Powerpoint - Physics and Astronomy
... them => growth of first clumps of matter. 2) Accretion: Clumps collide and stick => larger clumps. Eventually, small-moon sized objects: "planetesimals". ...
... them => growth of first clumps of matter. 2) Accretion: Clumps collide and stick => larger clumps. Eventually, small-moon sized objects: "planetesimals". ...
Chapter 7 Notes
... – Jupiter: A gaseous giant – Saturn: Gaseous with spectacular rings – Uranus: A gas giant with a highly tilted axis – Neptune: Similar to Uranus but with normal axis – Pluto: An icy “misfit” more like a comet than a planet ...
... – Jupiter: A gaseous giant – Saturn: Gaseous with spectacular rings – Uranus: A gas giant with a highly tilted axis – Neptune: Similar to Uranus but with normal axis – Pluto: An icy “misfit” more like a comet than a planet ...
What is a Solar System?
... All planets orbit the sun in almost-circular elliptical orbits on approximately the same plane (the ecliptic). Dwarf Planets, comets, asteroids, and meteoroids also orbit the sun Most Satellites/Moons orbit planets (some orbit dwarf planets or even asteroids) Almost all planets, dwarf planets, and m ...
... All planets orbit the sun in almost-circular elliptical orbits on approximately the same plane (the ecliptic). Dwarf Planets, comets, asteroids, and meteoroids also orbit the sun Most Satellites/Moons orbit planets (some orbit dwarf planets or even asteroids) Almost all planets, dwarf planets, and m ...
Chapter 25.1: Models of our Solar System
... backwards relative to us for a while. This apparent (not actual) backward motion in known as “retrograde motion”. Ptolemy didn’t believe E. moved (it was the center of the universe) – so he couldn’t explain this “backward” motion of planets. That’s where Epicycles come in – but they are not ...
... backwards relative to us for a while. This apparent (not actual) backward motion in known as “retrograde motion”. Ptolemy didn’t believe E. moved (it was the center of the universe) – so he couldn’t explain this “backward” motion of planets. That’s where Epicycles come in – but they are not ...
Period of Revolution
... What is thought to have happened to Uranus to give it a 98 degree tilt? • It is thought to have had a collision with another planet ...
... What is thought to have happened to Uranus to give it a 98 degree tilt? • It is thought to have had a collision with another planet ...
File
... It exists in layers that get denser farther into the planet. Eventually, deep inside, the hydrogen becomes metallic. ...
... It exists in layers that get denser farther into the planet. Eventually, deep inside, the hydrogen becomes metallic. ...
Understand Planetary Motion
... A planet within its orbit will travel faster when it is at perigee and more slowly when at apogee. Because of this in the N. hemisphere, summer is 2 days longer than winter. ...
... A planet within its orbit will travel faster when it is at perigee and more slowly when at apogee. Because of this in the N. hemisphere, summer is 2 days longer than winter. ...
The Structure of Our Solar System
... • Outer solar system consists of Neptune, Saturn, Uranus, Pluto and Neptune. • Between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter lies the main asteroid belt. ...
... • Outer solar system consists of Neptune, Saturn, Uranus, Pluto and Neptune. • Between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter lies the main asteroid belt. ...
9ol.ASTRONOMY 1 ... Identify Terms - Matching (20 @ 1 point each =...
... 28. .Radioactive dating techniques have revealed that our Earth and Moon are approximately how old? 29. According to our theory of solar system formation, what three major changes occurred in the solar nebula as it shrank in size? 30. According to our present theory of solar system formation, why w ...
... 28. .Radioactive dating techniques have revealed that our Earth and Moon are approximately how old? 29. According to our theory of solar system formation, what three major changes occurred in the solar nebula as it shrank in size? 30. According to our present theory of solar system formation, why w ...
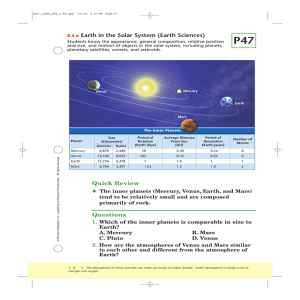
Quick Review Questions 8.4.e Earth in the Solar System (Earth
... 2. How are the atmospheres of Venus and Mars similar to each other and different from the atmosphere of Earth? 1. D 2. The atmospheres of Venus and Mars are made up mostly of carbon dioxide. Earth’s atmosphere is mostly a mix of nitrogen and oxygen. ...
... 2. How are the atmospheres of Venus and Mars similar to each other and different from the atmosphere of Earth? 1. D 2. The atmospheres of Venus and Mars are made up mostly of carbon dioxide. Earth’s atmosphere is mostly a mix of nitrogen and oxygen. ...
Introduction
... 1st Law (1609): Planets revolve around the Sun in elliptical orbits with the Sun at one focus ...
... 1st Law (1609): Planets revolve around the Sun in elliptical orbits with the Sun at one focus ...
Chapter 18: Inner and Outer Planets Name: 1. What is the study of
... 15. A space probe is a vehicle that carries cameras and other tools for different objects in space. ...
... 15. A space probe is a vehicle that carries cameras and other tools for different objects in space. ...
Chapter 25.1: Models of our Solar System
... 2. Saturn is 10 x farther from the sun than Earth. What is the distance between Saturn and the sun in AU? In kilometers or miles? (show your work) 3. The Andromeda galaxy is 2.5 million light years away. How long does it take the light from Andromeda to reach us ? ...
... 2. Saturn is 10 x farther from the sun than Earth. What is the distance between Saturn and the sun in AU? In kilometers or miles? (show your work) 3. The Andromeda galaxy is 2.5 million light years away. How long does it take the light from Andromeda to reach us ? ...
Chapter 25.1: Models of our Solar System
... backwards relative to us for a while. This apparent (not actual) backward motion in known as “retrograde motion”. Ptolemy didn’t believe E. moved (it was the center of the universe) – so he couldn’t explain this “backward” motion of planets. That’s where Epicycles come in – but they are not ...
... backwards relative to us for a while. This apparent (not actual) backward motion in known as “retrograde motion”. Ptolemy didn’t believe E. moved (it was the center of the universe) – so he couldn’t explain this “backward” motion of planets. That’s where Epicycles come in – but they are not ...
Astronomy 1010 - The University of Toledo
... Summary • The Earth is not the center of the universe but instead is a planet orbiting a rather ordinary star in the Milky Way Galaxy. • Celestial bodies in the gravitational field of each other move according to Kepler’s laws. • Newton’s discoveries showed that the same physical laws we observe on ...
... Summary • The Earth is not the center of the universe but instead is a planet orbiting a rather ordinary star in the Milky Way Galaxy. • Celestial bodies in the gravitational field of each other move according to Kepler’s laws. • Newton’s discoveries showed that the same physical laws we observe on ...
Summing up the solar system
... Jupiter, which was also thought to be a storm Uranus & Neptune are about the same size Jupiter is the largest planet ...
... Jupiter, which was also thought to be a storm Uranus & Neptune are about the same size Jupiter is the largest planet ...
Cool Dudes of Astronomy!
... Sun • His work was published in1543 – while he was on his deathbed! ...
... Sun • His work was published in1543 – while he was on his deathbed! ...
Astronomy Objectives
... Evolution of low mass (red dwarf) stars, medium mass main sequence stars, massive stars, all from nebulae to their final phases ...
... Evolution of low mass (red dwarf) stars, medium mass main sequence stars, massive stars, all from nebulae to their final phases ...
Stars, Planets, Moons, too Doing the Solar System
... The star nearest Earth is the Sun, It provides energy for everyone. The energy comes in the form of heat and light, It’s a ball of gases that burns just right. ...
... The star nearest Earth is the Sun, It provides energy for everyone. The energy comes in the form of heat and light, It’s a ball of gases that burns just right. ...
No Slide Title
... The sun is the center of our galaxy. The moon is part of our galaxy. There is one star in each galaxy. Our solar system makes up most of our galaxy. ...
... The sun is the center of our galaxy. The moon is part of our galaxy. There is one star in each galaxy. Our solar system makes up most of our galaxy. ...
Chapter Four Science Astronomy
... Charon: Pluto’s moon, is more than half the size of Pluto, Largest satellite relative to its planet in the solar system Miranda: small moon of Uranus, its surface has smooth cratered plains as well as regions That have grooves and cliffs. It may have once broken apart. Phobos: This moon of Mars has ...
... Charon: Pluto’s moon, is more than half the size of Pluto, Largest satellite relative to its planet in the solar system Miranda: small moon of Uranus, its surface has smooth cratered plains as well as regions That have grooves and cliffs. It may have once broken apart. Phobos: This moon of Mars has ...
Formation and evolution of the Solar System

The formation of the Solar System began 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed.This widely accepted model, known as the nebular hypothesis, was first developed in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg, Immanuel Kant, and Pierre-Simon Laplace. Its subsequent development has interwoven a variety of scientific disciplines including astronomy, physics, geology, and planetary science. Since the dawn of the space age in the 1950s and the discovery of extrasolar planets in the 1990s, the model has been both challenged and refined to account for new observations.The Solar System has evolved considerably since its initial formation. Many moons have formed from circling discs of gas and dust around their parent planets, while other moons are thought to have formed independently and later been captured by their planets. Still others, such as the Moon, may be the result of giant collisions. Collisions between bodies have occurred continually up to the present day and have been central to the evolution of the Solar System. The positions of the planets often shifted due to gravitational interactions. This planetary migration is now thought to have been responsible for much of the Solar System's early evolution.In roughly 5 billion years, the Sun will cool and expand outward many times its current diameter (becoming a red giant), before casting off its outer layers as a planetary nebula and leaving behind a stellar remnant known as a white dwarf. In the far distant future, the gravity of passing stars will gradually reduce the Sun's retinue of planets. Some planets will be destroyed, others ejected into interstellar space. Ultimately, over the course of tens of billions of years, it is likely that the Sun will be left with none of the original bodies in orbit around it.