earth's gravity. -much smaller than the Earth, about 1/4 of Earth's diameter (3,474 km) -Its surface is made up of airless, rock -We only see one face of the moon because of synchronous rotation. (which means it spins and rotates at the same rate, ...
Formation and evolution of the Solar System

The formation of the Solar System began 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed.This widely accepted model, known as the nebular hypothesis, was first developed in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg, Immanuel Kant, and Pierre-Simon Laplace. Its subsequent development has interwoven a variety of scientific disciplines including astronomy, physics, geology, and planetary science. Since the dawn of the space age in the 1950s and the discovery of extrasolar planets in the 1990s, the model has been both challenged and refined to account for new observations.The Solar System has evolved considerably since its initial formation. Many moons have formed from circling discs of gas and dust around their parent planets, while other moons are thought to have formed independently and later been captured by their planets. Still others, such as the Moon, may be the result of giant collisions. Collisions between bodies have occurred continually up to the present day and have been central to the evolution of the Solar System. The positions of the planets often shifted due to gravitational interactions. This planetary migration is now thought to have been responsible for much of the Solar System's early evolution.In roughly 5 billion years, the Sun will cool and expand outward many times its current diameter (becoming a red giant), before casting off its outer layers as a planetary nebula and leaving behind a stellar remnant known as a white dwarf. In the far distant future, the gravity of passing stars will gradually reduce the Sun's retinue of planets. Some planets will be destroyed, others ejected into interstellar space. Ultimately, over the course of tens of billions of years, it is likely that the Sun will be left with none of the original bodies in orbit around it.